Red Flags of Liquidity Providers in 2024: How to Find a Trustworthy Partner?
Dec 12, 2023
The trading industry has always been a competitive one, but in 2024, the stakes are higher than ever. With financial markets, whether cryptocurrency or Forex, continuing to recover from macroeconomic shocks and businesses vying for their share of profits, having a reliable liquidity provider by your side is a must for your exchange or trading platform.
However, not all liquidity providers are created equal. In this article, we will delve into the key red flags to look out for when choosing a crypto or Forex liquidity provider in 2024 to ensure you find a trustworthy partner for your needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Working with reputable liquidity providers is crucial for maintaining efficient markets.
- Selecting a reputable provider requires careful consideration of red flags, such as inadequate security measures, hidden fees, unreasonable terms, lack of transparency, and others.
- From established Forex and crypto CFD liquidity providers to well-known DeFi players, there are numerous reliable options available.
Why You Should Care About Liquidity
Before delving into the red flags, it’s important to grasp the concept of liquidity and its significance in the market.
In simple terms, liquidity refers to the ability to buy or sell an asset quickly and without affecting its market price significantly. Having high liquidity means that there are plenty of buyers and sellers in the market, making it easier to execute trades at desired prices.
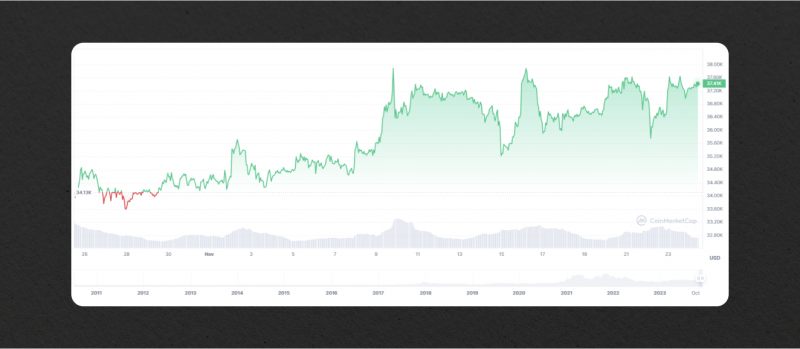
Let’s take Bitcoin as an example. In the second half of 2023, the most well-known and traded cryptocurrency has seen a significant decrease in its liquidity, with large amounts being withdrawn from centralized exchanges, with only 36,000 BTC remaining on these platforms compared to over 2 million just a few years ago.
But what did this liquidity crunch mean for cryptocurrency exchanges and the market as a whole? With less liquidity available, even smaller amounts of capital could have a significant impact on price movements. This can work in both positive and negative ways, as demonstrated by the potential for a small amount of short selling to cause a decrease in Bitcoin’s value.
In this volatile period, the BTC price could rise to the $38,000 mark and then plummet to $35,000 in just several hours. Such drastic movements resulted in millions of dollars in short positions being liquidated, showing the impact that a decrease in liquidity can have on market stability.
So, why should you care about liquidity? Here are some key reasons:
1. Efficient Order Execution
In a highly liquid market, orders can be executed quickly and accurately due to the large number of participants. This allows traders to enter and exit positions at their desired price points, maximizing their potential profits.
On the other hand, low liquidity markets often suffer from delays and slippage, making it challenging for traders to execute orders as intended. This can result in missed trading opportunities and increased transaction costs.
2. Stable Market Prices
High liquidity also contributes to market stability. With a large number of buyers and sellers, it is less likely for sudden price movements to occur due to the impact of individual trades. This provides traders with more predictable market conditions, allowing them to make informed decisions.
On the other hand, low liquidity markets are more susceptible to sharp price fluctuations as a single large order can have a significant impact on the market, as in the example above. This can lead to unexpected losses for traders.
3. Diverse Trading Options
Having high liquidity means that there are more options for traders to choose from. They have access to a variety of assets and can easily switch between them as market conditions change. This allows traders to diversify their portfolios and reduce their overall risk.
On the other hand, low liquidity markets may offer limited trading options, making it challenging for traders to adjust their strategies and adapt to changing market conditions.
The Role of Liquidity Providers in Financial Markets
Liquidity providers are entities that actively buy and sell assets to increase liquidity in the market. These providers have access to various order books and liquidity pools, allowing them to supply assets to platforms and facilitate trading activities.
By working with liquidity providers, brokers and exchanges can offer a wide range of trading services and execute orders with minimal slippage. The presence of reputable liquidity providers is crucial for maintaining efficient markets and ensuring smooth trading experiences for investors.
