What is an Order Book, and How Do You Read & Analyze it?
May 27, 2024

All individuals involved in financial markets, whether new to trading or experienced professionals, utilize a variety of intricate tools and techniques. Among these tools, the order book stands out as a crucial instrument. It provides a digital record of purchase and sale orders for particular securities, organized by price level. By showcasing the market’s depth, the order book offers traders essential data to inform their trading strategies and decision-making processes.
This article is intended to reveal the concept of an order book, as well as to tell about what key components such a system has, what types it is, and finally, to explain the principles that allow you to read and analyze the order book properly.
Key Takeaways
- The order book is a universal tool for monitoring market conditions. It allows you to analyze the balance between supply and demand, which is crucial for determining the market’s health.
- The order book consists of walls of purchase and sell orders. It also includes essential indicators such as volume, which reflect market participants’ interest level in a particular asset.
- There are two main types of order books — centralized and decentralized, depending on the kind of assets the exchange works with.
What Is an Order Book?
An order book is a record of all buy and sell orders for a particular asset or security in a financial market. It is a collection of pending orders from traders and investors who want to buy or sell the asset at specific prices.
In an order book, buy orders are typically listed on one side, while sell orders are on the other. Each order includes the quantity of the asset the trader wants to buy or sell and the price they are willing to transact. The order book hierarchically displays this information, with the highest buy bids and lowest sell offers at the top.
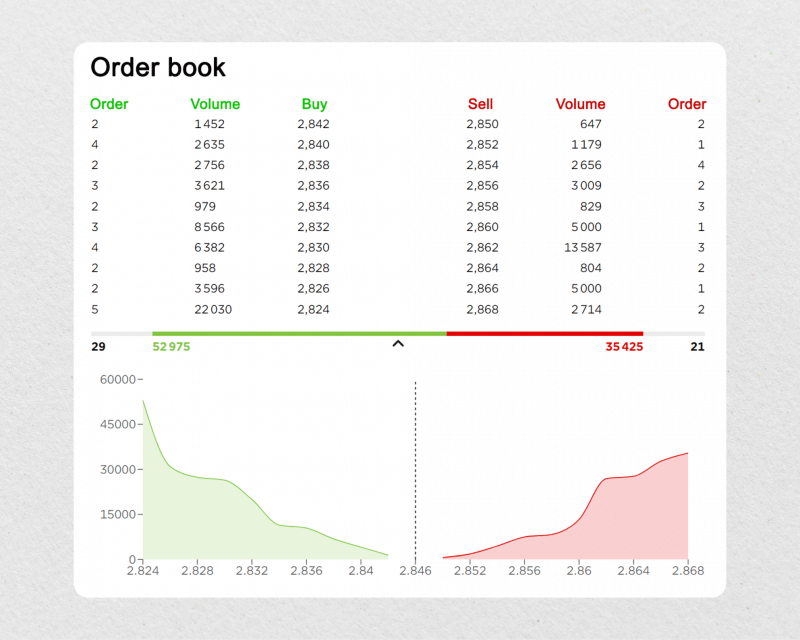
The order book provides a real-time snapshot of market activity and essential insights to market players. Traders can use it to assess an asset’s current supply and demand, identify price levels where there is significant buying or selling interest, and gauge market sentiment.
When a new order is placed, it is added to the order book according to its price level. If a new buy order has a higher bid price than existing sell orders or a new sell order has a lower ask price than existing buy orders, a trade may occur, and the order will be removed from the order book. This is known as an order-matching process.
The order book is continuously updated as new orders are placed, executed, or canceled. Traders can interact with it by placing market orders, which are executed at the best available prices, or limit orders, which are added to the order book until they are matched with a corresponding order.
Fast Fact
One of the important features of order books is the order matching process, which involves a mechanism called the matching engine.
Key Components of Order Book
The order book is crucial in financial markets, particularly stock and crypto platforms. It is a dynamic and constantly updated record of buy and sell orders for a specific asset, such as stocks, cryptocurrencies, or commodities. These orders are organized based on price and volume, providing valuable insights into market activity and liquidity.
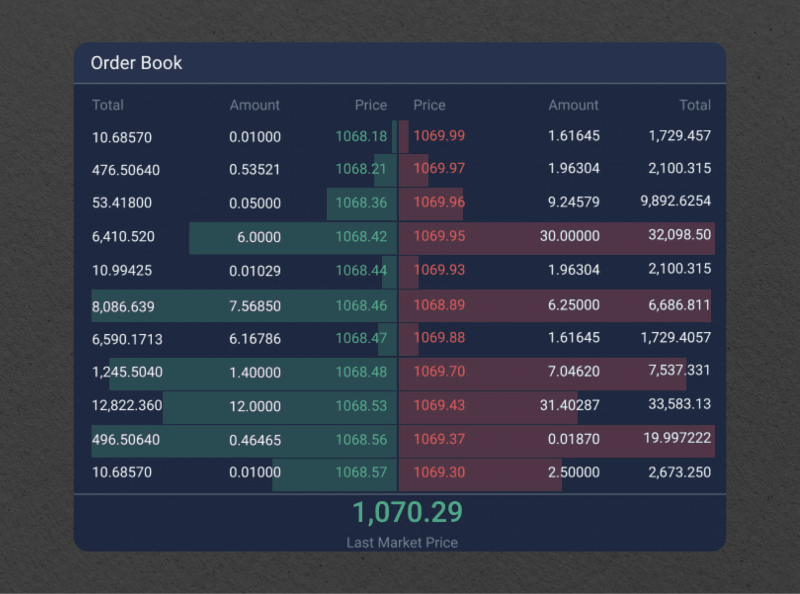
Let’s delve into its components and operational mechanism for a better understanding.
