Crypto Ransomware – How They Happen and How to Avoid Them
June 04, 2025

Cybersecurity is a crucial issue when it comes to the Internet, online platforms, and cloud storage. The emergence of decentralized networks encouraged more outlaws to deploy malicious tactics and embezzle funds while hiding behind an untraceable pseudonym.
Crypto ransomware has been rising in the last few years, especially since more entities and companies now store confidential information and sensitive files in cloud spaces. Hackers use various approaches and techniques to gain access to confidential data, lock it, and ask for money in exchange.
Let’s dive deeper into the types of this hack and some ransomware examples that you must be aware of.
Key Takeaways
- Crypto ransomware attacks lock data and demand money in exchange for returning it.
- These breaches are mostly silent and can enter networks and systems without notice.
- Most hackers demand ransom to be paid in cryptocurrency, leveraging its anonymity and immutability.
- Authorities advise against paying ransom to hackers, as there are no guarantees of receiving the unlock key or data back.
Understanding Crypto Ransomware
Crypto ransomware attacks are dangerous software that encrypts your files with advanced coding techniques, rendering them inaccessible until money is paid. Nowadays, cryptocurrency is used to receive ransom funds and transfer them anonymously.
This software infiltrates systems through phishing emails, downloaded viruses, or malicious websites. Once the file gets in, it employs robust encryption algorithms, making the decryption key needed for data recovery.
Victims may lose credit card data, financial credentials, crypto-stored funds, and other crucial information.
Cybercriminals will provide the key to a decentralized wallet upon paying the demanded amount, mostly in cryptocurrencies. The stealthy approach means victims often remain unaware until they try to access their files, by which time significant damage has already been done.
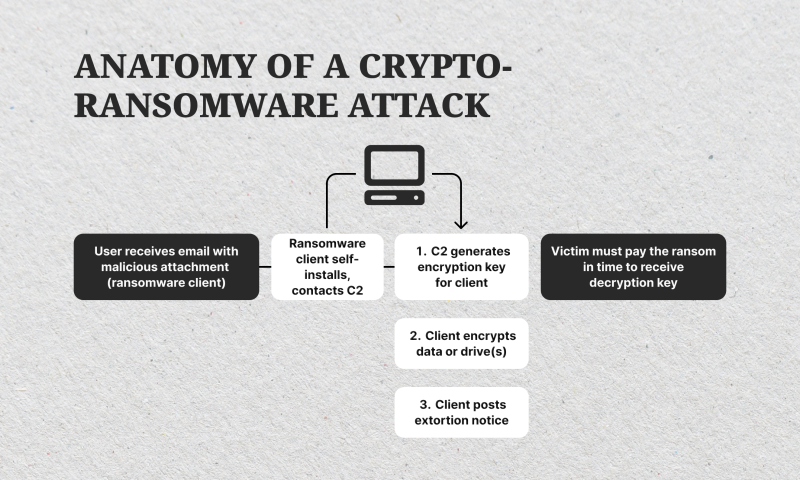
Step-by-Step: How Crypto Ransomware Happens?
Ransomware is a multi-staged attack that requires advanced technical skills to develop the malware, set its parameters, and specify its target. Typically, it goes the following way:
1- The Device is Infected

Ransomware infection means getting the malware file inside the device or computer, which happens after the user unknowingly enables access through malicious attachments or download links. Common infection methods include;
- Phishing Emails: These emails claim to be from a trusted source, like the user’s bank, workplace, or a business offer. They include a downloadable file that gets the malware in once it is clicked.
- Software Vulnerabilities: This approach takes advantage of security gaps within the software or the operating system to insert malicious code into a device or network.
- Trojans: These are files disguised as legitimate attachments, such as a software update or game installation. Once the user downloads the file, the malware enters the system.
- Compromised Websites: Viruses may spread when clicking on a malicious link in a website that has been infiltrated by attackers.