However, not all crypto or Forex liquidity providers are created equal. In fact, having a not reliable one can be detrimental to your business in more ways than one. Let’s explore why:

- Inefficiency in Market Operations: When working with an unreliable partner, brokers and exchanges may face challenges in executing orders smoothly. This can result in delays, slippage, and increased transaction costs for both the broker and the trader.
- Potential Risks: Inefficient liquidity providers can also pose risks to businesses. For example, if a provider fails to fulfill their obligations, it can lead to liquidity shortages and financial losses for the broker or exchange.
- Reputation Damage: In the financial market, reputation is everything. Working with a shady partner can result in negative experiences for traders, leading to a damaged reputation for brokers and exchanges.
Here are some red flags of a provider to watch out for:
Red Flag 1: Lack of Documentation
Regulation and compliance are essential factors to consider when selecting a liquidity provider. Operating in a regulated environment ensures that the provider adheres to industry standards and follows legal guidelines. It also provides a level of protection for both businesses and traders.
Before partnering with a liquidity provider, conduct thorough research to ensure they are compliant with relevant regulations in their jurisdiction. Check if they hold the necessary licenses and registrations to operate legally. Avoid providers that operate in jurisdictions with weak or non-existent regulations, as this may expose you to unnecessary risks.
Red Flag 2: History of Complaints
A provider’s reputation and feedback from clients are valuable indicators of their reliability and trustworthiness. Before making any commitments, take the time to research the provider’s reputation and read testimonials and feedback from their clients. Look for red flags such as repeated complaints about poor service quality, delays in fund transfers, or unresponsiveness to client inquiries.
Additionally, consider if the provider has received any accolades or awards from reputable financial organizations. While not a definitive measure of their reliability, such recognition can be an encouraging sign of their commitment to excellence. Remember, a provider with a tarnished reputation is likely to cause more harm than good to your trading activities.
Red Flag 3: Limited Information about Team Members
The people behind a liquidity provider Forex or crypto are just as crucial as the company itself. Before partnering with any provider, make sure you know who their team members are and what their backgrounds are. A reputable provider will have a transparent and easily accessible list of key team members on their website or through other channels.
Do your due diligence on the team’s expertise and experience in the financial industry. Lack of information or vague backgrounds should raise a red flag. After all, you want to partner with professionals who have the necessary knowledge and skills to support your trading activities.
Red Flag 4: Lack of Transparency and Communication
Transparency and effective communication are vital for a successful partnership with a liquidity provider. A provider should be transparent about their operations, pricing, and the risks associated with their services. They should provide clear documentation and agreements that outline the terms and conditions of the partnership.
Furthermore, a reputable provider should have responsive and knowledgeable customer support. Lack of communication or delays in addressing client inquiries can be red flags indicating potential issues down the line. Choose a provider that prioritizes transparency and maintains open lines of communication to ensure a smooth and satisfactory experience.
Red Flag 5: Limited Offerings and Services
The breadth of offerings and services provided by a liquidity provider is another crucial aspect to consider. A reputable provider should offer a comprehensive range of solutions that meet your specific trading needs. This may include access to multiple markets, various trading instruments, cutting-edge trading platforms, such as MT4/MT5, many options for connecting, comprehensive AML/KYC verification modules, and more.
Evaluate the provider’s service packages and compare them against your expectations. Consider whether they offer the necessary tools, such as charting capabilities, market news updates, or risk management features. Be wary of providers that have limited offerings or lack the flexibility to cater to your unique requirements.
Red Flag 6: Inadequate Technology and Security Measures
Technology and security are critical aspects of any provider’s infrastructure. In the fast-paced world of trading, it’s essential to work with a provider that leverages advanced technology to ensure efficient order execution and minimize downtime.
Consider if the provider has adequate risk management protocols in place to mitigate potential market volatility and protect against fraudulent activities. Providers that lack sufficient technological and security measures may put your users’ assets and investments at unnecessary risk.
Red Flag 7: Lack of Track Record or Experience
Consider the provider’s history in the industry and their experience in offering liquidity services. How many clients do they have? How many exchanges or brokers use their solutions? Look for providers that have been operating successfully for a significant period and have established a solid reputation.
While newer providers may offer competitive pricing or innovative solutions, they may lack the necessary experience to navigate potential challenges effectively. It’s generally safer to work with providers that have a demonstrated track record of delivering reliable and consistent liquidity services.
