How Do Crypto Liquidity Pools Work in 2023-2024?
Nov 30, 2023
Market liquidity in the world of trading is what ensures smooth transactions and seamless operations between users. This holds particularly true in the fast-evolving realm of cryptocurrencies. While centralized exchanges (CEXs) rely on market makers to maintain liquidity, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms present a unique challenge. How can we achieve sufficient liquidity levels in an ecosystem that champions the concept of decentralization?
There is a solution for this, called “liquidity pools”, which allows for financial activity in decentralized crypto platforms. In this article, we dive into the world of liquidity pools, exploring their significance and shedding light on the leading platforms that offer fund pooling services.
Key Takeaways:
- Liquidity pools power decentralized crypto exchanges with liquidity and are formed from the funds pooled by liquidity providers.
- The operation of these pools is supported by automated market makers.
- Thanks to liquidity pools, DeFi apps and protocols can offer users yield farming and liquidity mining, as well as different services without third-party oversight.
- A liquidity pool can be subject to impermanent losses, smart contract errors, or developer risks.
What are Liquidity Pools?
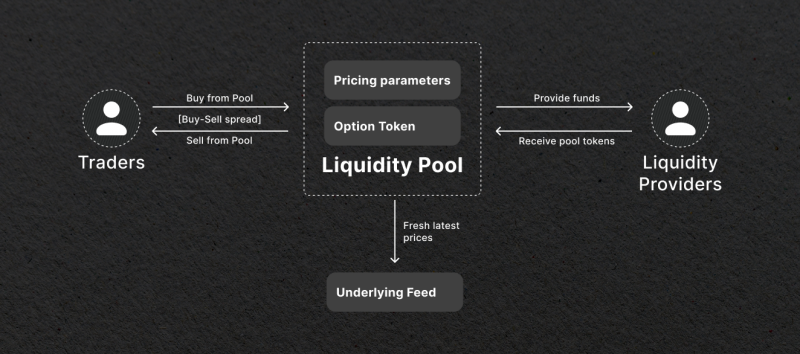
Liquidity pools are essentially a collection of funds locked within a smart contract on a blockchain. Their primary purpose is to provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and different applications and protocols to support trading and facilitate asset swaps.
Those who contribute their assets and form the pool are called liquidity providers (LPs). Usually, LPs are regular investors and users seeking to capitalize on the incentives that come with such forms of investing. To do this, they lock two tokens at equal value in a protocol for a certain period of time. For their contribution, LPs earn trading fees proportional to their share of their supplied liquidity or specific LP tokens.
Liquidity pools have become an integral part of the DeFi world, serving as the foundation for decentralized trading and other financial activities.
How Do Liquidity Pools Work?
Liquidity pools operate in conjunction with automated market makers (AMMs). These are algorithmic protocols that facilitate the automatic trading of assets within the pool.
AMMs dynamically adjust the prices of assets based on supply and demand, ensuring that the pool maintains a balanced allocation of the two tokens.
The most common formula used by AMMs looks like this: x * y = k, where x and y represent the quantities of the two tokens, and k is a constant value.

Let’s say we have a typical liquidity pool with a 50/50 balance of SOL and USDC, with a constant value of $1 million. If the demand for SOL increases, causing its price to rise, the AMM algorithm will automatically decrease the total share of SOL in the pool and increase the share of USDC. This ensures that the total value of both tokens remains equal to $1 million.
Fast Fact
The idea of AMMs was first introduced by Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, in a Reddit post back in 2016.
Smart Contracts and Transaction Execution
Liquidity pool operations are governed by smart contracts, self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain. Smart contracts automatically handle transactions within the pool, including deposits, withdrawals, and trades, according to the instructions they are programmed with.
When a user interacts with a liquidity pool, they interact directly with the smart contract, which eliminates the need for an intermediary or an overseeing party. The transparency and trustlessness of smart contracts enable secure and efficient transaction execution within liquidity pools.
Algorithmic Adjustments and Pricing
As mentioned previously, AMMs continuously adjust the allocation of tokens within a liquidity pool to maintain a balance between supply and demand.
As users trade assets in the pool, the AMM algorithm recalibrates the prices to reflect the impact of the trades on the overall pool liquidity. This algorithmic adjustment ensures that the prices within the pool remain competitive and close to the market rate.
AMMs vs Order Books
To better understand liquidity pools, let’s compare them with traditional centralized exchanges.
