Understanding Algorithmic Trading: A Guide for Beginners
Sep 05, 2023

Algorithmic trading is a relatively new field in the world of finance. It has become increasingly popular over the last decade as more and more traders are turning to the use of computer-aided techniques and tools to make decisions in their trading activities.
In this guide, we will explore what algorithmic trading is, as well as discuss the risks associated with automated trading and tips for developing profitable strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Computer programs are used in algorithmic trading to automate financial trades based on mathematical models.
- The introduction of electronic stock exchanges and the adoption of decimalisation led to the development of algorithmic trading in the 1990s.
- Algorithmic trading offers many benefits for traders, from automation and efficiency to cost reduction. However, it also carries certain risks, such as code errors, market changes, market volatility, overconfidence and poor execution.
- The best strategies depend on the market conditions and trader objectives, but popular options include trend following, mean reversion, and arbitrage. When speaking about execution tactics, TWAP, POV, and VWAP are the most common.
What Is Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading (or algo-trading / black-box trading) is the use of computer programs to trade financial instruments in an automated fashion. These computer algorithms, which are based on mathematical models, can be used to identify patterns in market data and then execute trades accordingly.
Algorithmic trading has become increasingly popular for a number of reasons, including the fact that it can reduce transaction costs while increasing the speed of execution. Additionally, algorithmic traders are less likely to be influenced by emotion or fear when making decisions about what trades to make. This is because computer programs execute trades based solely on the mathematical models they are programmed with.
History of Algo Trading
Algo-trading has been an established practice in financial markets since the late 1980s and 1990s. This was a result of advancements in technology, which allowed for the completely electronic execution of stock trades and the subsequent automation of buying and selling different assets.
What Has Led to the Development of Algo-Trading?
In 1998, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allowed electronic exchanges to trade stocks and options, allowing algorithmic trading to flourish. This led to the emergence of different strategies that utilise electronic and automated sides of financial markets, ultimately paving the way for computerised high-frequency trading (HFT).
The adoption of decimalisation, which reduced the minimum tick size from 1/16 of a dollar ($0.0625) to $0.01 per share in the United States, may have also played a role in encouraging this type of trading. This altered market microstructure by allowing smaller differences between bid and offer prices, reducing the advantage of market-makers and increasing liquidity in the markets.
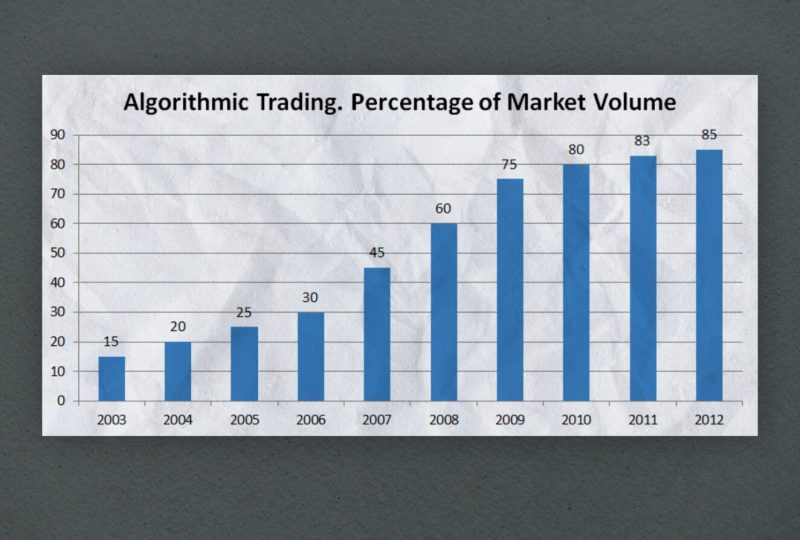
High-Frequency Trading
High-frequency trading is a form of automated trading that takes advantage of speed and accuracy to execute transactions far faster than any human could do, at 1000 times increased speed. Since its inception, HFT has grown in popularity and has become an important part of the financial industry.
HFT has been criticised for its potential to allow traders to manipulate markets and take advantage of other investors, though proponents of the technology argue that it increases liquidity in the markets.
How Does Algorithmic Trading Work?
Algorithmic trading works by using computer-generated algorithms that are programmed to identify patterns and trends, analyse data, monitor changes in the markets, and execute trades. The systems can be programmed to carry out a wide variety of tasks at lightning-fast speeds, often within milliseconds of market changes occurring.
The algorithms are programmed to take into account factors such as volume, order type, price movements, time of day and other variables that may have an impact on trading decisions. Once these parameters are set, the algorithms can be triggered to initiate trades when certain conditions are met.
