How Does Tokenization Work in Blockchain?
Mar 12, 2024

Tokenization is a topic of considerable interest today, especially in the realm of blockchain, a technology that powers cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. Crypto tokens not only symbolize ownership but also give access to various digital asset classes that are otherwise inaccessible through traditional means.
The purpose of this article is to shed light on blockchain tokenization, its benefits, and what role it plays in finance.
Key Takeaways
- The technology behind tokenization involves key components such as smart contracts, unique digital identifiers, distributed ledger technology, and cryptographic protection.
- Token standards, such as ERC-20 and ERC-721, promote interoperability between different platforms and applications, making it easier for assets to be transferred and traded.
- Despite the many benefits of tokenization, businesses must carefully navigate regulatory challenges and cybersecurity risks to ensure the effective adoption of the technology.
What Is Tokenization?
Tokenization is a transformative process that converts the rights to an asset into a token on a blockchain. This approach is not limited to a single asset type – it encompasses a wide range of assets, both physical, such as real estate and art, and digital, like intellectual property.
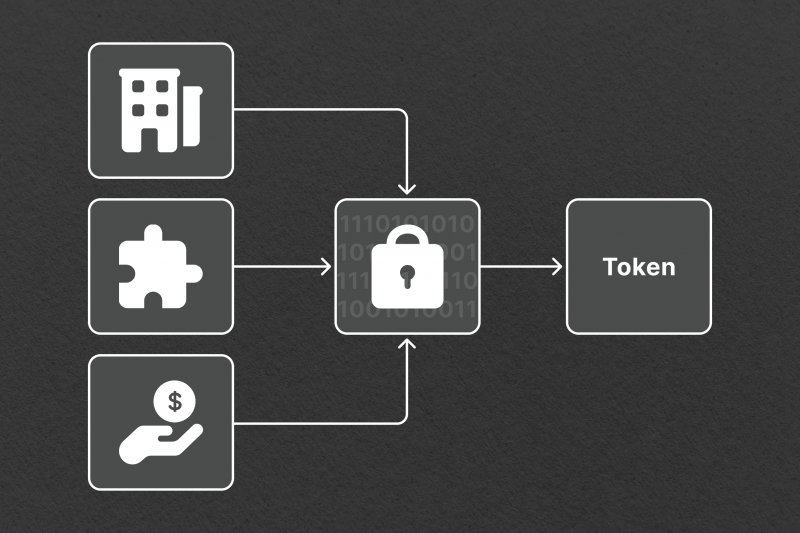
Here are the key aspects of asset tokenization:
Fractional Ownership
Tokenization introduces the concept of fractional ownership, where an asset can be divided into tokens representing shares of the underlying resource.
This model allows multiple individuals to own a portion of the asset, democratizing investment opportunities that were traditionally accessible to a select few due to high costs or barriers to entry.
With fractional ownership, buying and selling shares of an asset becomes significantly easier, increasing the asset’s liquidity and marketability.
Liquidity and Accessibility
One of the most significant advantages of digital asset tokenization is the enhancement of liquidity. Tokenized assets can be traded on secondary markets, making it simpler for investors to enter and exit positions.
Accessibility is also greatly improved as tokenization opens up investment opportunities to a broader audience, allowing participation in markets that were previously out of reach for many due to financial constraints or market illiquidity.
Disrupting Multiple Industries
The potential of asset tokenization is enormous, and it has caught the attention of many major enterprises. Many industry leaders have recognized that asset tokenization can have a profound impact on projects, businesses, and sectors, including the global securities market.
The adoption of asset tokenization is not just a future possibility, as it is already happening today. Companies like Microsoft have announced or launched projects involving the tokenization of industrial assets and securities.
Tokenization in Blockchain: A General Overview
The blockchain ecosystem facilitates the creation of various types of tokens. These include, for example, stablecoins, which are cryptocurrencies pegged to real-world currencies to maintain a stable value, and NFTs (non-fungible tokens), which serve as digital proof of ownership for unique items or assets.