CEXs rely on a centralized party to match buy and sell orders and facilitate trades. Order book is an electronic list of all buy and sell orders for a particular asset, with the best bids and asks displayed at the top. All the orders are overseen through the central third party, an exchange itself.
Liquidity pools, used in AMMs, eliminate the need for an order book and an intermediary. Rather than relying on a direct counterparty like in CEXs, trades on AMM are executed against the crypto market liquidity in the pool. This peer-to-contract approach allows for efficient decentralized trading.
Total Value Locked
One of the most important metrics for liquidity pools is Total Value Locked (TVL), which refers to the total amount of assets locked in a contract.
The TVL of different liquidity pools can vary greatly, with some pools reaching hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars in value. The significant amount of locked assets signifies the trust and confidence that users have in a certain token, project or pool, making it an attractive destination for participants looking to engage in activities such as lending, borrowing, or trading.
Why Liquidity Pools Are Important in DeFi
Liquidity pools are essential components of the growth and development of DeFi systems. Here are several reasons that prove this statement:
Liquidity Provision for Decentralized Crypto Markets
Liquidity pools play a vital role in enabling activity on DEXs. Thanks to liquidity pools and contributions by LPs, users can seamlessly swap between different tokens without relying on a central authority. Liquidity pools eliminate the need for order books and intermediaries, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions in a safe environment.
All in all, the essence of DeFi lies in its decentralized approach, encouraging financial freedom, transparency, and accessibility for all users in the crypto space.
Counterparty Risk Elimination
One of the key advantages of liquidity pools is the elimination of counterparty risk. In traditional trading, a CEX is one which facilitates transactions and guarantees that trades will go as intended. Before starting trading, you need to entrust your funds to the platform.
Liquidity pools, on the other hand, allow users to maintain custody of their assets within their own wallets. Thus, they reduce the risk of exchange hacks, bankruptcies, or other centralized failures that could result in the loss of your crypto tokens. Users have full control over their assets and can transact on a DEX directly from their wallets.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining
Liquidity pools have paved the way for innovative concepts like yield farming and liquidity mining. These practices incentivize LPs to contribute funds to pools by offering token rewards or a share of trading fees. This has created new opportunities for users to generate passive income and participate in the growth of DeFi ecosystems.
Governance and Protocol Development
Liquidity pools also play a role in decentralized governance within DeFi protocols. Users who contribute to liquidity pools often receive governance tokens that grant them voting rights in decision-making processes. This allows the community to have a say in the development and evolution of the protocol.
Thus, active users who contribute liquidity can actively participate in shaping the future of DeFi projects, ensuring a more inclusive and distributed ecosystem.
Insurance and Risk Mitigation
Some DeFi platforms leverage liquidity pools to provide on-chain insurance against smart contract risks. Users can contribute funds to a liquidity pool and receive insurance coverage in return. In the event of a smart contract exploit or loss, the pool can compensate affected users. This innovative use of liquidity pools enhances the security and trustworthiness of DeFi protocols, mitigating the risks associated with potential vulnerabilities.
Tranching and Synthetic Assets
Liquidity pools have also opened the door for tranching, a concept borrowed from traditional finance. Tranching involves dividing financial products based on their risks and returns.
In decentralized finance, liquidity pools can be used to create customized risk and return profiles, allowing investors to select the tranches that align with their investment preferences. Additionally, liquidity pools support the creation of synthetic assets. These are tokens pegged to real-world or digital instruments. By collateralizing assets in a liquidity pool and connecting it to a trusted oracle, users can mint synthetic tokens, enabling broader access to diverse investment opportunities.
Why Liquidity Pools Can Be Risky
Undoubtedly, liquidity pools serve an important function in the realm of DeFi. Nevertheless, it is crucial to remain vigilant of the inherent risks involved with this technology:

Impermanent Loss
One of the risks associated with liquidity pools is impermanent loss. It refers to the potential loss in value that occurs when providing liquidity to a pool as compared to HODLing the underlying assets separately. This loss is not caused by any external factors but rather by the nature of how these AMMs operate.
As the market moves and the value of the assets in the pool changes, so does the price ratio between them. This can create a scenario where the LP tokens held by a user are worth less than what they initially deposited. If they were to withdraw their assets at this point, they would experience impermanent loss. This is because the value of their assets would have been greater if they had simply held onto them in their personal wallet instead of depositing them into the AMM.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Liquidity pools rely on smart contracts, which are subject to potential vulnerabilities and exploits. If a smart contract contains a bug or loophole, hackers may exploit it and drain the funds from the liquidity pool.
