How Strong is The US Economy Today?
Dec 01, 2023

The state of the US economy has been a topic of much discussion and speculation in recent times. With rising gas prices, unaffordable housing, and high interest rates, many people assume that the economy is in a dire state. However, when we delve into the numbers, we find that the US economy is actually doing quite well.
In fact, recent economic growth data for the third quarter of 2023 indicates that the economy is experiencing its fastest pace of growth in over two years. So, what exactly is driving this unexpected strength in the economy? Let’s take a closer look.
Key Takeaways:
- Consumer spending in the US increased by 4.0% in the third quarter of 2023, indicating some signs of strength.
- The inflation rate data in October came in at 3.2%, lower than analyst expectations.
- The economy of the United States may slow down in 2024.
Consumer Spending as a Driving Force in 2023
One of the key factors contributing to the robustness of the US economy is consumer spending. People continue spending money on various goods and services, from automobiles to cinema tickets. This sustained, and even growing consumer spending has been instrumental in expanding the economy at a faster rate than initially predicted.
Currently, consumer spending accounts for more than two-thirds of the US economic activity. In the third quarter of this year, consumer spending grew at a rate of 4.0%, a significant improvement compared to the 0.8% growth in the previous quarter.
Fast Fact
The US economy showed an impressive gross domestic product (GDP) growth of nearly 5% in the third quarter of 2023, the fastest since the fourth quarter of 2021
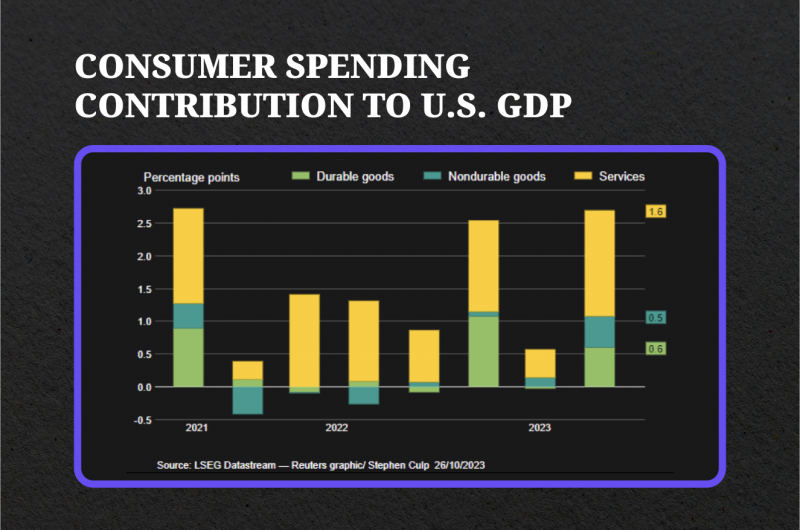
This surge in consumer spending contributed 2.69 percentage points to the overall GDP growth. While wage growth has slowed, it is worth noting that it is still outpacing inflation, thereby increasing households’ purchasing power.
Possible Spending Slowdown
However, we need to consider the potential challenges that may impact consumer spending in the future.
The declining savings rate and potential fuel price rises, combined with other factors, could adversely affect spending. Economists estimate that the excess savings accumulated during the COVID-19 pandemic, which are primarily concentrated among high-income households, may run out by the first quarter of 2024.
Additionally, low-income consumers increasingly rely on debt to fund their purchases, which may lead to higher credit card delinquencies as borrowing costs rise.
Government Spending and Investment by Businesses
Government spending, including federal, state, and local expenditures, has significantly contributed to the US economy. In the third quarter of 2023, government spending increased, providing an additional boost to the overall GDP growth. This increase can be attributed to various factors, such as infrastructure projects and social welfare programs.
However, it’s worth noting that while government spending has risen, business investment has taken a dip for the first time in two years. This decline can be attributed to decreased spending on equipment, such as computers, and the fading effects of President Joe Biden’s administration’s semiconductor manufacturing campaign.
Fast Fact
Americans started 2023 financially strong, per a recent Fed report. Typical household net worth surged 37% from 2019 to 2022. Home prices and the stock market soared, setting new records.
The Impact of the Inflation
Inflation is another critical aspect to consider when assessing the strength of the US economy.
Inflation is a key indicator which refers to the general rise in prices of goods and services over time, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money. Inflation can significantly impact individuals, businesses, and the overall economy.