The potential market for tokenization is vast. According to a report by Boston Consulting Group, the total size of tokenized illiquid assets could expand to $16 trillion by 2030, or 10% of global GDP. These illiquid assets include pre-initial public offering (IPO) stocks, real estate, private debt, revenues from small and medium businesses, physical art, exotic beverages, private funds, wholesale bonds, and many more.
This shift towards tokenization is not limited to just institutions but also governments. For instance, the U.K. government’s Asset Management Task Force released a report in November 2023 outlining a “blueprint” for the asset tokenization market in FCA-authorised funds.
The growth of this sector signifies the increasing acceptance and integration of tokenization into the global financial landscape.
The Technology Behind Blockchain Tokenization
The technology underpinning the tokenization process in the blockchain is multifaceted, involving several critical components necessary for the integrity and functionality of tokenized assets:
Smart Contracts
Central to the tokenization process is smart contracts, which are programmed to execute and enforce the terms of an agreement automatically. These are written in code and live on the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the potential for human error or fraud.
Unique Digital Identifiers
Each tokenized asset is assigned a unique digital identifier, which acts as a digital fingerprint, ensuring that each asset is distinguishable from another on the blockchain. This identifier encapsulates all the relevant details about the asset, including its ownership, value, and history.
Distributed Ledger Technology
The backbone of tokenization is a distributed ledger, a type of database that is spread across multiple sites, countries, or institutions. This decentralized storage method ensures that all transaction records are transparent and immutable, making it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the data without consensus across the network.
Cryptographic Protection
Blockchain’s inherent security features are critical for building trust and confidence in the tokenization process. The cryptographic protection of sensitive data, coupled with the decentralized nature of the ledger, means that tokenized assets are less vulnerable to hacks and unauthorized alterations.

The Process of Tokenization
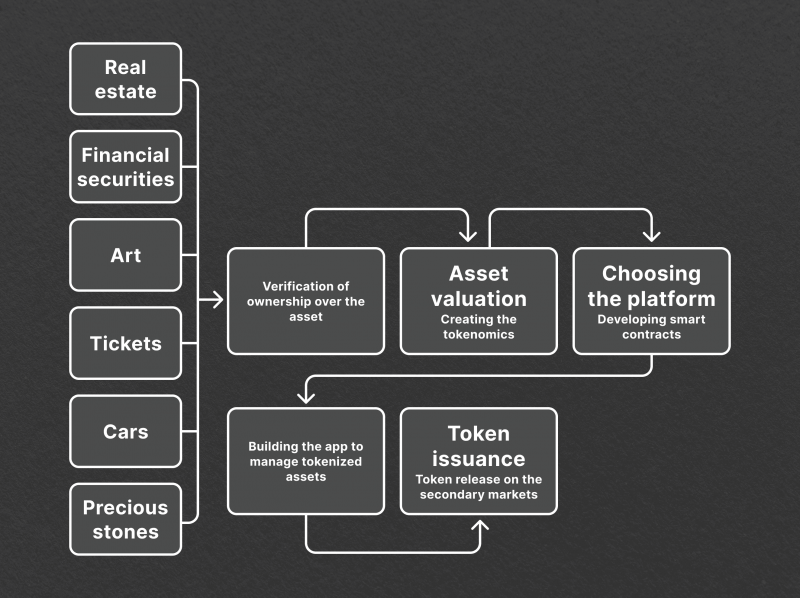
The tokenization process can be distilled into four essential steps:
- Asset Sourcing: The initial phase involves selecting and appraising the asset for tokenization. This could be any asset, from real estate to intellectual property, which is then divided into discrete tokens. The selection process is based on various factors such as market demand, business needs, and target audience.
- Token Design: The next step is to decide on the type of tokens to be issued. This decision is based on the nature of the asset being tokenized. For instance, fungible assets like commodities or currencies could be tokenized into utility tokens, while non-fungible assets like art pieces or real estate can be tokenized into security tokens.