Bid Side
The buy side of the order book showcases all purchase orders made by traders and investors, revealing the price points at which buyers are interested in acquiring the asset, as well as the quantities they are looking to purchase.
Ask Side
The sell orders are displayed on this section of the order book, showcasing the various price levels at which sellers are looking to sell the asset, along with the corresponding quantities available for sale.
Price Levels
The order book organizes the buy and sell orders based on their corresponding price levels. The highest bid price is typically displayed at the top of the bid side, while the lowest ask price is usually shown at the top of the ask side. The price levels represent different levels of demand and supply for the asset.
Quantity
Each order in the order book includes the asset quantity that a trader wants to buy or sell. The amount can range from a single unit to many units.
Time Priority
Orders in the order book are arranged based on the time they were placed. The orders placed earlier have higher priority, and as new orders come in, they are added to the appropriate price level in the order they were received.
Market Orders
Market orders are orders to buy or sell an asset at the best available price in the market. When executed, they match the order book’s corresponding opposite order. Market orders can impact the order book immediately, filling existing orders at the best available prices.
Limit Orders
Limit orders are orders to buy or sell an asset at a specified price or better. They are added to the order book until they match an opposite or canceled order. Limit orders provide liquidity to the market and can stay in the order book for an extended period until the specified price level is reached.
Order Matching
The order book facilitates the arrangement of buy and sell orders. When a buy order lines up with a sell order, a trade occurs, and the orders are removed from the order book. The order-matching process determines the price at which the trade occurs.
Types of Order Books
An order book is a complex system of order matching that works on the basis of mathematical algorithms and computing systems processing large arrays of data about market orders. At the same time, such books have a certain categorization depending on the specifics of work and application. Here are the main frequently encountered types of order books:
Centralized Order Books
These order books are managed by centralized exchanges, which act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. Examples include traditional stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and online crypto platforms like Coinbase or Binance. Centralized order books often offer a high level of liquidity and facilitate trading through a single platform.
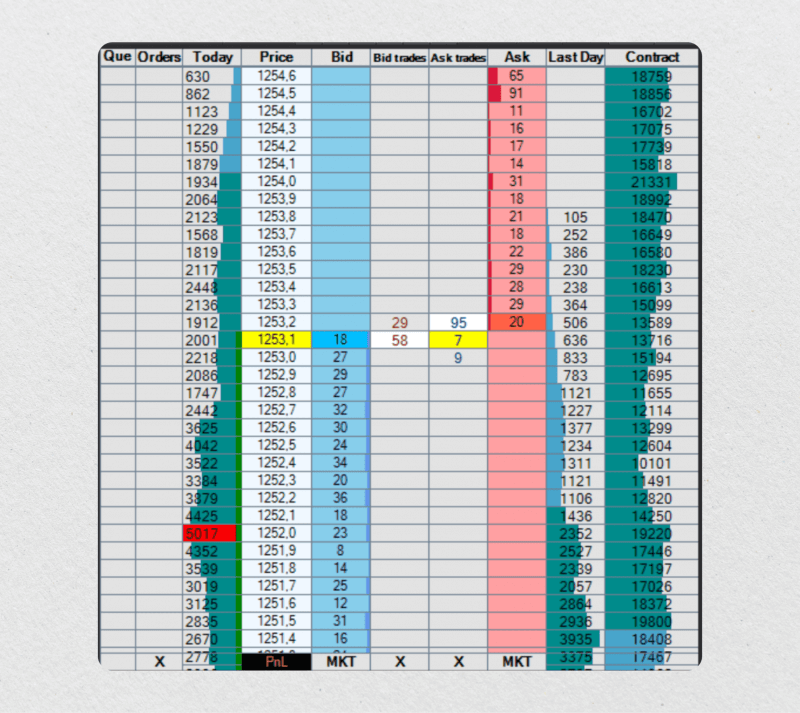
Decentralized Order Books
Decentralized order books operate on blockchain networks, where trades are executed directly between peers without the need for intermediaries. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and SushiSwap use decentralized order books. They offer advantages such as greater privacy, security, and censorship resistance, although they may have lower liquidity compared to their centralized counterparts.
Limit Order Books
A limit order book is the most common type of order book. It displays all the pending limit orders to buy or sell an asset at a specific price or better. The buy orders are listed on the bid side, and the sell orders are listed on the ask side.