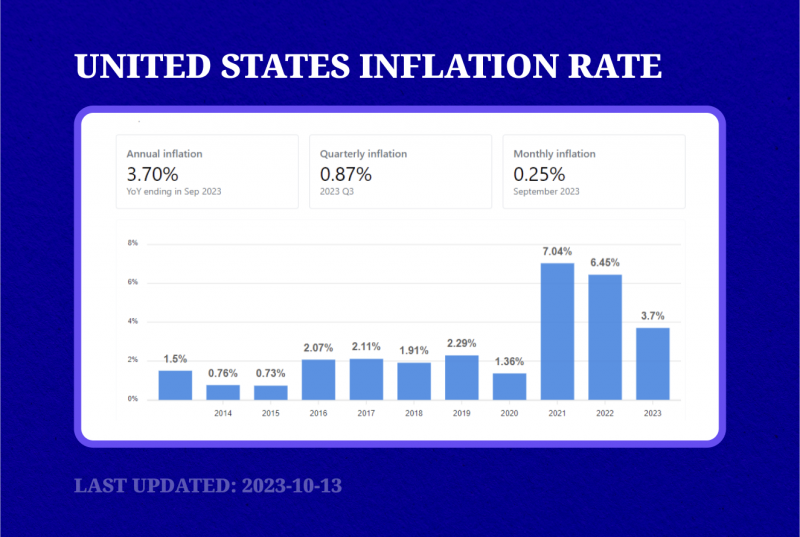
The recent data for October indicates a considerable slowdown of underlying inflation in the third quarter:
The report showed that the year-on-year inflation rate in October came in with 3.2%, lower than analyst expectations of 3.3% and a decrease from September’s 3.7%. Additionally, core year-on-year inflation slightly declined from 4.1% in September to 4% in October.
“We’ve seen for a period of time now a post-pandemic induced negative bias about an imminent recession and persistent inflation. But not only is the economy surprisingly resilient, but we also got productivity-driven growth for two consecutive quarters in 2023, meaning the business cycle still looks very solid,” says Brian Bethune, an economics professor at Boston College.
Personal Consumption Expenditures
The price index for personal consumption expenditures (PCE), excluding food and energy, rose at a rate of 2.4%. This is the slowest pace since the fourth quarter of 2020, following a 3.7% increase in the second quarter.
The Federal Reserve uses the PCE metric as one of its key indicators to assess the economy’s overall health. In particular, the central bank closely monitors the core PCE price index as it provides a better indication of underlying inflation trends.
The Future of Interest Rates
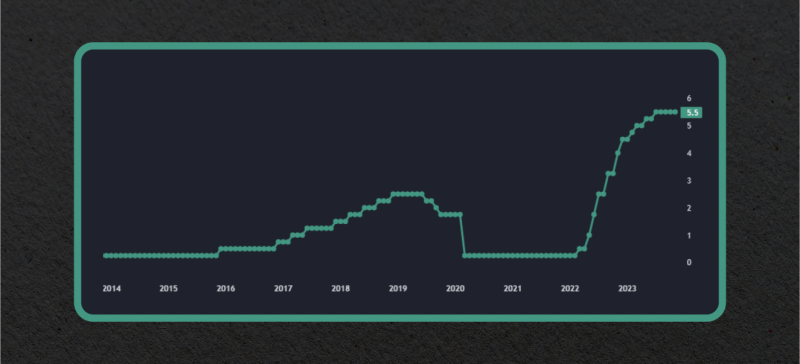
Despite increasing investor optimism, the Federal Reserve remains cautious and continuously warns about the impact of inflation on the economy.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated that if inflation continues to remain high or economic data is unsatisfactory, the central bank may have to resort to further interest rate hikes to get inflation back in line with the 2% target.
What does this mean for the US economy? The higher interest rates can lead to slower economic growth as borrowing becomes more expensive for businesses and individuals. This can result in decreased consumer spending, reduced business investments, and potentially even a slowdown in the housing market.
However, given the recent economic data and the overall outlook for the US economy, the Federal Reserve is expected to leave interest rates unchanged in the near future.
The central bank has already raised its benchmark interest rate several times in recent years, but the current economic indicators do not suggest an immediate need for further rate adjustments.
What Is Next for the US Economy? – US Economy Forecast
In recent months, economists and financial experts have expressed growing concerns about the potential slowdown. As was already mentioned, with declining savings rates and increased reliance on debt for purchases, there are fears that consumer spending could decrease significantly in 2024.
While excess savings accumulated during the COVID-19 pandemic may have boosted spending in the short term, these savings are expected to run out by the first quarter of 2024. As a result, this may lead to a sharp slowdown, as seen with some companies cutting their revenue forecasts for the coming years.