Once executed, the ransomware installs itself silently to evade detection by antivirus software. The malware may remain dormant for a period, allowing it to reproduce silently. By the time symptoms appear, such as inaccessible files or ransom notes, the virus has already established itself deeply within the system.
2- Data is Encrypted
Upon activation, the ransomware scans your system for valuable files, such as documents, images, and databases, and encrypts them using advanced algorithms like AES or RSA. This process is swift and often goes unnoticed until the user fails to access their affected files.
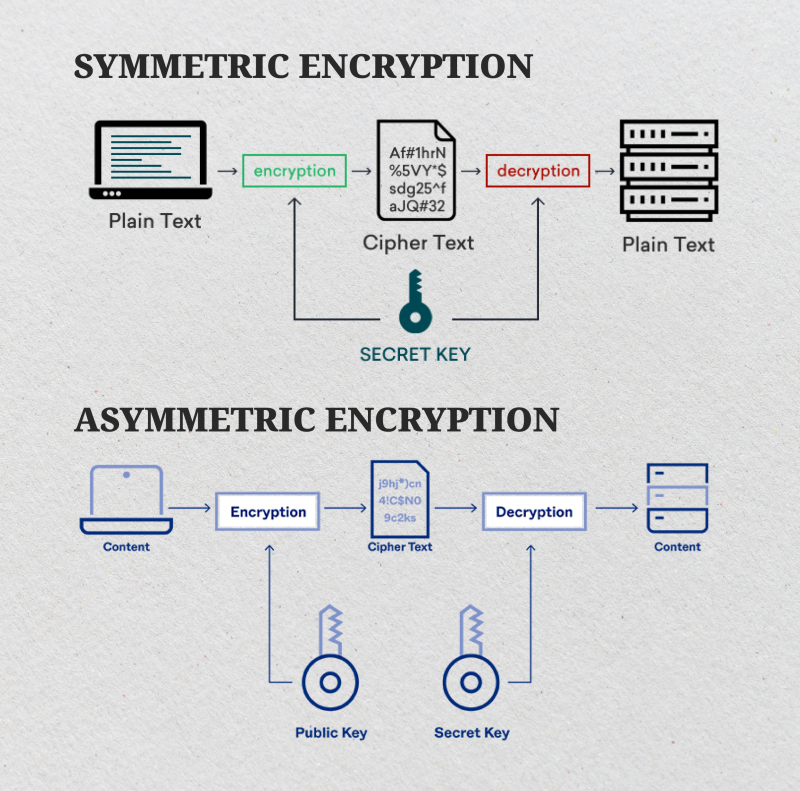
Encryption methods fall into two categories: symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. This way is faster but can be recovered by tech-savvy users.
Asymmetric encryption employs a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This locks the files and requires more computational resources to generate a decryption key. Hackers usually demand a ransom in exchange for the unlock information.
3- Ransom Demands
After encryption, the ransomware displays a note demanding payment, usually in cryptocurrency, to provide the decryption key. The note often includes threats of data deletion or public release if the ransom is not paid promptly. Deadlines and escalating demands are common tactics to pressure victims into compliance.
4- Payment and Decryption
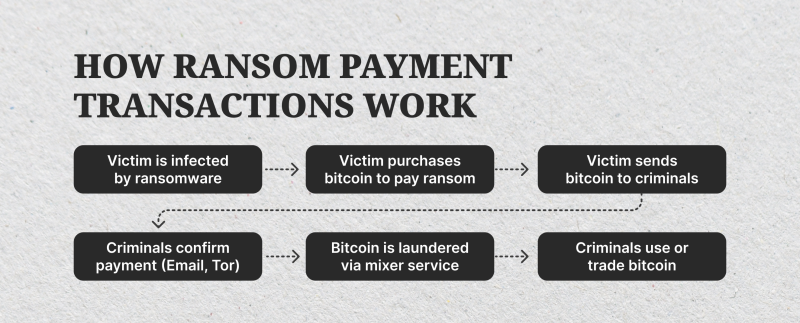
Users may pay the amount and receive their data back. However, you must remember that there is no guarantee the attackers will provide the decryption key. Some victims receive keys that do not work or are ignored entirely.
