Spot vs Perpetual Futures: Which Is Right for You?
Aug 4, 2025

Derivatives trading volume of the crypto market today dwarfs the spot market, according to real-time exchange data. This means the majority of modern price action is driven by leveraged speculation, not just the simple buying and selling of assets.
This creates a critical distinction for traders: spot vs perpetual futures. A trader must understand the mechanics of both to make informed decisions. This guide provides a direct comparison of their structure, risks, and strategic applications.
Key Takeaways
- Spot trading is for actual asset ownership and long-term investing; perpetual futures are contracts used purely for short-term speculation on price.
- Leverage is the main feature of perpetual futures trading, offering high capital efficiency but also creating the primary risk of liquidation.
- The funding rate is the core mechanism of perpetuals, acting as a regular payment between long and short traders to keep the contract price pegged to the spot price.
What is Spot Trading?
Spot trading is the most straightforward way to engage with financial markets. It involves buying or selling an asset, like cryptocurrency or a stock, for immediate settlement and delivery. The transaction is direct, with no future obligations attached.
The Principle of Direct Ownership
The core principle here is direct, immediate ownership. When you execute a spot buy order for one Bitcoin, you receive one Bitcoin in your wallet.
This ownership gives you the right to hold the asset indefinitely, collect any dividends paid, or sell it at a later date. The mindset of a spot trader is that of an investor, focused on acquiring the underlying asset itself based on a belief in its long-term value.
Advantages and Limitations
The structure of spot trading presents a clear set of benefits and drawbacks for a trader.
Advantages
- Simplicity: There are no complex derivative mechanics like expiry dates, funding rates, or liquidations to manage. Your profit or loss is tied directly to the price movement of the asset you hold.
- True Ownership: You hold the actual asset, giving you the freedom to withdraw it to your own custody or use it in other applications like staking or DeFi.
Limitations
- Capital Intensive: All positions are unleveraged. To control $50,000 worth of an asset, you must have $50,000 in cash. This makes building large positions very capital-intensive.
- Difficult to Short: The market is primarily structured for long positions. Profiting from a price decrease is often impossible for most retail users on a standard spot exchange.
What Are Perpetual Futures?
Perpetual futures contracts are a modern type of derivative designed purely for speculation. Unlike spot trading, when you trade perpetuals, you are not buying or owning the underlying asset. Instead, you are placing a leveraged bet on its future price direction.
Trading an Agreement, Not the Asset
The main feature of these contracts is their “perpetual” nature—they have no expiration date. Unlike traditional futures contracts that settle on a specific day, a perpetual futures position can be held as long as a trader maintains sufficient margin to cover it.
Their popularity in certain markets is immense. For example, crypto derivatives trading volume in early 2025 has been consistently 5-7 times larger than spot volume. Perpetual futures contracts drive the vast majority of this activity, showing their dominance among active traders.
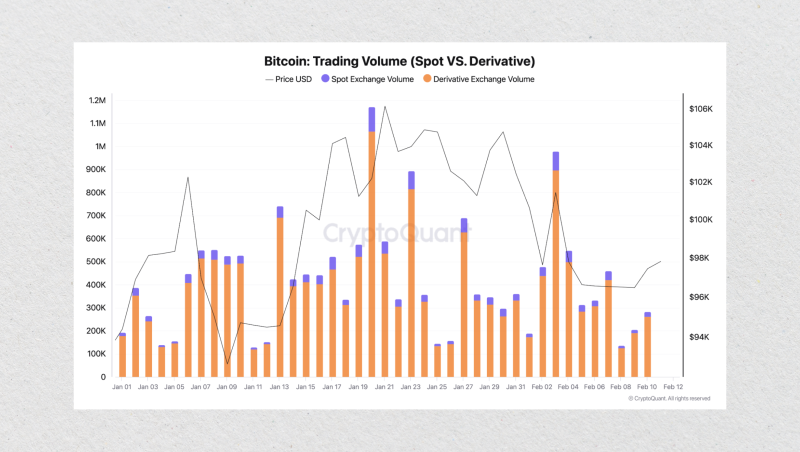
The sheer scale of this market has made perpetuals a standard, required feature for any modern trading platform. In response, technology providers are integrating these instruments to meet broker demand. The B2TRADER platform, for instance, recently added full support for perpetual futures trading, a move that directly addresses this growing market segment.
Advantages and Limitations
The design of perpetual futures offers a distinct set of benefits and risks:
Advantages
- Capital Efficiency: Traders can control a large position with a small amount of capital (margin). With 10x leverage, a mere 1% move in the asset’s price becomes a 10% gain or loss on the trader’s initial capital.
- Flexible Directional Trading: These contracts allow traders to easily profit from falling prices. If a trader believes an asset is overvalued after a major event, they can open a short position on falling markets without needing to first own and sell the asset.
Limitations
- No Underlying Asset: You are trading a price-tracking contract. You have no ownership rights, such as collecting dividends (for stocks) or taking custody of the asset.
- Increased Risk Profile: Leverage magnifies losses just as it does gains. The primary risk is liquidation, where a position is automatically closed at a loss.
To make this system work without an expiration date, perpetuals use the funding rate mechanism to keep the contract’s price anchored to the spot price. This system of regular payments between traders is the most important concept to understand, and we will break it down in the next chapter.
Fast Fact
A widely cited guideline in futures trading is the “80% rule.” It suggests that if the price, after trading outside the main “value area” (the zone of highest volume), re-enters it and holds for a period (e.g., two 30-minute bars), there is a high probability it will traverse the entire zone to test the opposite edge.