- Legal Compliance: Before the asset can be tokenized, it is essential to ensure compliance with global and local regulations. Each country has its own laws regarding securities and investments, which need to be analyzed and adhered to for a successful tokenization process.
- Blockchain Implementation: It is time to create your token on a suitable blockchain platform. This involves writing smart contracts that will govern all aspects of token issuance and management, from supply and demand to ownership rights.
- Tokenization in Action: The tokens can now be issued and made available for sale or purchase through an Initial Token Offering (ITO) or Security Token Offering (STO). The tokens can also be listed on crypto marketplaces, making them available for secondary market trading.
Types of Tokens in Blockchain
Token is a central concept in blockchain technology. Tokens serve as the currency for transactions and can also represent ownership rights or access to services on a blockchain platform.
There are various types of tokens in blockchain, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes:
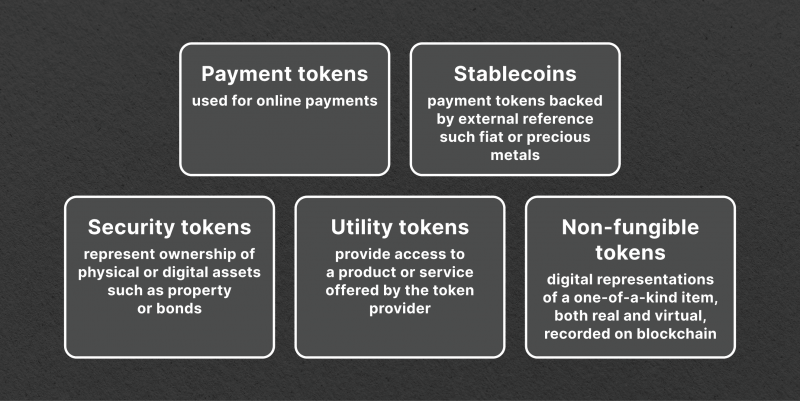
Utility Tokens
Utility tokens are not investments; instead, they offer access to products and bonuses provided by the issuing platform. Often utilized in crowdfunding initiatives, these tokens grant holders certain rights within the network, such as the ability to vote on decisions or access specific functions within the ecosystem.
Security Tokens
Security tokens, on the other hand, represent ownership of a real-world asset, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. These tokens are subject to regulatory laws and must adhere to securities laws in their jurisdiction.
These tokens act as digital analogs to traditional securities. Holding a security token typically represents an investment in a company, mirroring the concept of stocks. They fall under the purview of securities law, necessitating compliance with the relevant securities regulations.
Non-fungible Tokens
Each NFT is a unique digital asset, which has led to its widespread use in representing ownership over items such as artwork, collectibles, and in-game assets.
The uniqueness of NFTs is what differentiates them from other token types, as each NFT has a distinct value and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis like cryptocurrencies.
Payment Tokens
Payment tokens are designed specifically for transactions and can be used as a form of payment on various platforms. These tokens have a fixed value and can be exchanged for goods or services within their respective networks.
Unlike utility tokens, payment tokens are not tied to any specific product or service and can be used as a general currency in the cryptocurrency market.
Crypto enthusiasts often identify other types of tokens, such as equity tokens, governance tokens, and loyalty tokens. However, the above categories are the most commonly used classification.
Token Standards
Each type of token used in the process of asset tokenization is governed by a set of standards that defines its creation, transfer, and usage. These standards act as a framework for all parties involved to ensure smooth and secure handling of digital tokens on the Blockchain.
The most commonly used token standards are ERC-20, ERC-721, BEP-20, and ERC-1400. They serve as guidelines for creating fungible tokens. These standards outline the technical requirements and protocols for token creation, storage, transfer, and purchase.
