What Are Automated Market Makers (AMMs)?
Jan 11, 2024
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) has been a hot topic in recent years, with its promise of democratizing and improving the traditional financial system through peer-to-peer trading. However, while DeFi has brought about many innovations and opportunities, it also faces challenges, such as low liquidity and high price negotiation costs due to the use of smart contracts.
To address these issues, new exchange protocols known as Automated Market Makers (AMMs) have emerged. In this article, we will explore the concept of AMMs and how they can enhance the DeFi landscape for both projects and traders.
Key Takeaways:
- AMMs are smart contracts that allow for automated trading and liquidity provision in decentralized exchanges.
- They offer benefits such as lower fees, no need for intermediaries, and greater market access.
- However, challenges such as impermanent loss, slippage, and bugs/glitches exist.
- Popular AMM platforms include Uniswap, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, Curve Finance, Orca, and others.
What Are Automated Market Makers?
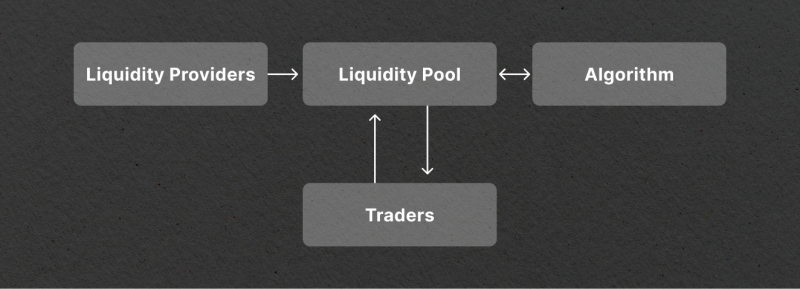
Automated market makers are a class of algorithms used in decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to provide liquidity and determine asset prices. Unlike traditional crypto or stock exchanges that rely on order books, AMMs operate through liquidity pools and mathematical formulas.
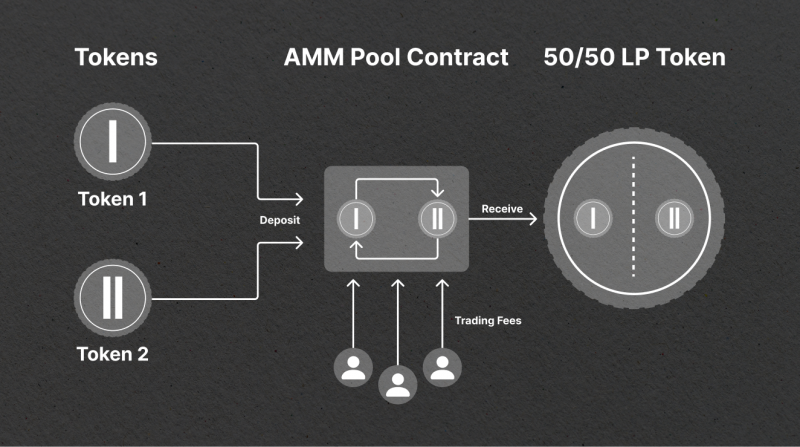
When a user wants to trade on the decentralized trading platform, they interact directly with the AMM, swapping one token for another at a price determined by the liquidity pool’s algorithm.
A liquidity pool is an underlying technology behind AMMs. It is a crowdsourced collection of crypto assets used for trading. Liquidity providers (LPs) deposit their assets into these pools and are rewarded with a fraction of the fees generated on the AMM. This practice, known as yield farming, incentivizes LPs to contribute to the liquidity pool.
AMMs: Principles of Functioning
AMMs are designed to maintain the balance of assets in a liquidity pool through mathematical equations, such as Uniswap’s x*y=k equation. This ensures that the prices of the pooled assets remain stable and eliminates price discrepancies.

The formula works by keeping a constant ratio between two assets, where one asset’s value increases as the other decreases. In this way, the value of the assets in the pool remains in equilibrium.
Different Automated Market Maker (AMM) Models
There are various AMM models, each with its unique characteristics and mathematical formulas. Let’s explore each model in more detail:
Constant Product Market Maker (CPMM)
The CPMM is based on the mathematical formula x * y = k. This formula establishes a range of prices for two tokens based on the available quantities (liquidity) of each token in the pool. As the supply of one token increases, the supply of the other token must decrease to maintain the constant product. The resulting price curve is a hyperbola, where liquidity is always available but at increasingly higher prices.
