Fed Meets Markets With First Indications of Interest Rate Cuts 2024 Causing Inflation Stock Market Rally.
Dec 14, 2023
In an anticipated move, the Federal Reserve’s Open Markets Committee has decided to maintain its key policy rate at between 5.25% and 5.5%, marking a 22-year high. This decision comes on the heels of a quarter-point rate hike implemented in July.
While the decision to hold the rates was expected, the Federal Reserve has added an intriguing twist to the narrative. The newly issued Summary of Economic Projections – colloquially known as the ‘dot plots’ – forecasts a 0.75% drop in the federal funds rate for the next year. This development is a striking departure from recent statements that hinted at a persistent high-rate environment in the inflation stock market.
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell expressed the committee’s cognizance of potentially holding onto higher rates for an extended period, a pitfall they are keen to avoid. Powell underscored the committee’s dedication to circumventing such a scenario.
The Federal Reserve anticipates that core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) prices, its favored inflation measure, will conclude the year at 2.8%. It is then expected to diminish to 2.4% in 2024. Concurrently, GDP growth is projected to descend to 1.4% after wrapping up this year at 2.6%, while headline unemployment is anticipated to ascend to roughly 4.1% by the end of next year.
Despite the current environment, Seema Shah, Chief Global Strategist at Principal Asset Management, noted that the Federal Reserve appears to support the market‘s view of a downward rate trajectory, albeit with a disparity in the projected degree of cuts. She highlighted the FOMC’s change in stance from a prolonged high-rate scenario to a shorter one.
According to Shah, if economic growth is decelerating and inflation is reverting to the target, a handful of rate cuts would be reasonable, albeit not as drastic as the market’s expectation of five cuts. A significant economic downturn and the Federal Reserve’s subsequent distress would be necessary for five cuts to be plausible.
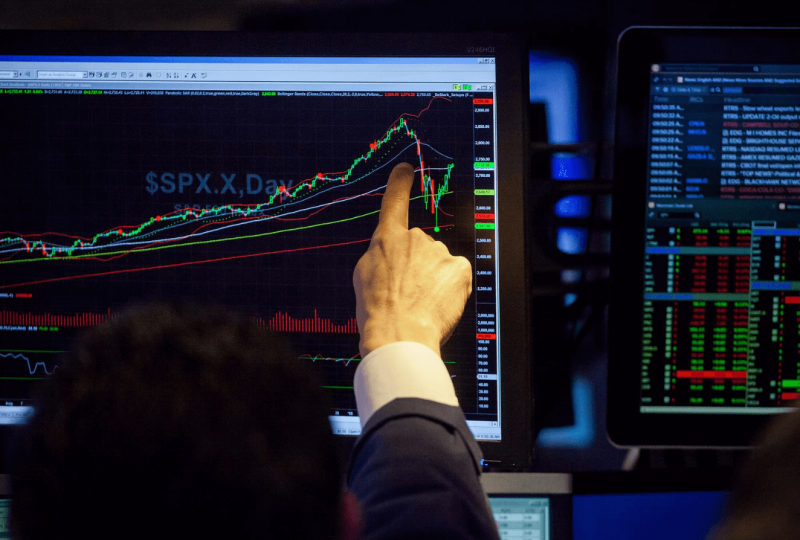
The Federal Reserve’s decision was well received in the stock market, with U.S. stocks extending earlier gains, followed by a surge in the S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average, which hit a new all-time high. Meanwhile, the tech-focused Nasdaq also saw an increase. On the flip side, the yields in Benchmark 10-year Treasury notes dropped to 4.045%, while 2-year notes decreased to 4.479% following the interest rate decision.
The U.S. dollar index also fluctuated, eroding most of its earlier gains and last observed at 1.03% lower against six global currencies. The CME Group’s FedWatch tool also reflected this evolving landscape, with a 62.3% probability of a March cut and a subsequent May cut currently traded at 53.8%.
As for the most optimistic forecast for 2024, the year-end federal funds rate is expected to be between 4% and 4.25%, essentially incorporating one quarter-point reduction from the Federal Reserve’s predictions with a positive inflation stock market rally.