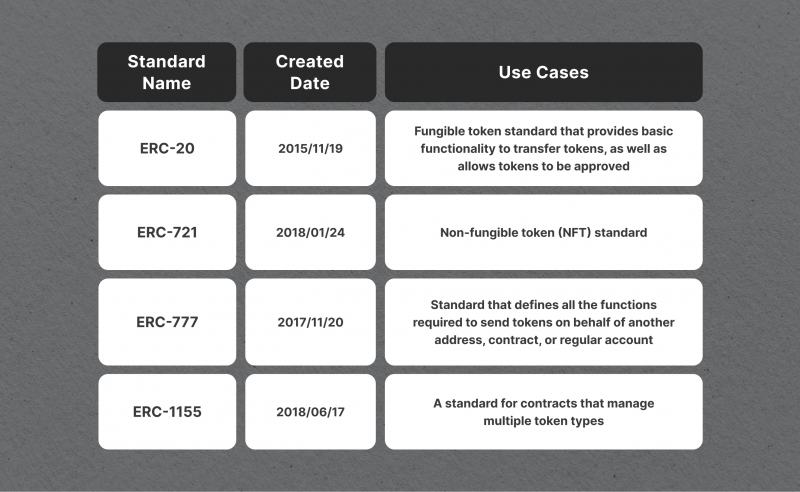
Token standards also enable composability in the development process. By following these standards, developers can focus on creating innovative solutions instead of spending time on basic functionality.
In addition, using these standards helps to achieve interoperability between different platforms and applications. Since tokens created using the same standard can easily interact with each other, it promotes a more efficient and seamless transfer of assets. For example, ERC-20 assets can be traded for another ERC-20 token without any complications.
Token standards provide efficiency in the interaction between smart contracts. As tokens created using these standards come with essential functions like address retrieval and balance tracking, smart contracts can easily monitor and transact with them, which streamlines processes and reduces the risk of human error.
Benefits of Tokenization
Tokenization offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance the efficiency and accessibility of financial transactions:
Faster Transaction Settlement
Traditional settlement periods, such as the T+2 timeframe, can be bypassed with tokenization, enabling almost instantaneous transactions. This acceleration in the settlement process can lead to significant savings for financial firms, particularly in environments where interest rates are high.
Operational Cost Savings
Tokenization can streamline operationally intensive manual processes, resulting in operational cost savings. The 24/7 availability of data and the programmability of assets are particularly beneficial for asset classes that historically have been prone to manual and error-prone servicing or issuing processes. This can be seen in the way tokenization reduces the overhead associated with these activities.
Democratization of Financial Services
By simplifying complex and costly processes, tokenization has the potential to democratize access to financial services. It makes it economically feasible for financial service providers to cater to smaller investors, thereby expanding the inclusivity of the financial landscape.
Enhanced Transparency
The use of smart contracts in tokenization augments transparency. With features such as programmatic compliance and digital asset tracking, stakeholders can quickly identify any fraudulent or illegal activities.
Market Readiness for Adoption
The current financial environment is increasingly conducive to the adoption of tokenization. With hundreds of billions of tokenized cash in circulation today and the growing presence of digital asset teams within financial institutions, the stage is set for a broader acceptance of tokenization.
Application to Non-Traditional Assets
Tokenization can transform various non-traditional assets, such as real estate, art, and even intellectual property rights. The accessibility to a wider pool of potential buyers can increase the liquidity of these traditionally illiquid assets.
Fast Fact
In 2021, the German company Siemens issued the first digital bond on Polygon, a public blockchain platform, which was worth $60 million.
Challenges of Tokenization
Tokenization is beset by a range of regulatory and operational challenges. These challenges necessitate careful navigation to ensure that the adoption of tokenization is both effective and compliant with the prevailing legal frameworks.
Regulatory Uncertainty
In different countries, there are varying laws and regulations regarding tokenization, leading to a landscape of regulatory uncertainty. This disparity poses risks for businesses and investors alike, as they must navigate a complex web of legal requirements that can vary significantly from one region to another.
Compliance Complexities
Adhering to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations is a critical aspect of tokenization. However, the process of compliance can be intricate and financially burdensome, especially for smaller entities or startups venturing into the token blockchain space.