Cybercriminals use cryptocurrencies and DeFi wallets to hide their identities and move the money without being noticed by regulators.
Therefore, authorities advise against payment, recommending restoration from offline backups, professional assistance, and engaging cybersecurity experts.
Crypto Malware vs Ransomware
Malware and ransomware are two typical ways hackers use to lock or corrupt your data. However, their objectives differ slightly.
Crypto ransomware restricts access to entire systems, displaying a lock screen that prevents any use until payment. Attackers may use symmetric encryption for speed or asymmetric encryption for enhanced security, ensuring that users cannot obtain their data without paying the demanded amount.
Crypto malware is a subset of ransomware, specifically encrypts files, leaving systems operational but data inaccessible. It operates stealthily, encrypting files without immediate signs, which can delay detection and response.
These malware typically employ strong encryption algorithms to restrict your access to data. Their aim is to corrupt and damage your files without necessarily asking for money in exchange.
Both breaches can be avoided with regular backups, tech training, and robust security measures to mitigate cyberattack risks.
Crypto Ransomware 2024-2025: Industry Overview
These breaches are not entirely new. They trace back to 1989 when malware was installed and distributed through floppy disks during a World Health Organization AIDS conference.
However, with higher access to the Internet and advanced encryption techniques, hackers are employing much more sophisticated attacks, especially with the popularity of cryptocurrencies.
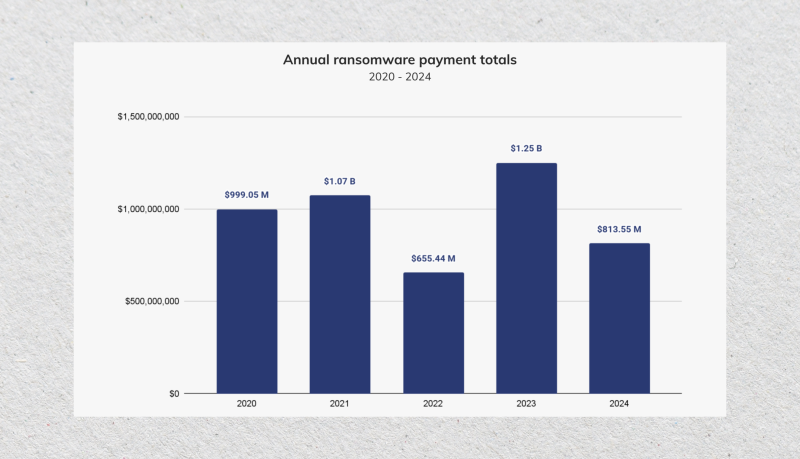
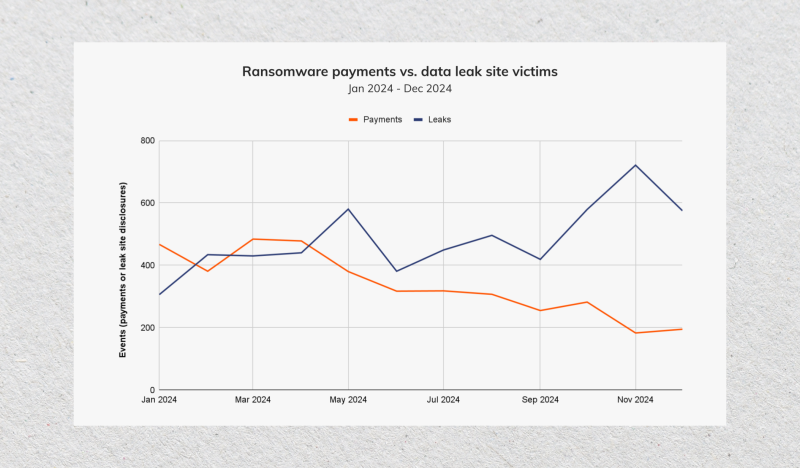
A study by Chainalysis revealed that 2023 was the peak for the annual ransom payment total, with $1.25 billion paid by victims. However, this trend declined in 2024 due to stronger law enforcement, better global collaborations, and growing tendencies to refuse payments.