However, some experts argue that the current level of debt and reliance on credit is not cause for immediate concern. They point to a strong labor market and government transfers during the pandemic as factors that have kept spending afloat. Additionally, they argue that any potential slowdown in spending will be temporary and not have long-lasting effects on the overall economy.
Economy of the US: The Basic Theory
While there are various factors and indicators that contribute to the overall health of the US economy, it is necessary to understand the fundamentals that govern economic principles.
What type of economy does the US have?
The US has a mixed economy, combining elements of capitalism and a command economy. This means that while individuals are free to own businesses and make economic decisions, the government also regulates specific industries and provides social services.
There are several theories used to explain how a country’s economy functions:
- One such theory is Adam Smith’s theory of the “invisible hand”, which suggests that a free market economy, without government intervention, will naturally self-regulate and lead to efficient allocation of resources.
- On the other hand, John Maynard Keynes’ theory focuses on the role of government intervention in economic management. Keynes argued that during times of economic downturn or recession, the government should take an active role in stimulating demand through fiscal policies, such as increased government spending and tax cuts.
Which best describes how the US government affects the economy?
In reality, it is a combination of both theories that contribute to the overall economic policy in the US. The government intervenes in certain areas to regulate and promote competition while providing support during economic hardship.
How the US Government Affects the Economy
The US government plays a significant role in shaping the economy through various policies and interventions. Here are some ways in which the government affects the economy:
Fiscal Policies: As mentioned earlier, fiscal policies refer to government spending and taxation. The US government uses fiscal policies to manage the overall health of the economy, with specific goals such as promoting growth, controlling inflation, and reducing unemployment.
For example, during an economic downturn or recession, the government may introduce tax cuts to stimulate consumer spending and provide financial aid to businesses. On the other hand, in times of economic growth and potential inflationary pressures, the government may increase taxes to reduce demand and prevent excessive price increases.
Monetary Policies: The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in setting monetary policies that affect the economy. This includes setting interest rates, controlling the money supply, and regulating banks.
By increasing or decreasing interest rates, the Federal Reserve can influence borrowing costs for businesses and individuals, which in turn affects consumer spending and business investments. The central bank can also impact inflation by controlling the money supply.
Regulations: The US government also implements regulations to ensure fair competition and protect consumers. This includes antitrust laws, which prevent monopolies and promote healthy competition in the market.
Additionally, the government has regulations in place for industries such as healthcare, finance, and energy to protect consumers from potential harm or exploitation.
US Economy in Retrospective
Let’s look at the history of the US economy. The United States has undergone remarkable transformations and faced numerous challenges.
Overall Assessment
Over the past 100 years, the US economy experienced exponential growth, expanding from $0.8 trillion in 1923 to $26 trillion in 2023. Additionally, the US population grew from 106 million in 1920 to 334 million in 2023, driven by immigration, increased life expectancy, and natural increases.
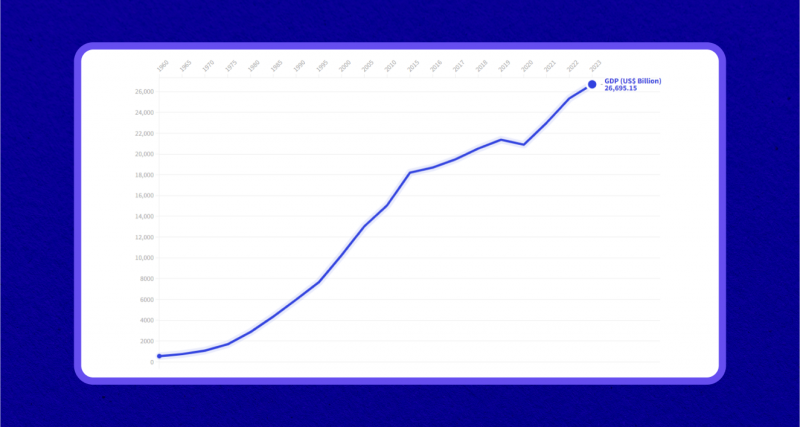
Per Capita Income and Economic Welfare
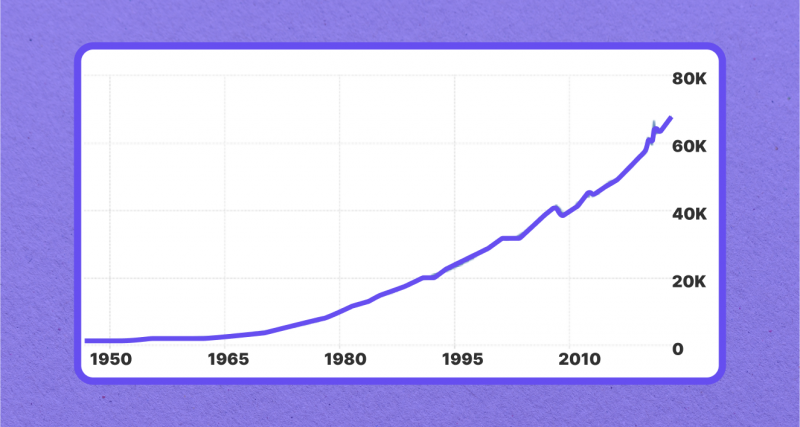
One of the most significant indicators of economic prosperity is per capita income. In 1917, the per capita income in the US was $7,500. By 2023, it had soared to $78,400 in current prices. This substantial increase in per capita income reflects the improvement in the overall welfare of the US population.