Cybersecurity Risks
Cybersecurity threats, including hacking and fraud, are ever-present challenges that threaten the stability and safety of tokenized systems. These risks underscore the need for advanced security protocols and continuous vigilance to protect the integrity of blockchain tokenization platforms and the assets they represent.
Anonymity vs. Transparency
The dual imperatives of anonymity and transparency present a regulatory conundrum within the realm of blockchain-based tokenization. Finding the right balance between these two aspects is a complex challenge, as the benefits of anonymity must be weighed against the need for transparency to prevent illicit activities and ensure trust in the system.

Tokenization Prospects
The tokenization of assets is poised to reshape the landscape of asset management and investment across a multitude of sectors.
- Expansion Across Sectors: Tokenization is expected to see considerable growth in many sectors, where it can enhance liquidity and democratize access to investment opportunities.
- Regulatory Evolution: Governments and financial authorities will continue to develop and refine regulatory frameworks. This evolution will support the creation of a more stable and predictable environment for tokenization blockchain activities. In the European Union, the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) proposal is a prime example of this proactive approach.
- Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in blockchain technology, particularly in areas of scalability and security, are expected to facilitate the widespread adoption of tokenization further.
- Interoperability Developments: The development of interoperability between different blockchain networks is likely to lead to a more diverse range of tokenization applications.
- Smart Cities and Resource Management: Tokenization could become a key component in the development of smart cities by enabling efficient management and trading of city resources.
- DeFi and NFTs: The rise of DeFi and NFTs underscores the growing relevance of tokenization in the digital economy. These developments are indicative of the innovative ways in which tokenization is being applied, highlighting its role in the evolution of business and technology.
How to Get Started with Tokenization and Create Your Own Tokens
To embark on the journey of tokenization and create your own tokens, you can refer to our article on creating tokens without needing coding skills. Here are also some tips to help you get started:
Understand the Basics
Conduct thorough research and gain a good understanding of what tokenization entails. This will help you decide wisely and avoid any potential pitfalls in the future.
Choose the Right Platform
There are various blockchains available for creating tokens, such as Ethereum, Tron, EOS, and Binance Smart Chain. Each platform has its own unique features and benefits.
Choose the Right Token Standards
Different platforms have different token standards, such as ERC-20 for Ethereum and TRC-10 for Tron. These standards dictate the functionalities of your token, so choose wisely based on your project’s needs.
Hire Experienced Professionals
While it is possible to create tokens without coding skills, having experienced professionals on board can greatly enhance the success of your token. Consider hiring a team of professionals to guide you through the tokenization process.
Continue Learning and Improving
Blockchain is a constantly evolving space, so it’s important to continue learning and improving your understanding of it. Stay updated on the latest trends and developments in the industry, and be open to adapting your token strategy as needed.
Bottom Line
Tokenization in blockchain is a rapidly growing trend with the potential to reach a market size of $16 trillion by 2030. It has numerous advantages, but its successful adoption by organizations depends on its ability to handle legal hurdles and cybersecurity threats.
FAQ
How do blockchain tokens operate?
Blockchain tokens serve as digital assets that facilitate the transfer, storage, and verification of information and value in a secure and efficient way. These tokens can be designed with specific features, allowing them to be used for various purposes within the blockchain environment.
Can you explain tokenization in the context of Web3?
In the realm of Web3, tokenization is the conversion of rights to an asset, whether physical or digital, into a digital token on a blockchain. This process is fundamental to the functioning of Web3 technologies.
Can blockchain work without tokens?
Yes, blockchain technology can operate without tokens. In fact, private blockchains do not require any form of cryptocurrency to function. Private blockchains are mainly used within organizations or closed networks and do not rely on external participants for validation.
On the other hand, public blockchains use tokens as a means of rewarding network participants for their contribution to the network’s security and overall functioning. These tokens can also be used as a medium of exchange on the blockchain.