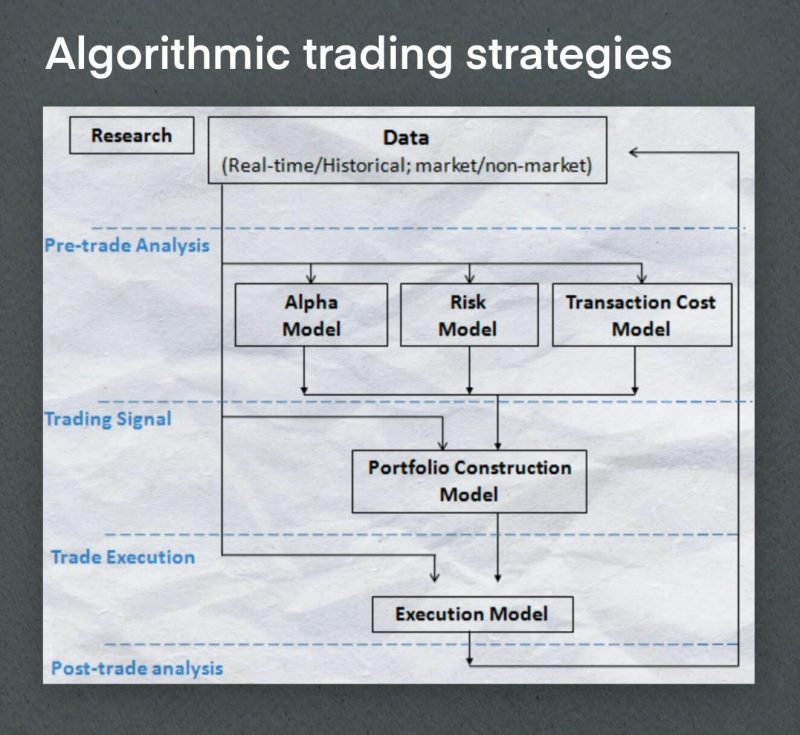
Some Examples of Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Let’s take the simple example of an algorithmic trading strategy.
- We have a trading pair of GBP/USD, and we want to take a short position if the pair rises above 1.2012. For every five-pip rise in the rate, we cover 2 lots, and for every five-pip drop in rate, we increase our short position by 1 lot.
The algorithm will be programmed to identify any rises or falls above or below the stated rates and will then execute the relevant trades automatically. This enables the trader to take advantage of potential opportunities without needing to be actively monitoring the markets at all times, as the algorithm will handle it for them.
Another example:
- We have programmed the algorithm to buy 10,000 shares of Microsoft (MSFT) if its price rises above $300 and sell them when the price falls below $300. For every 0.1% increase in MSFT’s price beyond 300, the system will buy an additional 500 shares, and for every 0.1% decrease in MSFT’s price below 300, the system will sell 500 shares automatically.
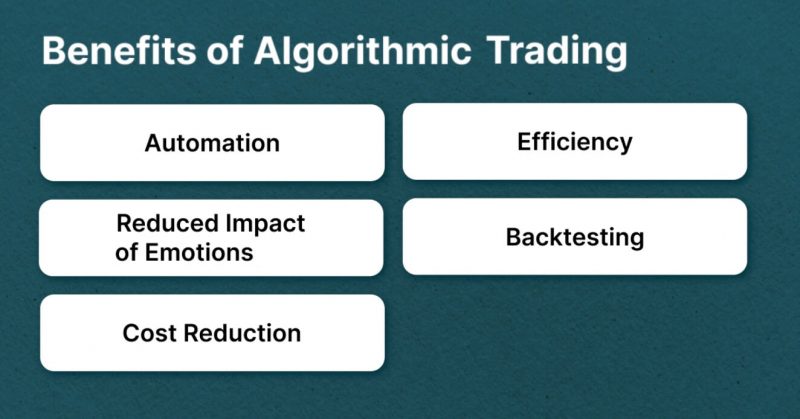
Benefits of Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading offers many benefits for traders who have a passion for it. Here are some of the main advantages that it can offer:
- Automation – By taking advantage of computer trading algorithms, traders can reduce their manual workload significantly. This allows them to focus on other aspects of their trading strategy and dedicate more time to research and analysis.
- Efficiency – Algorithmic trading is far more efficient than manual trading. It can quickly and accurately identify price movements, allowing traders to take advantage of these opportunities faster and without any human bias.
- Reduced Impact of Emotions – By eliminating the potential for emotions to influence decisions, algo trading can help traders avoid making costly mistakes due to fear or greed.
- Backtesting – Algorithmic traders can use backtesting to test their strategies against historical data and refine them before actually putting them into practice. This allows traders to make the most of their strategies and increase profits in the long run.
- Cost Reduction – Algorithmic trading can help to reduce transaction costs and commissions by executing orders quickly and with precision.