Therefore, victims paid less ransoms by 35% in 2024, with $813 million.
In 2024, around 700 ransomware attacks faced rejection to pay the demanded money, leading to information being leaked. Only 200 cases agreed to adhere to the hackers’ request.
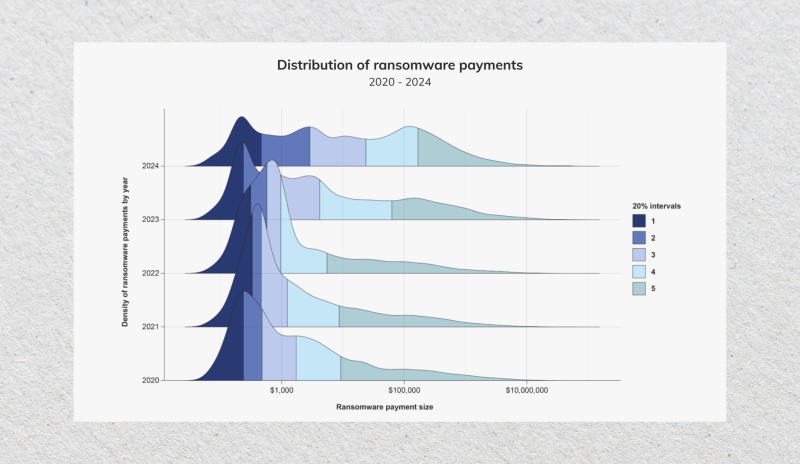
When it comes to the ransom amount, most cases used to be around the $1,000 range in 2020, and only a few cases asked for $100,000 or more.
However, this trend has changed remarkably. In 2024, more hackers are asking for $10,000 – $100,000, with more cases requiring payment of nearly one million dollars. This shift means that cybercriminals are targeting higher-class users, such as institutions, wealthy individuals, and government agencies.
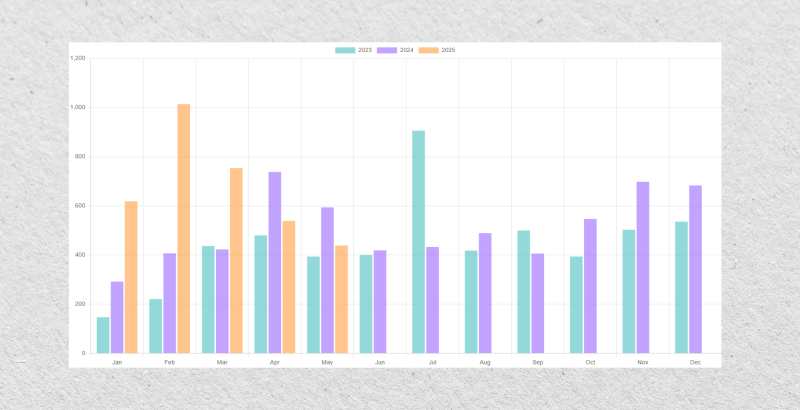
Ransomware.live revealed statistics that show more monthly attacks in February 2025 than any month in the past two years, probably due to the rising prices and inflow into cryptocurrencies and stablecoins.
This graph visualizes the recorded victims per month between the years 2023 and 2025 (as of May 2025).
Technology and manufacturing were the top two victims compared to other industries, especially the US, with 1,300 incidents reported so far this year.
5 Types of Ransomware Attacks
Cybercriminals deploy different types of attacks depending on their goals. Some target files, file-sharing networks, or the entire system. Here are five key types of ransomware attacks you should be aware of to protect your organization or personal devices.