How the Funding Rate Works
A perpetual futures contract needs a mechanism to keep its price tethered to the underlying asset’s spot price. Without an expiry date to force convergence, the two prices could drift apart indefinitely. The funding rate is the elegant solution to this problem.
The funding rate’s sole purpose is to act as an anchor. It creates a constant financial incentive for the perpetual contract’s price to stay extremely close to the spot price. It is a direct payment exchanged between traders holding opposing positions.
These payments typically occur every eight hours, though some exchanges adjust this interval in volatile markets. To trade perpetuals effectively, understanding who pays whom, and why, is absolutely critical.
Reading the Market Through Funding
Most of the time, the funding rate is positive. This happens when the perpetual contract trades at a premium to the spot price, signaling bullish sentiment. In this scenario, traders with long positions pay a small fee to those with short positions.
A negative funding rate is less common but just as important. This occurs when the perpetual price trades at a discount to spot, indicating bearish market sentiment. Here, the roles are reversed: traders with short positions must pay long-position holders.
For anyone holding a position through a funding timestamp, this rate is a direct cost or credit to their account. A trader with a large leveraged position can find their overall profit and loss significantly affected by these regular funding payments over time.
How Leverage Amplifies Your Exposure
Leverage is a tool that lets you borrow funds and control a large position with a small amount of initial capital, or margin. While this magnifies your potential profits, it also magnifies your sensitivity to market fluctuations. A small price move against you can result in a very large percentage loss on your margin.
Most modern platforms offer two margin modes:
- Isolated: confines the risk to the initial capital allocated to a single position.
- Cross: uses your entire account balance as collateral, which can prevent immediate liquidation but puts your whole account at risk if the market moves significantly against you.
Liquidation: The Automated Margin Call
Liquidation is the exchange’s automated risk management system. If the market moves against your leveraged position to the point where your losses are about to exceed your margin, the exchange will forcibly close your position to prevent you from falling into debt.
This is not a theoretical risk. During major market downturns, it’s common to see data from platforms like Coinglass showing over $1 billion in leveraged positions being liquidated across all exchanges in a single 24-hour period. This is a sobering reminder of challenging margin requirements.
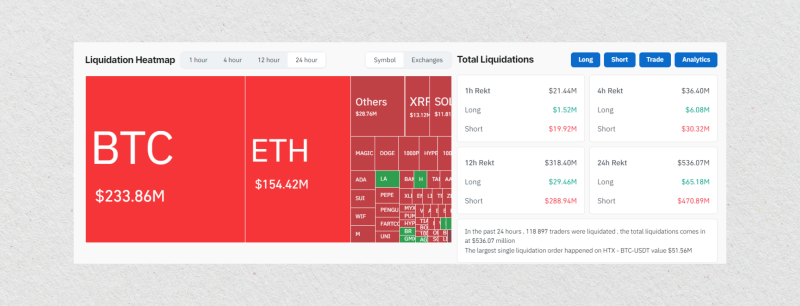
This forced closure isn’t a surprise event. A modern perpetual futures trading platform always displays the calculated “liquidation price” for every open position. A trader always knows the exact price point that will trigger the automatic closure of their trade at a loss.
Successful perpetual futures trading strategies require using leverage responsibly, while always being aware of and respecting your liquidation price. This is the core skill that separates experienced traders from gamblers.
Spot vs Perpetual Futures: A Comparison
The choice between spot and perpetuals comes down to a trader’s fundamental objective. The following is a direct comparison of their core mechanics, risks, and primary functions in a trading portfolio.
Spot Trading
- Asset Ownership: You own the actual underlying asset and have full custody rights.
- Leverage: None by default. Your exposure is always 1:1 with your capital.
- Primary Risk: Market exposure. Your main risk is that the price of the asset you hold will fall.
- Main Use Case: Long-term investing, accumulating an asset, and strategies like dollar-cost averaging.
Perpetual Futures Trading
- Asset Ownership: You do not own the underlying asset. You are trading a contract that merely tracks its price.
- Leverage: Yes. This is their core feature, allowing for highly capital-efficient trading.
- Primary Risk: Liquidation risk. The main risk is the forced closure of your position at a loss if the market moves against you.
- Main Use Case: Short-term speculation, hedging existing spot positions, and making leveraged bets on market direction.
Many traders operate in both markets simultaneously, creating a clear need for a unified trading environment. A platform that combines spot and perpetuals into a single interface simplifies portfolio management, making it much more efficient to rotate capital between long-term holdings and short-term hedges. B2TRADER is an example of a platform built around this hybrid model.
To learn more about offering a combined spot and perpetuals platform to your clients, you can contact the B2TRADER team here.
Conclusion
The functions of these two markets are entirely distinct. Spot trading involves buying and holding the actual asset, a strategy typically used by long-term investors. It is fundamentally a vehicle for direct ownership.
Perpetual futures trading, however, is a tool for short-term speculation. It provides traders with capital-efficient price exposure, making it ideal for tactical bets on market direction. The choice in the spot vs perpetual trading debate ultimately reflects your personal strategy: are you investing, or are you trading?
FAQ
What is the difference between spot and perpetual futures?
Spot trading refers to buying and owning the actual asset. Perpetual futures are contracts for speculating on the current market price with leverage, without any ownership of the asset.
Is perpetual better than spot?
Neither is better. Spot is for long-term investing and ownership. Perpetuals are for short-term, leveraged speculation.
How long can I hold perpetual futures?
You can hold them indefinitely since they have no expiration date. However, your position will be liquidated if your margin is no longer sufficient to cover potential losses.
What are the risks of perpetual futures?
The primary risk is liquidation due to leverage, where a small adverse price move can wipe out your entire margin. Funding rate payments can also be a significant cost.