Common Risks and Pitfalls in Algorithmic Trading
While there are many advantages to algorithmic trading, it also carries certain risks. Some of the main risks include:
- Code errors – Algorithms are only as good as the code they are written with. If there are errors in the code, it can lead to incorrect trades being taken and enormous losses.
- Dependence on Technology – Algorithmic trading relies heavily on technology, so there is a risk of technical breakdown or outages. This could lead to orders not being executed properly, resulting in missed opportunities or losses.
- Overconfidence – Overconfident traders may rely too heavily on their algorithmic strategies and overlook potential risks. It is important for traders to monitor their strategies closely and adjust parameters when necessary.
- Poor Execution – Algorithmic trading requires data connections that can be slow at times, resulting in poor execution of trades. This can lead to traders missing out on profits or facing losses due to slippage.
- Liquidity Risk – Algorithmic strategies can lead to liquidity problems in certain markets, as algorithms may buy or sell large volumes of securities at once. This could result in the market becoming illiquid and traders being unable to close out positions.
- Regulation Risk – Algorithmic trading is subject to various regulations in different countries. Traders must make sure that they understand the regulatory environment and any potential risks associated with it before getting started.
- Black Swan Events – Algo traders must take into account the possibility of unexpected events that could heavily impact the markets. These “black swan” events are nearly impossible to predict and can cause significant losses if not managed properly.
It is important to remember that technology plays a crucial role in the success of algo-traders, and it comes with a learning curve. To increase their chances of success, traders must invest a lot of time in understanding programming and markets and mastering algo-trading strategies.
How Can I Get Started with Algorithmic Trading?
If you’re interested in getting started with automated trading, there are several key skills you will need to learn. It is recommended that you have a background in technology and coding, as this can help speed up the learning process. Additionally, if you have some experience with statistics or machine learning maths, it can also prove beneficial.
What to Know for Algo-Trading
The necessary skills for (pure) algorithmic crypto, Forex or stock trading experience include coding in Python, understanding how to get financial data from an API, scraping the web for additional data, storing the data in a database, learning how to manipulate and clean the data, becoming an expert at time series analysis, learning statistics & machine learning maths, and developing & analysing trading strategies.
How Long Does It Take to Learn?
Usually, it will take about a year full-time to feel proficient in using data science for trading strategy development and four months or so to become comfortable with automated execution.
As you continue to learn, there are great online resources such as tutorials, courses and forums that can help you stay up-to-date on the latest developments in algorithmic trading. It is also important to keep practising and testing your skills to become a successful trader.
When you’re ready to start live trading, it is recommended that you begin with small amounts of capital while monitoring the performance of your strategies closely. As you gain confidence in your algorithms, you can gradually increase the size of your investments as well as the risk exposure. Finally, always remember to diversify your portfolio and ensure that you are following the relevant regulations for trading in your area.
What Algorithmic Trading Strategy to Choose?
Algo trading strategies offer a unique opportunity for traders to reap the benefits of big data and automation. Knowing what markets to target, what strategies to use and how to execute them correctly are all key components towards success with algorithmic trading.
When it comes to the markets, algorithmic traders should target those where institutional traders are capacity-constrained and data is plentiful. This allows traders to capitalise on opportunities that may be unavailable to large institutional investors as well as take advantage of the wealth of data that can provide insights into market movements.
Trading Strategies in Algo-Trading
In terms of strategies, there are various approaches algorithmic traders can take:
- Trend Following – Trend following strategies, also known as momentum strategies, are designed to identify and profit from long-term price trends in the financial markets. By analysing historical price data and market indicators, these strategies aim to capture and ride the waves of market trends, allowing investors to potentially profit from sustained upward or downward movements. Utilising 50-day and 200-day moving averages is a widely adopted strategy in such a way of trading.
- Mean Reversion – Mean reversion strategies are the opposite of trend-following strategies, as they attempt to identify and take advantage of short-term price movements that occur against longer-term trends. These strategies often use more technical indicators, such as Bollinger Bands, which look for prices that have diverged from their statistical mean.
- Arbitrage – Arbitrage strategies seek to capitalise on the price discrepancy between two or more different markets by simultaneously buying in one market and selling in another. This strategy is often used to take advantage of pricing discrepancies in highly liquid, well-regulated markets.
- Breakout/breakdown – Breakout strategies look for prices to move from a period of consolidation to a period of volatility. As soon as prices break out above or below their consolidation range, these strategies look to capitalise on the trend by entering trades in the direction of the breakout.
- Quantitative Momentum – Quantitative momentum strategies use quantitative indicators to identify stocks that are poised to outperform the markets in the near future. These strategies often use a combination of technical and fundamental data to make predictions about future stock prices.
These are just some examples of strategies. However, there are many more that can be employed.
Execution Strategies to Know
Finally, when executing trades, there are several main strategies that algorithmic traders can choose from:
Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
First of all, VWAP is an essential metric used by investors and analysts to evaluate the current price of a stock in comparison to its average trading price over a particular period.