Crypto Ransomware
Encrypts files using advanced algorithms and demands a ransom for the decryption key. It leaves your system operational but your valuable data inaccessible.
This is the most prevalent and financially motivated form of ransomware, where victims often do not realize they have been breached until they try to open a file and receive a ransom note.
Leakware
Also known as doxware, this strain threatens to publish your sensitive data online unless a ransom is paid. Attackers often steal data before encryption and place it in a different cloud location.
This double extortion ransomware applies additional pressure by threatening reputational or regulatory damage, especially in industries that value privacy, such as healthcare, finance, or law.
Locker
These attacks lock the victim out of their entire device and block access to all applications and functions. Unlike crypto ransomware, it does not encrypt specific files but prevents the entire system from being used.
Locker ransomware victims are shown a ransom message, often impersonating law enforcement agencies or governments, causing severe damage.
DDOS
DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attempts to crash the network by flooding it with traffic, rendering it dysfunctional. The attacker demands payment to stop the attack.
This approach often occurs against service websites or public-facing servers, causing downtime and loss of revenue. It is less destructive to data but is highly disruptive to business operations.
Scareware
This attack relies on fear tactics to manipulate users. Attackers display fake warning messages or pop-ups claiming your infected computer is malfunctioning, urging you to buy fake software or pay to “fix” issues.
This tactic is usually followed by illegitimate call centers, where they may not always encrypt or block data, but it often leads to malware infection or financial scams.
Popular Ransomware Groups
The world has seen a huge number of such attacks, and several hackers or groups have become known for dominating the cybercrime landscape.
They operate like businesses, with support channels and negotiation tactics, deploying increasingly sophisticated attacks. Here are the top ransomware hackers.
Clop
- Established: 2019
- Victims: Over 1,000
- Collected: Estimated $500 million
Clop is known for large-scale data breaches and double-extortion tactics, where data is encrypted and leaked. In 2023–2024, it exploited MOVEit software vulnerabilities, compromising hundreds of firms globally. The group operates with a high level of coordination and technical expertise.
RansomHub
- Established: 2024
- Victims: Over 500
- Collected: Data not publicly available
RansomHub emerged as a successor to several disbanded groups, offering ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS). Affiliates use their platform to execute attacks, splitting profits with developers. It is known for aggressive negotiation tactics and quick data leaks.
Akira
- Established: 2023
- Victims: Over 450
- Collected: $42 million
Akira surfaced in 2023 and quickly made headlines with its focus on mid-sized enterprises. The group encrypts data and threatens public leaks unless ransoms are paid. They favor VPN exploits to infiltrate networks and often use unique extensions to brand their attacks.
Qilin
- Established: 2022
- Victims: Over 200
- Collected: Data not publicly available
Qilin operates a highly customizable RaaS platform. They offer affiliates tailored ransomware builds targeting the healthcare and education sectors. Qilin emphasizes anonymity and speed, making it hard for law enforcement to trace, with victims listed on a leak site to apply pressure.
Play
- Established: 2022
- Victims: Over 700
- Collected: Data not publicly available
Play ransomware uses a unique “.play” extension and custom tools and files while avoiding detection. The group gained traction in 2023, targeting Latin American government entities. Play uses already-existing tools and software, such as native Windows tools and MS programs.
Historical Crypto Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware tricks have evolved over the decades. However, the core tactic remains extortion through encryption. As the Internet and technology grew in popularity, these attacks became more relentless and sophisticated.
The first attack started through physical hardware, while most of today’s breaches happen online and without direct contact with the victim. Let’s take a look at some ransomware attack examples.
AIDS Trojan (1989)
The AIDS Trojan was the first instance of ransomware that was distributed via floppy disks labeled “AIDS Information” sent to unsuspecting attendees at the World Health Organization.
Also known as the PC Cyborg virus, the malware counted how many times the system boosted, and after 90 times, it encrypted file names and demanded payment to a P.O. box in Panama.
