Queue Flow Basics: What Businesses Should Know
Sep 15, 2025

Queue flow affects every business that relies on live customer interaction. Long lines at checkout counters, lengthy phone holds, or extended wait times for support tickets frustrate customers and cost enterprises revenue.
Many executives don’t realize that customers don’t only count the minutes they have to wait. Customers pay attention to whether the process makes logical sense, seems fair, and keeps them in the loop. That is why so many companies rely on an enterprise scheduling system to match resources with demand and avoid unnecessary waiting.
What Is Queue Flow
Queue flow refers to the process by which people move from the moment they arrive until the moment they are served.
When businesses have a reliable scheduling system, they can reduce delays, keep customers calm, and make life easier for staff.
The sense of order, not the minutes on the clock, makes the experience. It can be okay to wait 20 minutes if things are moving along, but it can be terrible to wait 10 minutes if things are not going well.
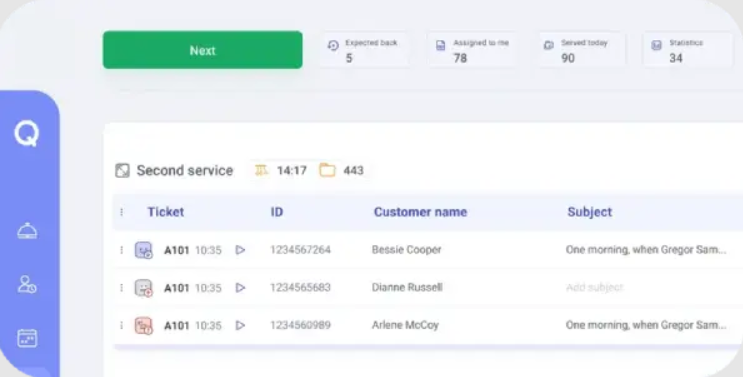
Key Components of Effective Queue Flow
Queues succeed or fail based on a handful of elements that drive movement. With automated scheduling, businesses can keep these components aligned and reduce the risk of failure.
| Component | Why It Matters | Example |
| Arrival Patterns | Understanding when and how people show up enables businesses to plan effectively instead of scrambling. | A coffee shop can schedule extra staff for the 8 a.m. rush. |
| Service Rules | How you decide who gets served first defines fairness. | FIFO (or First In, First Out) keeps retail lines orderly |
| Design and Communication | It’s not only about how the queue looks; it’s also about how the process is described. | Digital displays make wait times transparent and predictable. Mobile alerts let customers wait away from the counter without losing their place. |
Common Challenges Businesses Face with Queue Flow
Most queues fail for predictable reasons, and these failures cost more than lost minutes.
- Abandonment: Customers leave before being served. Supermarkets lose business when people leave their carts at checkout. People who call centers hang up after long waits lose their calls.
- Mismatch in capacity: staffing doesn’t match demand. Customers get angry when there aren’t enough personnel during busy times, and payroll costs go up when there are too many staff during calm times.
- Technology gaps: Tools without integration fail. Clinics that promise short waits through apps but cannot deliver damage trust more than if no promise was made.
6 Best Practices for Optimizing Queue Flow
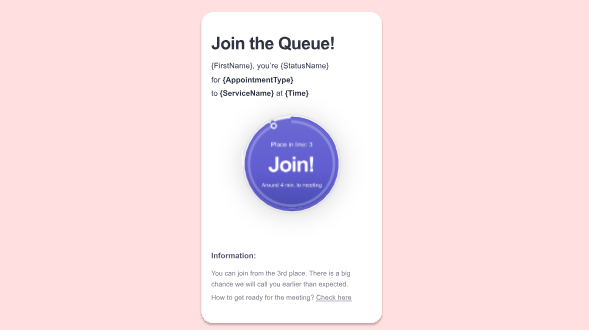
Queue flow improves when businesses plan with precision, respond quickly to changes, and rely on scheduling system services to coordinate staff and customer needs.
1. Forecast demand with data
Review actual records, such as sales, calls, or traffic patterns. Pair those insights with automated scheduling to prepare staff for busy hours.
2. Adjust in real time
Queues change fast. Use dashboards or floor managers to watch them. The moment demand spikes, provide relief by opening additional counters or transferring calls.
3. Design for clarity
Keep layouts simple. Mark entrances and exits clearly, and shows people where to go next. A clear design prevents confusion that slows everything down.
4. Use digital queue tools
Give customers the option to wait virtually. SMS alerts, app check-ins, or online booking systems reduce physical lines and give people the freedom to spend their time as they wish, rather than waiting in line.
5. Engage during the wait
Post updates, show wait times, or let customers tackle quick tasks at a kiosk. Seeing progress helps them stay patient.
6. Borrow proven models
Airlines board in groups, hospitals triage by urgency. Service businesses can use the same playbooks.
Measuring Success: How to Track Queue Flow Efficiency
You cannot improve what you do not measure. Success comes from watching both the numbers and the customer experience.
- Start with operational data. Track wait times, service times, customers served per hour, abandonment rates, and staffing levels. A regular weekly review helps you find the areas falling behind the curve.
- Do not wait for complaints to surface later. Use quick feedback tools: kiosks, app prompts, or micro-surveys to learn if expectations matched reality.
- Benchmark against your industry. Compare your results to standards that matter in your space: boarding times for airlines, patient flow for clinics, or response speed for call centers. Set internal targets based on these comparisons.
- Monitor queues live. Equip managers with dashboards or assign staff to watch lines in real time. Take immediate action when wait times start climbing, whether that means opening an extra counter, redistributing staff, or rerouting calls.
In Conclusion
Queue flow defines how customers perceive a business. When it runs smoothly, people stay engaged, staff handle demand more effectively, and revenue remains stable.
Platforms such as Q-nomy and other scheduling system services enable businesses to match staff availability with demand in real-time.