VWAP is calculated by taking the sum of all trade prices multiplied by their respective volumes and then dividing this total by the total number of shares traded for that period.
Institutional investors such as fund managers use VWAP as a benchmark to compare their average purchase price and assess the quality of executions. The aim is to acquire stocks at prices below the average price for that day, which can boost profits and minimise losses. As such, they closely monitor VWAP when trading in large orders and adjust their approach (active or passive) based on the current price of a stock.
Algorithmic trading is another application of VWAP. It involves the strategic breaking up of large orders and releasing dynamically determined smaller chunks into the market based on a stock’s historical volume profiles. The intention here is to execute the order as close as possible to the VWAP so that investors can acquire stocks at competitive prices while reducing market impact costs.
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP)
TWAP is another commonly used execution strategy by algorithmic traders. This approach involves breaking up large orders into equal parts and releasing them into the market at regular intervals throughout a defined period of time. This allows traders to execute their orders close to the average price between the start and end times, thereby minimising market impact.
Implementation Shortfall (IS)
Implementation Shortfall in algo-trading is a strategy intended to reduce order execution costs while allowing investors to benefit from favourable stock price movements. This strategy works by trading the real-time market in order to reduce the cost of order while taking advantage of the opportunity cost of delayed execution.
When a stock price is moving favourably, this strategy will increase its targeted participation rate. Conversely, when a stock price moves adversely, it will decrease its targeted participation rate.
Percentage of Volume (POV)
When trading with this execution tactic, the trader sets a desired volume percentage, and the algorithm automatically adjusts its execution rate to accommodate changes in market activity. The algorithm works to maintain the target participation rate of volume throughout trade execution, thus ensuring that the order is not only completed at an optimal speed but also in line with the trader’s desired volume percentage.
The algorithm is designed to continuously adapt its rate of execution, enabling the trader to have greater flexibility in executing trades at an agreeable speed and volume percentage.

What to Choose?
The two most popular trading strategies in the market today are TWAP and POV. For example, Binance offers both strategies to its users for trading cryptocurrencies with algorithm-driven execution.
TWAP is ideal for traders who are looking to execute their trades at an average market price over the desired duration of time. It’s perfect if you have an exact timeframe in mind, as it will ensure that your order is executed evenly throughout that period.
On the other hand, POV trading allows users to adjust the rate of their order execution based on market volume. It’s highly beneficial for traders who don’t have a specified duration in mind but still want to take advantage of market volatility.
Last Words
Whether that be VWAP, TWAP or POV, ensure that you do your research and consider all factors before entering an algorithmic trade. Algorithmic trading can be a great way to increase profits but also poses higher risks when done incorrectly. So make sure you know what you’re doing and are comfortable with the strategy you choose.
Also, do not forget about risk management. Make sure you have a plan in place to protect yourself should the market move against you, and ensure that your strategies align with your risk appetite. Never invest more than you can afford.
FAQs
How can algorithmic trading benefit me as a trader?
Algorithmic trading can help traders by providing them with the ability to automate their trading strategies. This means that a trader can set up an algorithm that will execute trades on their behalf, and they don’t have to manually monitor the markets throughout the day. Algorithmic trading also helps traders reduce risk as algorithms are designed to follow pre-defined rules and execute trades at the most advantageous times.
What is technical analysis?
Technical analysis is a form of market analysis that focuses on price action. It involves looking for patterns in historical data such as prices, volume, and other indicators to identify potential trading opportunities. Technical analysts use these patterns to make predictions about where the markets will move next. Technical analysis can be used to identify support and resistance levels, trend reversals, and the likelihood of a breakout or reversal.
What types of orders are used in algorithmic trading?
The most common execution strategies used in algorithmic trading are VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price), TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price), and POV (Percentage of Volume). Additionally, other strategies, such as Implementation Shortfall, may also be employed depending on the market conditions and trader objectives.
How complex is algorithmic trading and what do I need to know in order to succeed with it?
If you want to learn algorithmic trading, there are plenty of platforms and resources available to help traders get started. Generally speaking, traders need to have a good financial market knowledge as well as the understanding of the specific strategy they plan to use.
Additionally, a solid grasp of coding languages such as Python or R may also be beneficial for those who want to build more advanced algorithms. Finally, having a risk management and money management plan in place is essential for success in trading with algorithms.
Are there any regulatory or legal considerations I should be aware of when using algorithmic trading strategies?
Yes. Algorithmic trading strategies are subject to the same regulations and laws as any other type of trading activity. Depending on your location, you may also be required to register with a regulatory body and obtain appropriate licences before you can trade using algorithmic strategies. Additionally, many jurisdictions require traders to report profits or losses from algorithmic trading activities for tax purposes.