Employment and Economic Structure
The US employment structure has undergone significant transformations over the past century. In 1900, approximately 38% of the population was employed in agriculture, while manufacturing accounted for 24.7% and services for 40.7%. Fast forward to 1950, and the US economy experienced a shift, with agriculture employing only 10.5% of the population, manufacturing employing 24.8%, and services dominating at 64.7%.
The US Economy’s Share of the Global Economy
The US economy’s share of the global economy has fluctuated over the years. In 1917, the US economy accounted for 20% of the world’s economy, reaching its peak at 27% in 1950. However, since 1950, the US economy’s share has experienced a decline due to the rapid economic development of East Asian countries.
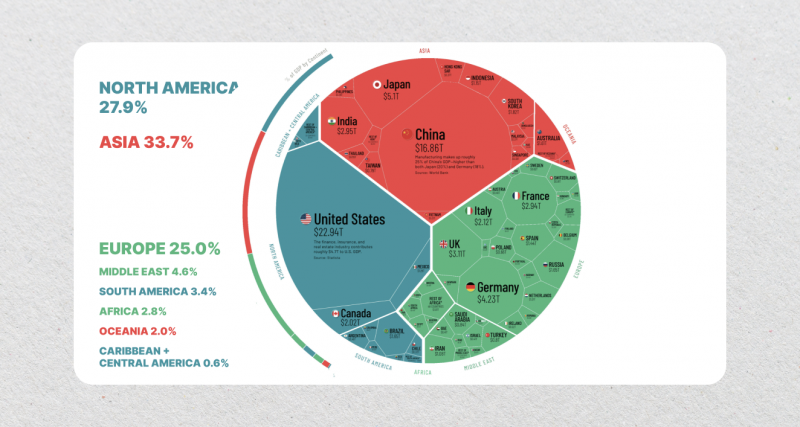
By 2022, the US economy comprised approximately 25.32% of the world’s economy. Notably, China GDP and Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) are close to surpassing that of the US. PPP considers the difference in cost of living between countries and provides a more accurate comparison of economic strength than GDP.
Economic Performance in the Early 20th Century
In the early 20th century, up to 1929, the economy experienced an average annual growth rate of 3%. The US economy after World War I relied in large part on construction, consumer spending, and investment in new technologies such as automobiles and electricity.
The establishment of the Federal Reserve System in 1913 played a crucial role in maintaining the country’s currency system. Furthermore, the rapid electrification of the US economy and the rise of New York as the world’s financial capital contributed to economic growth. This period was known as the “Roaring Twenties” due to the rapid economic growth and prosperity.
However, this economic boom was not sustainable as it relied heavily on speculation and borrowing. Easy credit conditions led to excessive consumer spending, which fueled inflation.
The Great Depression
The 1930s marked a challenging period for the US economy with the onset of the Great Depression. The stock market crash in 1929, followed by high unemployment rates, bank failures, and a decrease in industrial production, had severe repercussions.
The US economy lost almost twelve years of development, and it wasn’t until 1940 that it began to regain its economic capacity. The government intervened actively to rescue the country from the recession, increasing budget expenditures and stimulating cooperation between the state and the private sector during World War II.
The Economic Renaissance and Global Influence
The period from 1948 to 1972 witnessed an economic renaissance for the US and solidified its position as the world’s most powerful economy. It was experiencing steady growth from wartime production – this best describes the state of the US economy at the end of World War II.
