Liquidity Provider vs Market Maker in 2024: What Is the Difference?
Dec 19, 2023
Two types of key players hold significant influence over the markеt – liquidity providеrs and mаrket makers. While the former term is predominantly associated with OTC Forex trading, the latter is commonly found in stock and commodities markets. Both entities play vital roles in facilitating seamless asset exchange for investors, but how do they differ?
At first glance, their roles may seem similar, but a closer examination reveals the nuances that set them apart.
In this article, we’ll delve into the concept of a liquidity provider vs. market maker, their functions, and how they impact traders’ experiences and the market as a whole.
Key Takeaways:
- Forex liquidity providers are usually intermediaries connecting brokers to deep liquidity pools.
- Market makers are institutions that “make the market” for certain assets.
- Both types of participants benefit the market by guaranteeing liquidity, turnover volumes and price stability.
What is Liquidity?
Let’s first understand the concept of liquidity itself.
Liquidity refers to the ease with which traders can buy or sell assets on the market at any given time. It is a measure of the depth of the market and the volume of tradable financial instruments available. Think of it as the ability to convert an asset into cash quickly without affecting its price significantly.
To illustrate this concept, let’s take the job market as an example. In this scenario, liquidity would refer to the availability of job opportunities and the number of applicants looking for jobs. If there are plenty of job openings and a large pool of qualified candidates, we can say that the job market is highly liquid, as both employers and potential employees have a wide range of options available to them, making it easier to find suitable matches.
Similarly, in the Forex, stock or crypto markets, liquidity is a crucial factor that reflects an investor’s ability to buy or sell currencies and other assets quickly. High liquidity ensures timely execution of orders, while low liquidity may result in order execution delays, leading to unexpected losses.
In Forex, which is, by the way, the most liquid market today, with an average daily turnover of $7.5 trillion in 2022, the most liquid pair is EUR/USD, which accounts for 28% of the total transaction volume in the whole market.
Another example is the crypto market, where the most liquid asset is Bitcoin, which accounted for 53% of the total volume of crypto in December 2023.
So, how do brokers and exchanges manage liquidity risks and make sure that there is always enough trading activity on their platforms? That’s where market makers and liquidity providers come in.
About Liquidity Providers
Liquidity providers are market participants, often major financial institutions or companies, that ensure there is an ample supply of assets in the market for active trading.
In a broad sense, liquidity providers can include a variety of actors, such as:
- Large commercial banks and hedge funds: These institutions serve as market makers and speculators, boosting market liquidity.
- Central banks: Government central banks actively engage in the forex market to manage currency reserves and facilitate their movement.
- Transnational corporations: Companies conducting business in multiple countries require multiple currencies and actively move funds, making them significant liquidity providers.
- Retail speculators: Individual traders with substantial capital trading less popular currency pairs technically also operate as liquidity providers.
- Foreign investment project managers: Organisations investing in foreign businesses add liquidity to the Forex market as they hedge and close positions.
All of these actors are involved in supplying liquidity to the marketplace.
In a narrow sense, the term “liquidity provider” is typically associated with the realm of Forex trading. These are professional companies whose services meet the needs of numerous brokers seeking access to pools of quotes for their order books. These firms are also called “prime brokers” or bank brokers.
Different liquidity providers can offer different levels of services for their clients. Generally, there are three main types of connection that these companies offer:
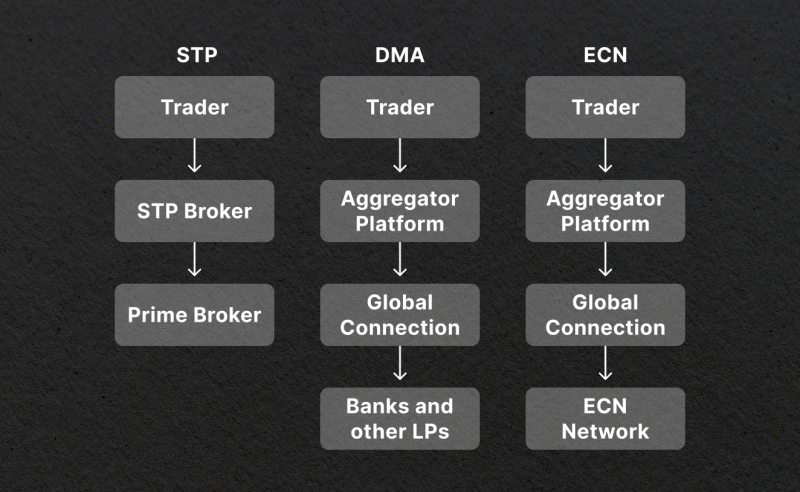
- STP (Straight Through Processing) – This type of connection refers to a scenario where a Forex broker has direct access to a liquidity provider. Orders of broker’s clients are transmitted directly to the liquidity provider, who subsequently executes these trades on its behalf. In this case, the broker does not intervene in the execution process.