Example: Uniswap
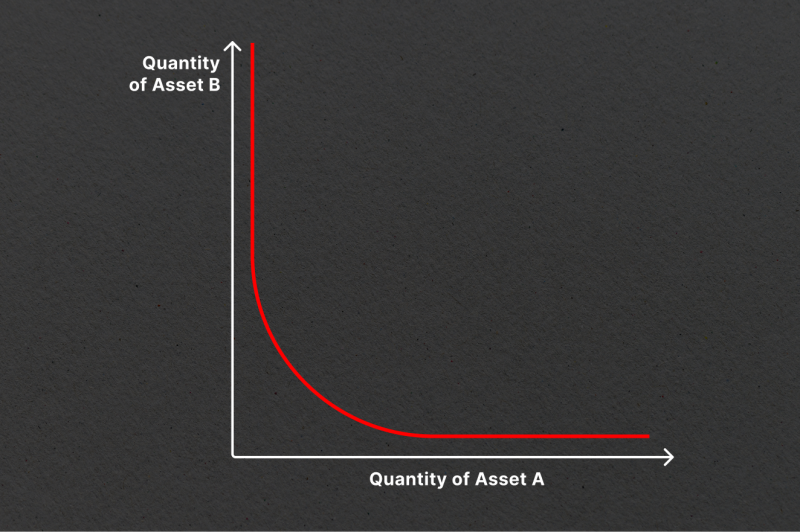
Constant Sum Market Maker (CSMM)
The CSMM, although less commonly used, follows the formula x + y = k. It is ideal for zero-price-impact trades but does not offer unlimited liquidity. The CSMM’s linear price curve can be problematic if the off-chain reference price between tokens deviates from the 1:1 ratio, leading to one side of the liquidity pool being drained and leaving no liquidity for traders.
Example: Solidity
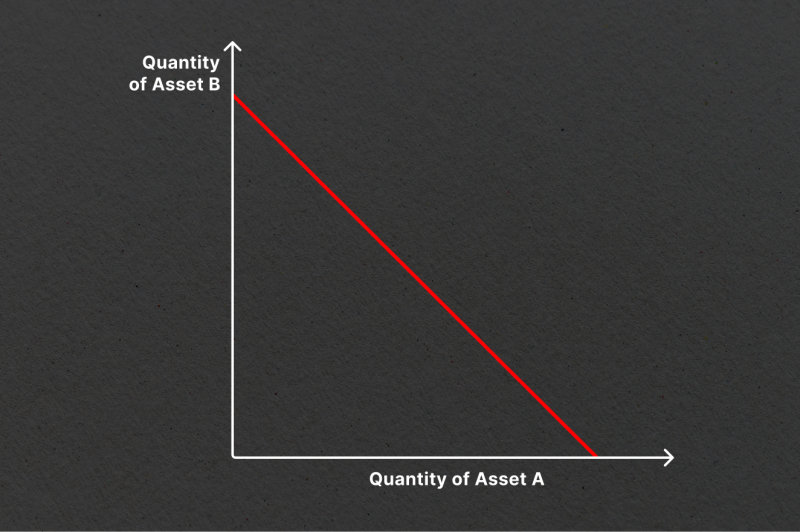
Constant Mean Market Maker (CMMM)
The CMMM allows for more than two tokens in a liquidity pool and supports weighted distributions beyond the standard 50/50 ratio. For a liquidity pool with three assets, the formula would be (x * y * z)^(1/3) = k. This model enables variable exposure to different assets in the pool and allows swaps between any assets within the pool.