The US aided Western Europe and Japan through initiatives like the Marshall Plan, contributing to their post-war economic recovery. Major economies tied their currencies to the US dollar, as the US became the guarantor of credibility for approximately 50 countries. The US economy experienced an average annual growth rate of 4% during this period.
Oil Shocks and Economic Reforms
The US economy faced significant challenges in the 1970s and 1980s, including the oil shocks of 1973 and 1979. There was a significant increase in oil prices and subsequent inflation and recession. President Ronald Reagan implemented economic reforms, reducing income tax and government regulations to tackle inflation. By the 1990s, the US economy had stabilized, experiencing steady growth and a declining unemployment rate.
The Crisis of 2008
The US economy experienced growth from 2001 to 2008 but was hit hard by the global financial crisis in 2008-2009. The crisis highlighted inadequate financial sector regulation and excessive money supply. The US government implemented Keynesian policies to stimulate economic recovery, and the economy grew again.
The COVID Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 brought the US economy to a halt, with businesses closing and unemployment rates soaring. The government responded with significant fiscal stimulus measures, including the CARES Act, to provide financial relief for individuals and businesses. By late 2020, the economy began to recover as lockdowns were lifted and vaccinations rolled out.
Fast Fact
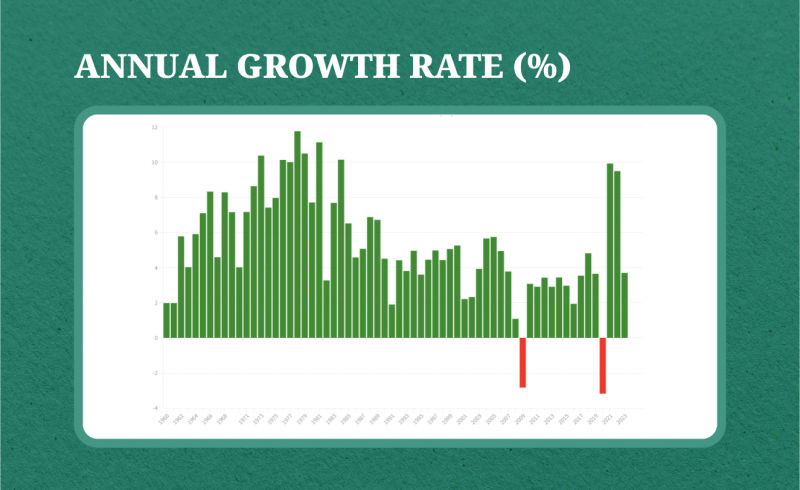
In the years 2021-2022, the United States saw a remarkable annual growth rate of 9.50% and 9.93%, respectively. This impressive performance can be attributed mainly to the reopening of businesses after the devastating effects of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Summing Up – Returning to the Challenges of Today
The US economy has showcased its resilience in the face of various challenges, including recent aggressive interest rate increases from the Federal Reserve. The GDP growth of nearly 5% is a testament to the economy’s strength and stamina.
Despite the Fed’s vigorous attempts to curb growth and inflation by raising its benchmark short-term interest rate to the highest levels in 22 years, the data suggests that the economy not only maintained its momentum but even managed to accelerate.
So, what is the US economy outlook for 2024 and beyond? As we look ahead, there are potential factors that could slow down the economy in the coming months. Rising debts, macroeconomic factors, and the lagged effects of the previous rate hikes can still contribute to a potential slowdown in 2024.
FAQs
What is the economic system in the United States?
The US type of economy is known as a mixed economy, where both private and public enterprises coexist. The government plays a significant role in regulating the market, but most of the businesses are owned and controlled privately.
US vs China economy – which is stronger?
The question of which is stronger between the US and China economy is a topic that is often debated. In terms of nominal US vs China GDP, the US has been at the top for decades. However, in recent years, China has overtaken the US in terms of PPP GDP. In 2022, both countries together shared 42% and 34% of the entire world’s GDP in nominal and PPP terms, respectively.
What is the US’s biggest contributor to GDP today?
As of 2022, the financial services and real estate industries are the largest contributors to the GDP of the United States. These sectors make up a significant portion of the US economy and continue to add value year after year.
What state has the most millionaires per capita?
According to 2020 data, New Jersey has the highest ratio of millionaire households per capita at 9.76%. This is followed closely by Maryland, Connecticut, and Massachusetts, with ratios of 9.72%, 9.44%, and 9.38%, respectively.
How is the economy in the US right now?
The US economy is currently experiencing a steady growth rate despite some challenges and potential factors that could slow it down in the future. The latest GDP data shows a growth of nearly 5%.