- DMA (Direct Market Access) – In this case, a Forex broker has direct access to a large Tier1 liquidity provider or a pool of several small Tier2 liquidity providers.
- ECN (Electronic Communication Network) – ECN-brokers, as they are called, have direct access to the liquidity pool of large Tier1 providers. This network is also known as the interbank market.
ECN brokers are considered to be the most reliable and transparent, as they offer direct access to the best available quotes from the biggest banks and institutions. They also typically have lower spreads and allow for faster execution of trades.
However, it is important to note that there are very few pure ECN-Forex brokers on the market due to the very high entry requirements. Most companies prefer the standard STP model of operation.
But what are those tiers? Tier1 liquidity providers are the most reputable banks and institutions, such as Deutsche Bank and Bank of America. These organisations interact and trade with each other directly through the ECN system, thus forming the interbank market. Tier2 providers are smaller companies which usually serve as intermediaries between brokers and the interbank market.
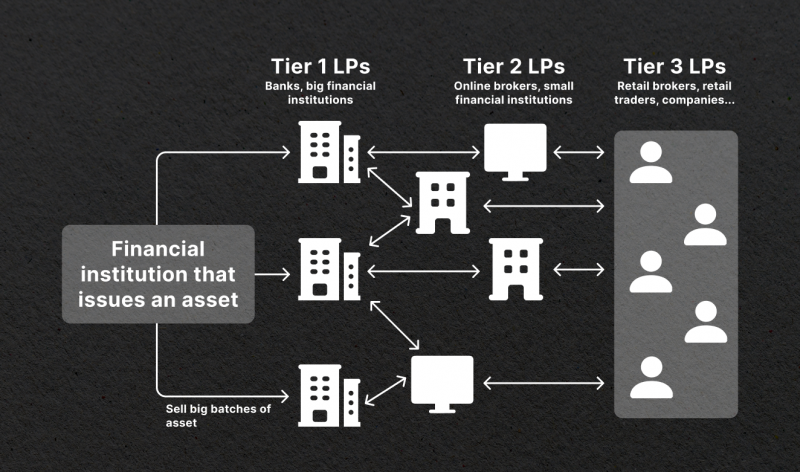
Fast Fact
Brokers who work with liquidity providers are called NDD (no-dealing desk) brokers. In contrast to DD brokers, which trade with clients using their own assets, NDD companies compile their order book using quotes from liquidity suppliers.
So, liquidity providers have direct access to the Forex market and continuously generate and transmit quotes to liquidity aggregators – software that keeps brokers connected to liquidity pools of one or multiple providers.
The Role of Market Makers
Market makers, on the other hand, are specialised participants in financial markets who ensure the continuous trading of assets by providing bid and ask prices for specific securities and assets.
They create a market for securities by enabling buyers and sellers to transact at any time. Market makers do not rely on external liquidity providers but instead commit their own capital to facilitate trades.
The role of a market maker is firmly established in legislation, so they are not some “mysterious whale players” but rather esteemed members of the market with their own set of defined responsibilities alongside brokers and traders. They are required to adhere to specific rules and regulations, such as the one outlined by the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States.
As a good example, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) distinguishes a category of market-making participants called “specialists”. A specialist becomes the second party to each transaction in a particular security on the exchange.
So, what are the main functions of a market maker?

Maintaining Two-Sided Quotes
One of the primary functions of market makers is to maintain two-sided quotes. This means that they are required to always quote both a buy and sell price for a specific volume of standard lots at the same time. By doing so, they provide liquidity and allow buyers and sellers to execute trades efficiently.
Stabilising Spreads
Another important responsibility of market makers is to maintain a stable spread. The spread refers to the difference between the buy and sell price of a financial instrument.
Ensuring Trading Volumes
They also play a huge role in maintaining trading volume. By providing liquidity and facilitating trades, these institutions reduce the likelihood of the market halting due to a lack of buyers or sellers. This, in turn, ensures that there is a continuous flow of trading activity and helps maintain the attractiveness of the market for issuers looking to raise capital.
Moreover, market makers are given special privileges by exchanges, such as access to pending orders and stop-losses. This information allows them to be more informed about the market conditions, further contributing to the maintenance of trading volume.
Market makers can be divided into two main types:
- Institutional market makers: These entities operate under a contract with the exchange or trading platform and are regulated by relevant authorities.
- Speculative market makers: Unlike institutional market makers, these ones operate in markets without a centralised exchange, such as the forex interbank market or crypto. They voluntarily assume the role of market makers to еnsure liquidity and profit from the spread.
Liquidity Provider vs Market Maker: How Do They Differ?
