Forex Liquidity Providers: Their Role in the Forex Market
Aug 16, 2024

The foreign exchange market is a complex network of currency exchanges driven by numerous traders. FX markets rely heavily on liquidity. It guarantees a sufficient number of buyers and sellers to facilitate smooth trading. It also aids in avoiding significant fluctuations in prices. The role of Forex Liquidity Providers (LPs) is to ensure enough capital in the market for the efficient exchange of currencies. They assist in maintaining the smooth flow of currency transactions.
This article aims to explore how liquidity suppliers work in the foreign exchange market, their functions, and their impact on trading conditions. Understanding these providers’ inner workings helps traders make informed decisions and fully leverage opportunities in the global FX market.
Key Takeaways
- Liquidity is a key component of the FX market.
- LPs aid FX brokers in offering lower spreads, stabilising them during volatile markets, and enhancing trade execution speed, thereby reducing higher spreads and large requotes.
- LPs generate revenue through bid-ask spread, order flow, trading volume, market making, and volume-based incentives.
- When choosing an LP, ensure its adherence to regulations, reputation, commissions, competitive spreads, and effective order execution.
Understanding Forex Market Liquidity
Liquidity is the lifeblood of the FX market. It denotes the availability of a resource in the foreign exchange markets. In the FX market, completing trades swiftly at a price near the market value is highly significant.
FX liquidity is essential for maintaining market equilibrium and stability, ensuring efficient and rapid trade execution with minimal price fluctuations and narrow bid-ask spreads. A large presence of buyers and sellers in a market ensures fast and accurate trade executions. Prices remain relatively stable, leading to minimal losses for investors. This ensures that all participants in the market pay an equitable price.
Liquidity in Forex is not constant but has a baseline level. Factors such as market size, government regulations, global news, and trading hours can all influence the ease of buying and selling assets. High demand for well-known currencies like the US dollar, euro, and Japanese yen makes them easily accessible for buying and selling.

Monetary policies and interventions by central banks can influence investors and market sentiment, affecting liquidity levels. Global news and events, such as political decisions, economic news, and natural disasters, can influence market sentiment and liquidity. Trading hours, adopted by major financial centres, ensure liquidity during trading hours but may be reduced for traders outside these hours.
Measuring Forex liquidity involves comparing trade currency pairs’ historical and present trading volumes to determine liquidity level changes. Price action, market depth, and liquidity ratios are popular metrics for measuring liquidity. Traders often analyse market order books to gather insights into market liquidity.
Explaining the Role of a Liquidity Provider in Forex
Foreign exchange LPs lend large currency pools to smaller firms for trading and order execution. They set prices and commissions and act as counterparties, excluding direct market access to traders. These LPs, including major banks and financial institutions like Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, Citigroup, and Barclays, play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market. They offer bid and ask prices, facilitate trade execution, enhance market efficiency and stability, and reduce transaction costs and slippage.
LPs can take two main roles: market makers, who continuously buy and sell assets or securities, and brokers, who help buyers and sellers buy or sell assets. Market makers ensure stability in the market by providing liquidity, reducing the bid-ask spread, and ensuring trades go through. Brokers act as intermediaries between retail traders and the broader financial markets, providing access to liquidity but not producing it themselves. Both roles are essential for businesses of all sizes to function effectively.
LPs assist FX brokers in offering lower spreads, stabilising spreads during volatile markets, and improving trade execution speed. They provide better stability by enabling brokers to execute orders more effectively, reducing higher spreads and large requotes. This is particularly beneficial for smaller brokers, who may not have enough adequate liquidity to provide their clients with.
LPs’ competitive pricing and services are influenced by market conditions, regulations, technological advancements, and market competition. Regulations can impose stricter capital requirements, while technological advancements like algorithmic trading and AI enhance efficiency. Market competition leads to tighter spreads and reduced costs, and innovation and differentiation are crucial for client retention.
How do LPs work?
LPs play a crucial role in market-making by quoting currency pairs’ buy and sell prices simultaneously. They use complex algorithms and trading tactics to reduce exposure and ensure adequate market depth by providing substantial volumes of currency for trade. Retail traders benefit from tighter spreads, improved execution, enhanced openness, and decreased slippage. This makes trading results more predictable and efficient.
LPs play a crucial role in the FX market ecosystem, serving as a hedge counterparty for retail brokers. Retail brokers act as the initial counterparty to traders’ orders, taking the opposite position in the trade. They externalise counterparty risk through hedging to manage and mitigate risks associated with being the counterparty to many trades.