Red Flag 8: Hidden Fees and Unreasonable Terms and Conditions
Carefully review the terms and conditions set forth by the liquidity provider before entering into any agreements. Be cautious of providers that impose overly restrictive terms or hidden clauses that may limit your flexibility or expose you to unnecessary risks.
Pay close attention to execution policies, minimum deposit requirements, and any penalties or fees associated with transaction volumes.
Red Flag 9: Lack of Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are essential considerations, particularly if you anticipate future growth or changes in your trading activities. A liquidity provider should be able to scale their services to meet your evolving needs and accommodate increased trading volumes.
Evaluate the provider’s capacity to handle larger trading volumes and their ability to adapt to changing market conditions. Consider if they have the necessary infrastructure and resources to support your future expansion plans. Avoid providers that lack the capabilities to keep up with your growing requirements.
Red Flag 10: Limited Market Access and Liquidity Pools
The availability of multiple market access and liquidity pools is crucial for a liquidity provider. They should have connections to various exchanges and markets, allowing them to offer a wide range of trading instruments and access deeper liquidity pools.
Evaluate the provider’s network and partnerships to ensure they can provide sufficient liquidity across multiple markets and trading pairs. Providers with limited market access may restrict your trading opportunities and hinder your ability to capitalize on market fluctuations.
Red Flag 11: Resistance to Due Diligence and Audit Requests
Finally, be wary of liquidity providers that resist due diligence or audit requests. A reputable provider should be open to sharing necessary documentation and financial statements and undergo independent audits to verify the integrity of their operations.
Resistance to due diligence may indicate potential issues, such as poor financial health, lack of transparency, or non-compliance with regulatory requirements. Avoid partnering with providers that refuse or make it difficult to conduct proper due diligence, as this could expose you to unnecessary risks and potential legal complications.
Examples of Reliable Liquidity Providers
If you’re looking for reputable liquidity providers to partner with, here are some examples of established and reliable options in the Forex / crypto CFD markets:
- Leverate
- B2Broker
- GBE Prime
- Brokeree
- X Open Hub
Some well-known institutional liquidity providers offering crypto spot and derivatives liquidity for exchanges and projects:
- Binance
- Coinbase
- BitGo
- NinjaPromo
- GSR Markets
These are prominent liquidity pool providers in decentralized finance (DeFi) space:
- Balancer
- Uniswap
- Curve Finance
Of course, there are more reputable liquidity providers in the market. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and due diligence to find the best fit for your specific needs.
Meanwhile, you can check out our comprehensive list of the best Forex liquidity providers in the market.
Closing Thoughts
Selecting the best liquidity provider can be a daunting task, but it’s crucial to take the time to thoroughly evaluate potential options before making a decision. As in any business partnership, trust and transparency are key factors in ensuring a successful and mutually beneficial relationship.
Wondering how these solutions can boost your business?
Leave a request, and let our experienced team guide you towards unparalleled success and growth.
FAQs
Is a bank a liquidity provider?
Yes, banks are considered to be one of the main liquidity providers in financial markets. They play a crucial role in providing funding and credit to individuals, businesses, and governments. Banks also facilitate the transfer of funds between different parties, helping to maintain the flow of liquidity in the market.
How do liquidity providers earn money?
Liquidity providers can earn from the difference between bid and ask prices, also known as spreads. When a trader buys or sells a currency pair, they pay the spread to the liquidity provider as compensation for facilitating the trade. This is how liquidity providers make a profit in the market.
Some liquidity providers may also charge a commission for each transaction made on their platform. This is typically seen in Electronic Communication Network (ECN) and Straight Through Processing (STP) trading models, where traders have direct access to liquidity providers. The commission charged is usually based on the volume of trades executed and can vary depending on the liquidity provider and trading platform used.
How does liquidity provision work in DeFi?
In DeFi, liquidity provision is typically done through automated market makers (AMMs). These are smart contracts that use algorithms to determine prices and execute trades without the need for intermediaries like banks. Liquidity providers are investors who contribute funds to the AMM pools, which are used to facilitate trades. In return, they earn a portion of the trading fees generated in the pool based on their contribution.
Liquidity provider vs market maker: what’s the difference?
Market makers and liquidity providers both play important roles in the financial markets, but they differ in their methods of operation. Market makers are usually large banks or institutions that provide quotes for buy and sell orders. They make money by buying assets at a lower price and selling them at a higher price, profiting from the spread.
On the other hand, liquidity providers act as intermediaries between brokers and market makers, ensuring there is enough liquidity in the market for traders to execute their trades. They earn from the spread or commission charged by brokers and also by providing additional services such as risk management solutions.