The limit order book provides transparency by showing the available liquidity at different price levels. Traders can place new limit orders in the book, and when a new order matches an existing order, a trade occurs, and the orders are removed from the book.
Market Order Books
A market order book, also known as a transaction book or trade book, focuses on the execution of market orders. It displays the incoming market orders and matches them with the best available opposite orders in the book.
The market order book is primarily used to execute trades at the prevailing market prices. It does not show the complete depth of the market or the pending limit orders. Instead, it focuses on immediate order execution by matching market orders with the opposite side of the market.
Hybrid Order Books
Some exchanges combine features of both centralized and decentralized order books to leverage the benefits of each. For example, a hybrid exchange might have a centralized order matching engine but utilize decentralized settlement for trades. These platforms aim to offer the liquidity and speed of centralized exchanges while maintaining the security and user control of decentralized ones.
Dark Pools
Dark pools are alternative trading platforms where large institutional investors can execute orders anonymously. Dark pools typically operate off-exchange and do not display order book information to the public. Instead, trades are matched internally, providing participants with reduced market impact and increased privacy. Dark pools are primarily used for large block trades and may offer advantages such as price improvement.
How to Read and Analyse an Order Book
Reading and analyzing an order book involves understanding the information presented and interpreting it to gain insights into the market dynamics. Here are the steps to read and analyze an order book effectively:
1. Identify the Bid and Ask the Sides
The order book is divided into two sides: the bid side and the ask side. The bid side displays buy orders, while the ask side shows sell orders. The highest bid price and the lowest ask price are usually listed at the top of their respective sides.
2. Check Price Levels and Quantity
Each price level on the order book represents a different order, and it displays the quantity of the asset being bought or sold at that price. Analyze the quantities to assess the depth of the market at various price levels. Higher quantities indicate more significant interest or liquidity.
3. Look at Market Depth
By evaluating the entire market depth, you can uncover potential trading opportunities. A deep market with substantial quantities at multiple price levels suggests higher liquidity and potential trading opportunities. Conversely, a shallow market with fewer orders may indicate lower liquidity, but it also presents potential challenges that can be overcome with the right strategy.
4. Observe Order Priority
Understanding the time priority of the orders is not just a detail, it’s a strategic advantage. Orders placed earlier have higher priority and are typically listed ahead of orders placed later at the same price level. This knowledge is crucial for analyzing the order-matching process and potential order execution, making you a more informed and strategic trader.
5. Analyze Spread
Calculate the spread by subtracting the highest bid price from the lowest ask price. The spread reflects the divergence between the best available buy and sell prices. A narrower spread generally indicates a more liquid market, while a wider spread may suggest lower liquidity or potential price volatility.
6. Analyze Order Flow
Monitor the order flow by observing changes in the order book over time. Look for patterns, such as increasing or decreasing quantities at specific price levels or significant orders being added or removed. Order flow analysis can provide insights into market sentiment and potential shifts in supply and demand dynamics.
7. Analyze Market Depth
Analyze the cumulative quantities at different price levels on both the bid and ask sides. Market depth analysis can help identify support and resistance levels where significant buying or selling pressure may exist. Deeper quantities at specific price levels can indicate areas of significant interest or potential turning points.
8. Monitor the Impact of Trades
Pay attention to how trades impact the order book. When trades occur, orders are filled, and the corresponding quantities are removed from the book. Analyzing the impact of trades on the order book can provide insights into market liquidity and the possibility of price movements.
9. Compare with Other Indicators
Consider combining order book analysis with other market analysis tools and indicators. The order book provides valuable information about supply and demand dynamics, but it can be enhanced by incorporating technical indicators, price charts, and other relevant data sources.
Conclusion
The foundation of contemporary trading and investing lies in the order book, which offers crucial real-time insights into the market depth and the assortment of buy and sell orders at distinct price points. Proficiency in deciphering and utilizing order book data can give traders a notable edge in maneuvering through the market.
With technology advancing and transforming the financial sector, the intricacies of the order book are bound to progress in tandem, emphasising the importance of ongoing education and adjustment of knowledge in trading.
FAQ
What is an order book?
An order book is a real-time, continuously updated repository of buy and sell orders for a specific asset, organized by price and volume.
How does an order book operate?
Traders place buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders at various prices and quantities. The order book aligns buy and sell orders based on cost and time priority.
What is the purpose of an order book?
The order book provides transparency and liquidity to financial markets, aiding in price discovery and allowing traders to make informed decisions.
What data does an order book display?
An order book displays buy and sell orders and their corresponding prices and quantities. It also shows market depth, indicating the total volume of orders at each price level.
How do traders use the order book?
Traders analyze the order book to gauge market sentiment, identify support and resistance levels, and execute trades at favorable prices.
What types of order books exist?
There are centralized order books (managed by exchanges), decentralized order books (operating on blockchain networks), limit order books, market order books, hybrid order books, and dark pools.