The encryption was weak and easily reversed, but the psychological manipulation laid the groundwork for future attacks. At the time, cybersecurity awareness was minimal, making the attack remarkably effective.
CryptoLocker (2013)
CryptoLocker spread via email attachments, marking a major evolution in ransomware tactics using RSA public and private keys to lock user files.
The malware encrypted files with unmatched strength at the time, making decryption nearly impossible without the private key and demanding victims pay a ransom within 72 hours or lose their data forever.
Estimated losses exceeded $30 million, setting the standard for modern crypto ransomware and demonstrating the profitability and scalability of these hacks that inspired many ransomware variants in the upcoming years.
The group was dismantled in 2014 after a successful law enforcement collaboration, Operation Tovar, which managed to cut communication channels between network operators and command centers.
WannaCry (2017)
WannaCry was one of the most devastating ransomware attacks in history, infecting over 230,000 systems across 150 countries. It caused total damage estimated at $4 billion.
It exploited a Windows vulnerability to infiltrate networks and spread rapidly without user interaction, encrypting files and demanding $300 in Bitcoin.
The attack compromised major institutions, including the UK’s NHS, Spain’s Telefónica, and Germany’s Deutsche Bahn, causing widespread disruption to vital electronic devices and machines.
Microsoft issued emergency patches, and a security researcher discovered a kill switch that halted its spread. This attack highlighted the need for timely patch management and stronger network segmentation.
What to Do When a Ransomware Attack Happens?
Ransomware attacks are critical situations that require swift, strategic action to minimize damage. Immediate, informed responses can dramatically reduce the damage. Here is what you should do:
- Isolate the Infected Systems: Disconnect affected devices from the network to prevent further spread. Disable Wi-Fi, unplug Ethernet cables, and remove external drives.
- Alert IT and Security Teams: Notify your internal cybersecurity team or external consultants. Prompt communication is essential to assess the scope and initiate containment.
- Do Not Pay the Ransom: Authorities advise against paying ransoms. You are not guaranteed to receive a decryption key after paying. In fact, paying fuels criminal operations.
- Preserve Evidence: Take screenshots of ransom notes and export system logs related to the attack. This will aid law enforcement and forensic investigations.
- Report the Incident: File a report with local authorities and national cybersecurity agencies to receive the necessary legal guidance.
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks?
Preventing ransomware is more effective and less costly than responding to hacks. Here is a checklist for proactive system defense:
- Keep all software and operating systems up to date.
- Use reputable antivirus and endpoint protection services.
- Back up data regularly and store copies offline.
- Use multi-factor authentication for all critical systems.
- Restrict administrative privileges to essential personnel.
- Implement email filtering and scan attachments automatically.
Conclusion
Crypto ransomware is one of the most dangerous threats in the cyber landscape. Its ability to silently encrypt vital data and demand payments puts businesses and individuals at serious risk.
However, proactive measures, like strong backups, cyber education, and updated defenses, can reduce vulnerability and mitigate impact. It is crucial to understand how many ransomware attacks work and how to react when they happen.
As ransomware evolves, staying informed and alert is your best defense. Do not wait until you are a target—prepare, protect, and stay one step ahead of the attackers.
FAQ
How does crypto ransomware affect your computer?
Crypto ransomware encrypts your files using a strong algorithm, making them inaccessible, then demands payment to decrypt files and restore your data.
What is the primary function of crypto-ransomware?
The main purpose of crypto-ransomware is to extort money by encrypting victims’ data and demanding a ransom to regain access and restore files.
Does a VPN stop ransomware?
A VPN protects your data in transit, but it does not stop ransomware. They typically spread through phishing emails, malicious software downloads, or system vulnerabilities, not through unsecured connections.
Shall I pay for ransomware attackers?
Regulators recommend against paying the ransom. Payment does not guarantee data recovery and encourages further attacks. Instead, report the incident and consult cybersecurity professionals for recovery options.




