What Is a Node in Cryptocurrency?
Feb 05, 2024
The core principle of blockchain is decentralisation, a feature that sets it apart from traditional centralised systems. As opposed to central authorities controlling and verifying transactions, blockchain technology relies on nodes spread across the network, thanks to which the system remains transparent and operational.
In this guide, we will explore the concept of nodes in crypto, their types, and their significance for a blockchain network.
Key Takeaways:
- Nodes in blockchain serve as validators, keepers of the ledger, and enablers of peer-to-peer transfers.
- Different consensus mechanisms help ensure the integrity between participating nodes.
- Setting up a node involves choosing the right hardware and software, syncing with the blockchain and ensuring the necessary conditions for continuous operations.
What Are Nodes in Crypto?
In computer science, a node can be described as a fundamental unit of a data structure. It contains data and is connected to other nodes, creating links that form intricate structures. These structures vary depending on the needs of a program and can range from simple linear lists to more complex tree systems.
In the world of crypto and blockchain technology, a node refers to a computer or device that participates in a decentralised network. They serve as validators and keepers of the ledger.
Each node stores a copy of the blockchain or the digital ledger that records all transactions within the entire network. Nodes communicate with each other, verify and approve operations and ensure that everyone follows the rules set forth by the ecosystem.
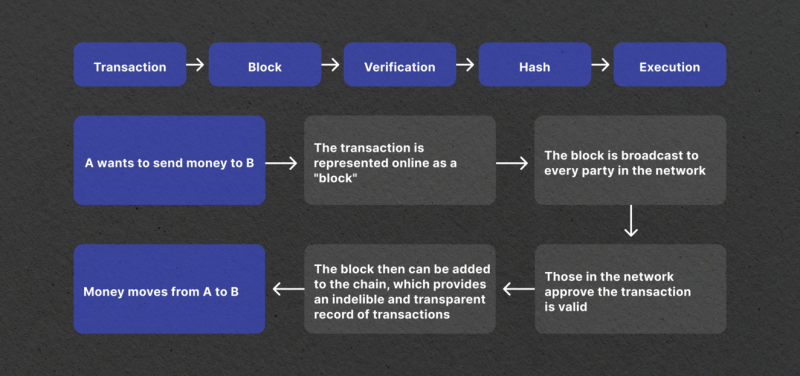
What Is a Consensus Mechanism?
Nodes work together to achieve consensus, which means they collectively agree on the state of the blockchain. The crypto industry knows many different types of algorithms that ensure consensus of the network, with proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) being the most common:
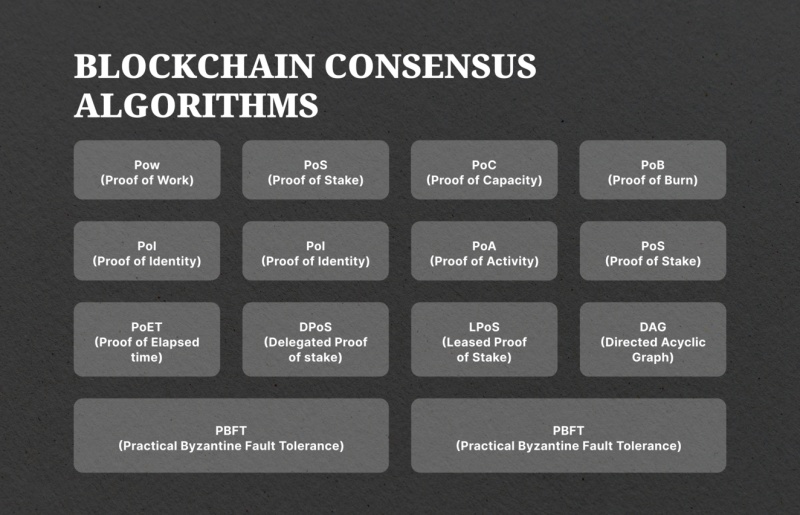
Proof-of-Work: This mechanism requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded with newly created coins for their efforts.
Examples: Bitcoin, Dogecoin
Proof-of-Stake: In this type of consensus, validators stake their tokens to prove their trustworthiness and earn the right to participate in adding new blocks of transactions to the blockchain.
Examples: Ethereum 2.0, Cardano
Proof-of-History (PoH): A newer consensus mechanism that uses historical timestamps to determine the order of transactions on a blockchain. This method aims to improve scalability and energy efficiency compared to PoW and PoS.
Examples: Solana
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS): Similar to PoS, but it involves delegates that are elected by coin holders as representatives who validate transactions on their behalf, which allows for faster transaction processing and lower costs.