Liquidity providers act as counterparties to the broker’s trade, transferring the risk to larger financial institutions better equipped to handle the fluctuations and risks inherent in FX trading. They also serve as official sources for FX brokers to obtain quotes for various currency pairs, ensuring traders can access real-time, competitive market prices.
Types of LPs
Liquidity providers are diverse in size, ranging from small-time brokers to global financial organisations controlling markets. They are divided into Tier 1 and Tier 2.
Tier 1 providers are the largest, such as large international banks and hedge funds, providing significant liquidity in the industry. The leading providers of this size are Deutsche Bank, UBS, and Barclays Capital.
Tier 1 LPs accept large volume orders, which smaller brokers cannot obtain. If an FX broker doesn’t generate enough volumes to request liquidity from a Tier-1 firm, they use Tier-2 liquidity partners.
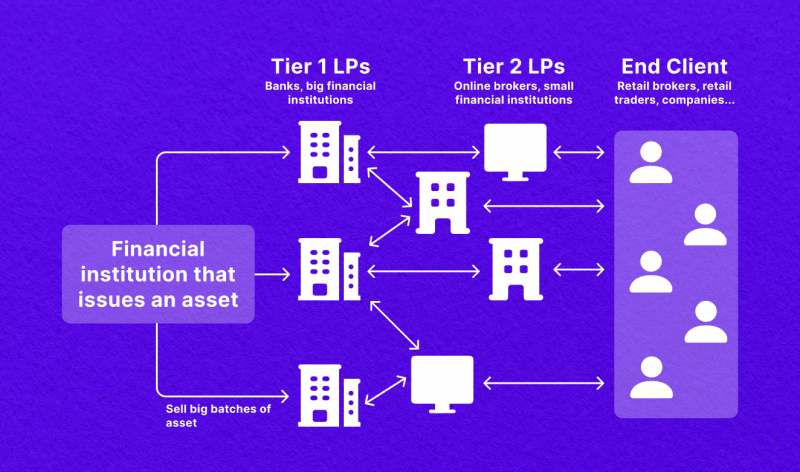
These firms, also known as Prime of Prime (PoP) or liquidity aggregators, can bridge the gap between smaller brokers and Tier 1 providers by aggregating small-volume orders from smaller brokers to send significant volumes to Tier 1 providers. Tier 2 liquidity providers, such as FXCM and Swissquote, are large, well-known, and reliable brokers.
Cooperation Models
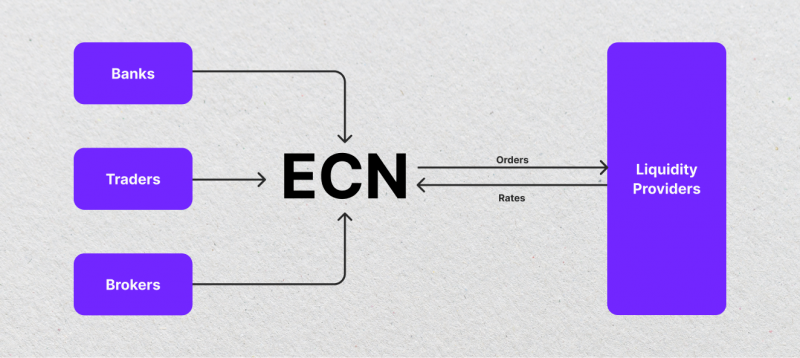
Brokers work with LPs in various ways, but all fall under the No Dealing Desk (NDD) concept. The NDD class includes ECN, DM, and STP models.
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) enhance liquidity provision, facilitating quick order execution and price aggregation. Sophisticated trading platforms continuously poll incoming liquidity, analyse market conditions, and generate customised pricing. ECN allows traders to receive bids and ask for offers, execute them based on market price, and act as both price givers and takers.
Direct Market Access (DM) allows traders to act as both price givers and takers, with brokerage firms presenting trades directly to liquidity partners.
STP (Straight-Through Processing) is a process where LPs provide bid and ask rates, and brokerage firms route orders to liquidity providers upon placement.
How LPs Make Money
Liquidity providers earn primarily from commissions from buying and selling currencies with partners. They charge a small markup on the spread when brokers finalise their orders and benefit from the continuous flow of orders and trading volume, taking a slice of each trade through transaction fees or commissions.
Liquidity providers in Forex generate revenue through various mechanisms, including the bid-ask spread, order flow and trading volume, market making, and volume-based incentives. They pocket the difference between buying and selling prices, attracting more traders and keeping the market moving.
They may negotiate volume-based incentives with brokers or platforms, including rebates or fee reductions, to encourage higher trading volumes and thereby increase their earnings.
How to Choose an LP
Selecting the right liquidity provider can be challenging. When choosing a Forex liquidity provider, consider several factors.