Example: Balancer
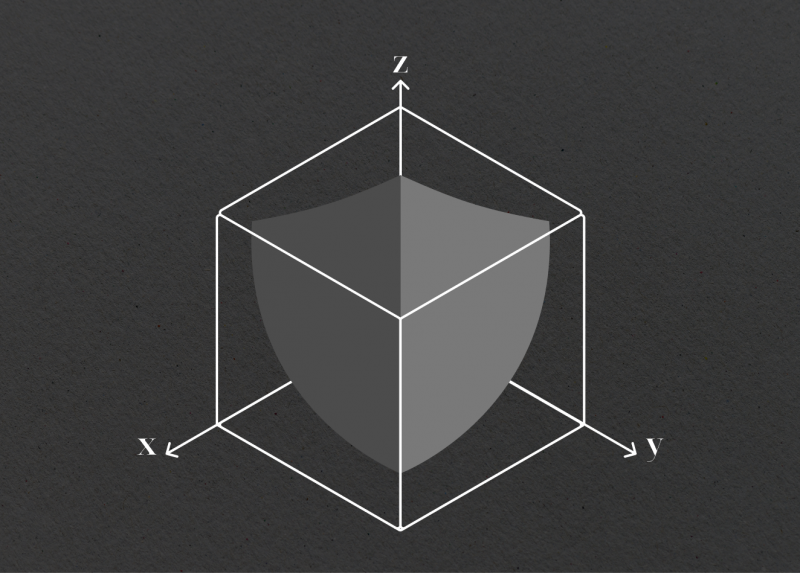
Hybrid CFMMs
There are projects that use hybrid approaches, combining elements of different AMM DeFi models to optimize for specific asset characteristics. Some function as a mix of CPMM and CSMM, while others incorporate a customizable utility function to maintain balance within a pool.
Examples:
- Curve
- Shell Protocol
The Beauty of Decentralization and Accessibility
AMMs operate on decentralized exchanges, which do not rely on intermediaries or central authorities to execute trades. This enables permissionless trading, where anyone with an internet connection can participate in buying and selling crypto assets.
Furthermore, the use of automated market makers eliminates the need for order books, making trading more efficient and less prone to manipulation. This accessibility and efficiency have allowed for faster adoption of DEXes, providing users with greater control over their assets.
Advantages of AMMs
AMMs offer many advantages over traditional exchanges, making them increasingly popular among crypto enthusiasts. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Continuous Liquidity
One of the primary advantages of AMMs is their ability to provide continuous liquidity. Liquidity pools ensure that there are always assets available for trading, regardless of the time or market conditions. Unlike traditional exchanges that rely on specific buyers and sellers, AMMs enable users to trade instantly, 24/7.
Lower Barriers to Entry
AMMs democratize trading by allowing anyone with tokens to become a liquidity provider. Traditional markets often have high barriers to entry, limiting participation to well-established businesses and financial institutions. However, with AMMs, individuals can contribute their tokens to liquidity pools and earn fees, providing them with an opportunity to participate in the market and generate passive income.
Lower Fees
AMMs typically offer lower fees compared to traditional exchanges. By eliminating intermediaries and automating the trading process, AMMs reduce costs associated with order matching and other services provided by centralized exchanges. This cost reduction benefits both traders and liquidity providers, making trading more affordable and profitable.
Decentralization and Security
AMMs operate on distributed ledgers or blockchains, removing the need for a central authority or intermediary. This decentralized nature enhances security and eliminates the risk of single points of failure. Users have full control over their assets and can trade directly from their wallets, reducing the risk of hacks or fund mismanagement.
Greater Market Access
AMMs enable trading of a wide range of crypto assets that may not be available on traditional exchanges. These platforms support various tokens, including newly launched or less popular ones.
Challenges and Limitations of AMMs
While AMMs offer numerous advantages, they also face certain challenges and limitations. Let’s discuss some of the key concerns:
Impermanent Loss
One of the primary concerns for liquidity providers in AMMs is impermanent loss. This phenomenon occurs when the price of an asset in the liquidity pool diverges from the market price. Liquidity providers may experience losses when withdrawing their funds from the pool if the prices of the assets have changed significantly since their deposit.
Slippage and Price Impact
AMMs may experience slippage and price impact, especially for larger trades. Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price and the executed price of a trade. As AMMs rely on mathematical formulas to determine prices, large trades can cause significant price impact, resulting in higher slippage. Traders and liquidity providers need to consider the liquidity and depth of the pool to minimize slippage and ensure efficient trade execution.
Bugs and Glitches
As AMMs operate without human interaction, there is a possibility of bugs and glitches occurring with smart contracts. These can lead to issues such as incorrect pricing or failed transactions. While developers constantly work to identify and fix these issues, they can still occur, causing inconvenience and potential losses for users.
Popular AMM Platforms
What AMM platforms are the most popular today? Let’s explore some options:
1. Uniswap
Uniswap is the leading decentralized cryptocurrency exchange on the market, with billions of dollars traded daily. Its simplicity and user-friendly interface make it a top choice for many traders. The platform allows users to trade a wide range of ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum network and has recently expanded to support tokens on other networks such as Polygon and Optimism.