Examples: EOS, Tron
Proof-of-Burn (PoB): This mechanism requires users to send coins to a verifiably unspendable address, effectively “burning” them, to participate in the consensus process and earn rewards.
Examples: Slimcoin
The industry can offer much more than just these five consensus mechanisms, though, with new ones constantly being developed and implemented for new cryptocurrencies.
Fast Fact
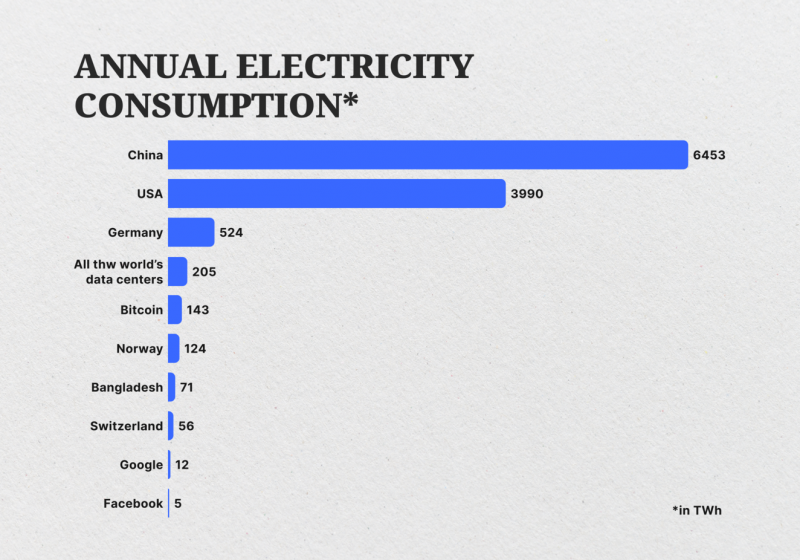
Bitcoin network’s annual energy consumption exceeds that of countries like the Czech Republic, Norway, Switzerland, Singapore, and New Zealand. The above illustrates the need for alternative consensus mechanisms that are more energy-efficient and scalable.
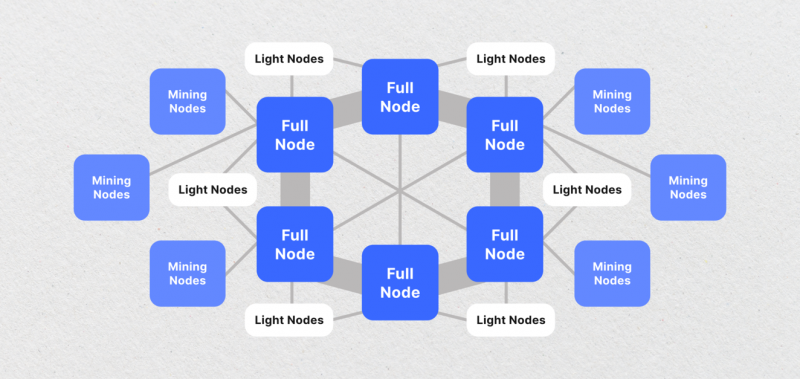
Types of Crypto Nodes
There are various types of nodes in crypto, each with its own function within the distributed ledger ecosystem. They include:
Full Nodes
Full nodes are the backbone of the blockchain. They store a complete copy of the chain and participate in the validation and verification of transactions.
Full nodes ensure the integrity of the network by independently validating each transaction according to the consensus rules. They receive and validate new transactions, verify their authenticity, and propagate them to other nodes in the chain.
Lightweight (SPV) Nodes
Lightweight (light nodes) or Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) nodes are intended for resource-constrained devices like mobile phones. These nodes don’t store all blockchain data but rather rely on trusted full nodes to validate transactions.
SPV nodes only download block headers and rely on Merkle proofs to verify the inclusion of specific transactions. Although lightweight nodes provide less security and decentralisation compared to full nodes, they offer faster synchronisation and lower resource requirements.
Miner Nodes
These nodes are specific types of nodes found in proof-of-work blockchains like Bitcoin. Miners are responsible for solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate and add new blocks to the blockchain.
These participants compete with each other to find the solution and are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency as an incentive for their computational work. Mining nodes require significant computational power and energy consumption to participate in the mining process.
Validator Nodes
Validator nodes are what you can find in proof-of-stake blockchains, where consensus is achieved through staking. Validators lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral and are responsible for verifying and validating transactions.
Validators propose new blocks and participate in the consensus process by attesting to the correctness of transactions. They are rewarded for their participation based on how many tokens they stake.
Master Nodes
Master nodes are special servers that handle advanced tasks. They validate transactions and enable additional features like instant and private transactions and decentralised applications (dApps).