When choosing an FX LP, conduct thorough research to ensure a provider has a solid reputation and a solid track record of trustworthiness and integrity to ensure safe trading.
It is important that a provider adheres to all relevant regulatory norms and has proper licensing in major jurisdictions for legitimacy and capital security.
Ensure the provider has top-notch technology and a smooth trading platform to handle high trading volumes efficiently. Prioritise safety by finding a liquidity provider with good risk management plans and market monitoring.
LPs should offer fast, efficient execution, time priority, and full post-trade transparency, meeting high standards, especially during market data releases and unexpected events. Automated trading software should be used to check execution and gather opinions from current clients.
LPs should offer competitive spreads and low commissions. Compare pricing and fees between providers to get the best deal possible. Some providers may charge flat fees or commissions, while others offer more competitive spreads. It’s essential to read the fine print to ensure no hidden costs are involved.
Liquidity providers should provide stable, reliable feeds reflecting prices from interbank foreign exchange markets and stock exchanges. Access to historical market data, tick data, and a complete order book is essential, as is access to deep liquidity pools.
Technical support and customer service are also important. Different providers may have various levels of technical capabilities and additional services, such as portfolio management or automated trading. Ensure that you can rely on the Forex provider for assistance when needed to focus on more important aspects of trading strategies or managing portfolios.
Top 3 Liquidity Partners
Choosing the right LP can significantly impact your trading experience. Here are the three best FX LPs offering top-notch services worldwide.
B2Broker
B2Broker is a leading liquidity provider in the market, offering a wide range of services across various asset classes, including FX, crypto derivatives, precious metals, energy assets, and indices. The company has won numerous awards and continues to set the standard for excellence in liquidity provision.
B2Broker offers innovative technology and liquidity solutions for FX brokers, crypto exchanges, and institutional clients. Concentrating on transparency, reliability, and competitive pricing, they provide customisable solutions for seamless trading experiences.
B2Broker provides liquidity services for FX brokers on MT4 and MT5 platforms, offering commissions at 0.1 pips, order execution speed under 20ms, and a maximum leverage of 1:100.
The company caters to large licensed brokers, crypto exchanges, crypto brokers, forex brokers, hedge and crypto funds, and professional managers. B2Broker offers integration and support for CFD brokers, Spot Exchanges, and Margin Accounts, offering competitive margins, a highly competitive crypto offering with support for over 140 individual pairs, and an aggregated pool of liquidity from Tier 1 banks and non-bank providers.
FXCM
FXCM is a reputable liquidity supplier that offers institutional and retail clients affordable and advanced risk management tools. As a pioneer, it provides reliable liquidity at competitive rates for brokers.
FXCM PRO is a tier 2 LP for small-medium businesses or HFTs, offering spreads starting at 0.1 pips in the FX market.
The FXCM Prime platform offers centralised access to FX market information, consolidates activities into a single account, and provides effective pre-trade and post-trade credit evaluations. Key features include affordable connectivity options, liquidity, FX market data services, and over 400 tradable currency pairings.
Finalto
Finalto offers global market access through its liquidity, risk, and technology solutions. It provides brokers with multi-asset liquidity from Tier 1 banks, enabling flexible, responsible, high-risk trade execution. Finalto’s financial instruments include 80 FX currencies, five base metals, 11 precious metals, 13 indices, 787 equities, 4 NDFs, three energy instruments, and five cryptocurrencies.
Bottom Line
FX trading is complex, with liquidity at its core. LPs are crucial in FX trading, providing stable prices, quick trades, and value-added services that help traders succeed and keep the market moving.
Top liquidity partners will offer traders and businesses resources for successful trades. Choosing the right provider depends on individual needs, compliance with regulations, and high technical support and customer service. Understanding the providers’ roles is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and ensure profitable and seamless trading experiences.
Wondering how these solutions can boost your business?
Leave a request, and let our experienced team guide you towards unparalleled success and growth.
FAQs:
How many fees do LPs charge?
Normally, LPs charge a markup on the spread and an additional fee on the bid-ask of an FX pair.
Are liquidity suppliers regulated?
FX LPs are subject to regulation, varying by jurisdiction. Regulatory bodies oversee their activities to maintain market integrity and protect traders and investors. Key areas of regulation include fair pricing, market manipulation prevention, client fund safeguarding, and financial stability and ethical conduct.
What is the difference between a broker and an LP?
LPs maintain market liquidity and consistent bid-ask spread, while brokers act as intermediaries to connect traders with these providers.
What is a Tier 2 liquidity partner?
Tier 2 LPs, such as FXCM, are large, reputable FX brokers that can aggregate orders from smaller ones.