With low fees and no need for account creation or identity verification, Uniswap offers a convenient way for users to swap cryptocurrencies. Additionally, users can earn rewards by staking their crypto into liquidity pools.
2. PancakeSwap
With over 2.2 million users, PancakeSwap is the largest AMM on Binance Smart Chain. Its focus on low fees and fast transactions has attracted many traders to the platform. The platform offers a range of liquidity pools for users to earn rewards in CAKE tokens.
What sets PancakeSwap apart is its daily lottery feature, where users can put their CAKE into a pool for a chance to win big prizes. This adds an element of excitement and gamification to the platform, making it appealing to many traders.
3. SushiSwap
SushiSwap is a popular fork of Uniswap which offers similar features such as trading, staking, and liquidity pools. However, it differentiates itself by having a multi-chain approach with support for over 16 blockchain networks. This allows for greater flexibility and accessibility for users looking to trade on different networks.
Additionally, SushiSwap’s use of smart contracts ensures that trades are executed quickly and efficiently without the need for a centralized middleman. Its token, SUSHI, is earned through liquidity mining and can also be used for voting on governance proposals.
4. Curve Finance
Curve Finance is another top contender in the AMM space, focusing specifically on stablecoin trading. Its low-cost and low-slippage swapping between stablecoins is a major draw for traders looking for efficient and cost-effective trading options. Additionally, Curve utilizes a liquidity aggregator model, allowing users to contribute their assets to various pools and earn rewards from transaction fees.
Curve has seen significant growth in recent years, with a strong community of contributors and developers continuously improving the platform. While its team remains relatively anonymous, the platform’s success and popularity speak for themselves.
5. Orca
Orca is a rising star in the world of DEXes, focused specifically on the Solana blockchain. With its emphasis on user-friendliness and quick transactions at low fees, it has quickly gained popularity among traders.
As one of the first AMMs on Solana, Orca offers unique features such as yield farming and concentrated liquidity pools. Its native token, ORCA, provides additional benefits such as discounts on trading fees and governance rights.
Closing Thoughts
AMMs’ algorithmic protocols and liquidity pools have replaced traditional order book models, offering a decentralized and efficient trading experience. While AMMs come with certain challenges and limitations, their advantages outweigh these concerns, making them a vital component of the DeFi ecosystem.
Wondering how these solutions can boost your business?
Leave a request, and let our experienced team guide you towards unparalleled success and growth.
FAQs
Is an AMM a smart contract?
Yes, AMMs (Automated Market Makers) are implemented as smart contracts on a blockchain platform. These smart contracts facilitate the automated swapping of assets between users and pools without the need for an intermediary or order book.
How do AMMs and traditional exchanges differ?
The main difference between AMMs and traditional exchanges is the absence of middlemen. Traditional exchanges rely on brokers, market makers, and clearinghouses to facilitate trading between buyers and sellers. These intermediaries charge fees for their services, adding an extra cost to the trading process.
On the other hand, AMMs use smart contracts to automate the swapping of assets, making them more cost-effective and efficient compared to traditional exchanges.
Who invented automated market makers?
Automated market makers were first introduced by Vitalik Buterin in 2017 in his post about on-chain market makers. Various approaches to AMMs have been developed since then.
What LP tokens are used for?
LP tokens have various use cases in the DeFi ecosystem. They are primarily used to demonstrate a share in a liquidity pool and earn trading fees. However, LP tokens also offer additional functionalities such as collateral for obtaining crypto loans, transferring to other users, and earning compound interest through yield farming.
How to participate in a liquidity pool?
Participating in a liquidity pool is relatively simple and can be done in just a few steps:
- Choose the right platform: Start by finding a reputable DEX that offers liquidity pools. Some of the popular ones are listed above.
- Connect your wallet: Once you have chosen a DEX, connect your cryptocurrency wallet to the platform. Most DEXs support various wallets, including Metamask, Coinbase Wallet, and Trust Wallet.
- Select the assets you want to provide liquidity for: Liquidity pools require users to provide pairs of tokens, so choose the tokens you want to contribute.
- Add funds to the pool: After selecting the tokens, you can add funds to the pool by using the ‘Add Liquidity’ function on the DEX platform.
- Receive LP tokens: In return for providing liquidity, you will receive LP tokens. These tokens represent your share of the pool.
- Monitor your returns: As users trade within the liquidity pool, you will earn a portion of the fees generated. Keep an eye on your returns and decide when to withdraw or add more funds to the pool.