In essence, master nodes are the blockchain warehouses that hold all the data and new blocks as they are added. Due to their scarcity and advanced functionalities, master nodes often receive direct rewards for their services.
Supernodes
Supernodes, also known as superpeers, act as intermediaries between regular nodes in a peer-to-peer network. They enhance network connectivity and enable efficient data transmission by establishing direct connections with multiple nodes. These are typically high-capacity or high-bandwidth nodes that facilitate faster and more reliable communication within the network.
What Does It Take to Set Up and Run a Node?
Running a node provides certain rewards for those looking to participate in the decentralisation and security of the ecosystem: either these are profits from mining or staking or governance rights in certain chains. While the setup process may vary depending on the specific network, here are some general steps to follow:
1. Choose the Right Hardware and Software
To run a crypto node, you’ll need suitable hardware and software. The hardware requirements may vary depending on the network, but a stable internet connection, sufficient storage capacity, and computational power are essential. Additionally, you’ll need to choose the appropriate software client compatible with the network you wish to participate in.
If you are willing to set up a blockchain node for mining, you need a computer with powerful graphics cards (or ASICs) to perform PoW calculations. On the other hand, staking nodes do not require such high specifications. It is always best to check the hardware requirements recommended by the chain’s official website.

To run a full node on the Bitcoin network, you can choose among several options available depending on the level of complexity you prefer. For instance, you can set up a lightning node using the RaspiBlitz software. This requires a computer with sufficient storage, a microSD card, and protective equipment for your device.
To be able to route payments, you will also need to download a Lightning wallet of your choice.
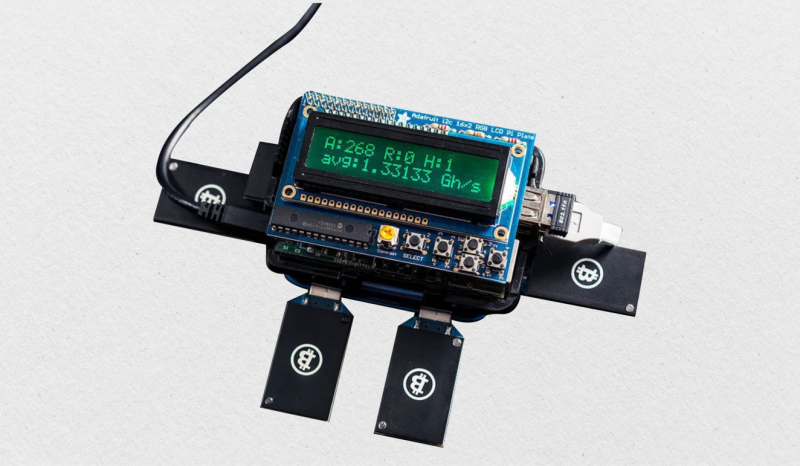
Another option is using a Raspberry Pi computer. This small but powerful device can support the operation of a full node when connected with compatible software like RaspiBlitz.
Fast Fact
Raspberry Pi was initially designed for educational purposes, but its low cost and compatibility with various operating systems have made it a popular choice for setting up Bitcoin nodes.
2. Synchronise with the Blockchain
Then, you need to sync your node with the blockchain to download the entire blockchain history or a partial copy, depending on the network and the type of node you’re running. This process may take some time and require hundreds of gigabytes of storage space. Some networks, however, allow the option to run a pruned node, which only downloads and stores essential data.
3. Configure Network Connectivity
Ensure that your node is properly connected to the network by configuring network settings and establishing the connection. This step is crucial for the effective receipt and broadcast of transactions and blocks. Nodes that experience prolonged disconnection from the network may require resynchronisation upon reconnection.
4. Secure Your Node
Make sure you protect your Bitcoin node from potential attacks by installing firewalls, using encryption, and maintaining the upgraded software. Additionally, consider the best practices for securing your private keys and ensuring the physical safety of your hardware.
5. Perform Continuous Maintenance
Running a node requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring. Keep your node updated with the latest software releases, regularly check for network updates and security patches, and ensure that your hardware and software function optimally.
Closing Thoughts
Today, a number of approaches have been proposed to tackle the scalability issues of blockchain, including sharding, layer-2 protocols, and off-chain scaling solutions. These solutions aim to improve network performance and allow for processing a higher number of transactions.
Similarly, cross-chain nodes pave the way for seamless interoperability between different blockchain networks, creating more opportunities for users to interact and transact across various platforms.
The blockchain industry is rapidly changing, bringing new challenges for node operators. Scalability, interoperability, and accessibility are key concerns that need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of the technology.