Now that we have a clear understanding of these types of liquidity suppliers, let’s explore their key differences:
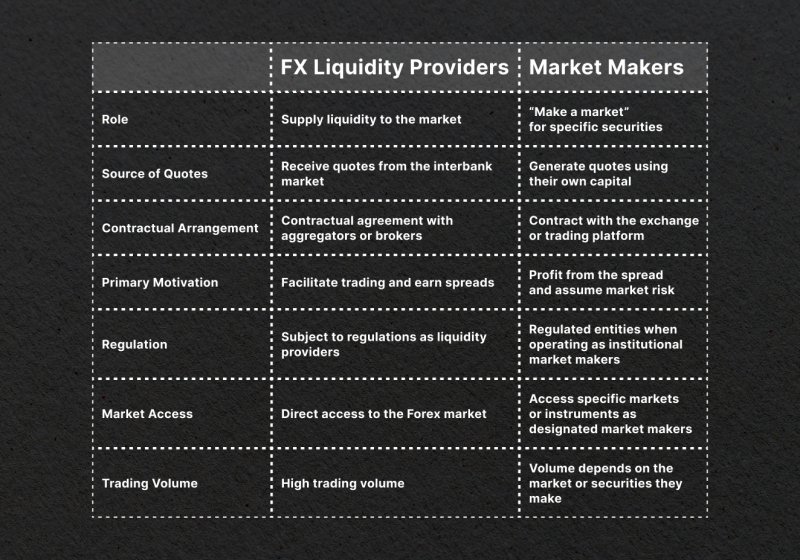
As liquidity providers ensure sufficient liquidity in the market by sourcing quotes from various entities, market makers сreate a market for specific securities by providing bid and ask prices using their own capital.
Liquidity providers typically have contractual agreements with aggregators or brokers, while market makers may have contracts with exchanges or trading platforms.
The primary motivation for liquidity providers is to facilitate trading and earn spreads, while market makers aim to profit from the spread by assuming market risk.
Liquidity providers are subject to regulations as they play a critical role in maintaining market stability. Institutional market makers, when operating as market makers, are also regulated entities.
Liquidity providers are directly connected to the interbank Forex market, while market makers operate in specific markets or instruments as designated participants.
The Significance for Traders & Markets
All in all, both these entities play the identical role for traders and investors – maintaining a sufficient level of liquidity and preventing risks. Moreover, by definition, liquidity providers are often considered market makers. Thanks to these institutions, market participants can take advantage of:

- Improved liquidity: Thanks to liquidity provision, investors can execute their orders quickly and at competitive prices.
- Price stability: The presence of market-making entities helps maintain stable prices. This stability prevents sudden price fluctuations and allows investors to get better deals.
- Reduced transaction costs: They help minimise transaction costs by narrowing the bid-ask spread. This reduction results in lower expenses for investors when buying or selling assets.
- Market accessibility: They ensure that investors can access markets and trade a wide range of assets, even in less liquid markets. This accessibility increases market efficiency and provides more opportunities for investors.
- Risk management: Market makers assume market risk by committing their own capital to facilitate trades. This risk absorption helps protect investors from sudden price shocks and ensures a more stable trading environment.
Closing Thoughts
Market makers and liquidity providers are both essential participants in financial markets, each with its own set of responsibilities. They ensure liquidity, stability, and accessibility, which contributes to the overall efficiency and success of different financial markets.
Wondering how these solutions can boost your business?
Leave a request, and let our experienced team guide you towards unparalleled success and growth.
FAQs
Are market makers human or bots?
Market makers can be either human traders or automated bots. In today’s financial markets, the majority of market-making is done by algorithms and computers, particularly in the crypto market.
What is the opposite of a market maker?
The opposite of a market maker is a market taker. While the former provides liquidity by posting bids and offers, the latter removes liquidity from the market by accepting those bids and offers. Market takers are usually traders who buy or sell securities for their own accounts at the prices offered by market makers.
How do liquidity providers make money?
They make money by charging a fee for their services, typically in the form of a spread of an asset. The larger the spread, the more profit liquidity providers can make.
How does liquidity provision work in crypto?
In DeFi, liquidity provision works by allowing users to deposit their assets into liquidity pools, which power decentralised exchanges and earn rewards for it. This creates a pool of assets that can be used to facilitate trades between different cryptocurrencies. This process is automated through smart contracts, eliminating the necessity for middlemen. However, when talking about centralised exchange, liquidity is usually provided by crypto market-making entities.
How to find a reputable liquidity provider?
There are several factors to consider when looking for a reputable liquidity provider. Here are some things you should keep in mind:
- Reputation: Look for a liquidity provider with a good reputation in the industry. You can do this by researching online or asking for recommendations from other traders.
- Regulation: A reputable liquidity provider will be properly regulated and licensed by the relevant authorities. This ensures that they operate within legal boundaries and follow strict financial regulations.
- Experience: It’s important to choose a liquidity provider with experience in the market. This will ensure that they have the necessary knowledge and expertise to handle your trades effectively.
- Technology: A good liquidity provider should have advanced technology and trading platforms, which can offer you fast execution speeds and reliable market data.
- Customer Service: Look for a liquidity provider that offers good customer service and support. This is important as you may need assistance or have questions regarding your trades.
- Pricing: Finally, consider the pricing offered by different liquidity providers. Compare their fees and commissions to find the most competitive rates for your trading needs.