Thorough research and due diligence of the code are important for developers to mitigate the risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities. Audits and security measures can greatly help in minimizing the likelihood of such attacks.
Developer Control and Protocol Risks
Liquidity pools are governed by the protocols and developers behind them. In some cases, developers may have privileged access or control over the liquidity pool smart contracts, posing potential risks to users.
Users should carefully evaluate the transparency and governance mechanisms of liquidity pool platforms. Ensure that you are aware of any centralized control or changes that developers can make to the protocol, as they may impact the security and stability of the liquidity pool.
Popular Liquidity Pool Platforms in 2024
The market offers investors a lot of different platforms to pool their tokens and coins. Let’s look at some of the best out there:
Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most popular decentralized exchanges that employs liquidity pools on the Ethereum network. It allows users to trade ERC-20 tokens directly from their wallets without the need for an intermediary.

Fast Fact
Uniswap was the first platform that used the AMM model.
PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap is a decentralized exchange built on the BSC, offering similar functionality to Uniswap. It enables users to trade tokens and participate in yield farming and liquidity provision on BSC, Athereum and Aptos.
Curve Finance
Curve Finance is a DEX focused on stablecoin trading and wrapped token trading. Through liquidity pools, it ensures minimal price discrepancies and efficient trading. Curve Finance is a popular choice for users seeking stablecoin liquidity and low-volatility trading.
Sushi
Sushi is a DEX that initially forked Uniswap’s codebase but has since evolved with additional features and improvements. It offers liquidity pools, yield farming, loans, and other DeFi services, providing users with opportunities to earn rewards and participate in the SushiSwap ecosystem.
Balancer
Balancer is a decentralized platform that offers various pooling options, including private and shared liquidity pools. It allows liquidity pool providers to customize the token weightings within a pool, enabling more flexibility and tailored risk-return profiles. Balancer provides advanced liquidity management features and has gained popularity for its innovative approach to liquidity provision.
Raydium
Raydium is a major DEX operating on the Solana blockchain, known for its high transaction speed and low fees. It relies on liquidity pools to facilitate trading and liquidity provision on the Solana network, offering users a seamless trading experience.
Last Thoughts
Liquidity pools certainly changed the DeFi landscape, enabling trading, lending, yield farming, and other financial activities. Combined with automated market makers, they give users the ability to transact directly from their wallets without relying on intermediaries. However, users must be aware of the risks associated with impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, and developer control. By understanding the importance and mechanics of liquidity pools, users can enjoy the benefits of DeFi with confidence.
Wondering how these solutions can boost your business?
Leave a request, and let our experienced team guide you towards unparalleled success and growth.
FAQs
How do you participate in a crypto liquidity pool?
To participate in a crypto liquidity pool, you will first need to have a good understanding of how these pools work. Once you are familiar with the concept, you can begin by choosing a reputable and widely used platform such as Uniswap or Sushi.
Next, make sure you have a compatible cryptocurrency wallet like MetaMask for Ethereum-based platforms and set it up securely. Transfer equal amounts of the crypto assets you want to provide liquidity for into your wallet; for example, an ETH-DAI pool would require an equal value of both ETH and DAI.
Then, connect your wallet to the platform and select the specific liquidity pool you wish to join. Pay attention to factors such as trading fees, liquidity, and token pairs before clicking the “Provide Liquidity” option. Enter the desired amounts of tokens, making sure they are of equal value. Once your transaction is processed on the blockchain, you will receive a confirmation once it is completed (this may take some time, depending on network congestion). In exchange for your contribution to the pool, you will receive liquidity tokens representing your share of the reserve.
Are crypto liquidity pools profitable?
Crypto liquidity pools can be a profitable investment, but it ultimately depends on market conditions and the specific pool you choose to invest in. Some factors that may affect profitability include the size of the pool, trading volume, fees, and incentives offered by the pool.
Can you lose crypto in a liquidity pool?
Yes, it is possible. Putting your tokens into a liquidity pool comes with risks that you should be aware of before participating. DApp developers could steal deposited assets or squander them by making poor investment decisions. Smart contracts might have flaws or exploits that lock or allow funds to be stolen. Additionally, market volatility can cause the value of your assets in a liquidity pool to decrease, resulting in potential losses.
Can liquidity pools be hacked?
Yes, just like any system or platform, DeFi protocols are vulnerable to hacks and security breaches. An example of this is the recent hack of Curve Finance. On July 30, 2023, unknown attackers exploited a vulnerability in the smart contract code and stole over $50 million in cryptocurrency from the platform.