Needs and Wants: Key Differences
Jul 9, 2024

Human life is a complex system of interconnected elements, processes, things, and phenomena that directly or indirectly affect human well-being, comfort, and several other factors conditioned by the satisfaction of needs and requirements. However, there is also the so-called category of wants — things that are not prioritized within the framework of maintaining regular human life activity but provide an additional level of comfort.
This article will explain wants and needs, their characteristics, examples, and central differences. You will also learn what to consider when budgeting for each category.
Key Takeaways:
- Needs and wants form the basis of normal human activity, regulating the level and quality of life.
- Needs and wants differ, first of all, by priority and degree of vital necessity in those things that constitute these categories.
The Needs — Definition, Characteristics, Examples
Needs are the essential items or requirements that are necessary for survival and basic functioning. These can include things like food, water, shelter, and clothing. Meeting these needs is fundamental for maintaining life and good health, and they form the basis for human survival and well-being.
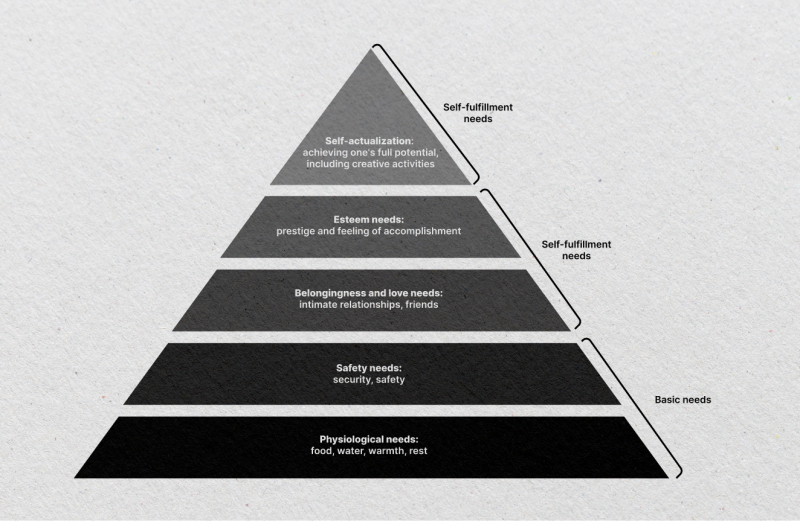
There is a large list of aspects necessary to meet the criteria for a person’s full life and health. However, the following examples are some of the main ones:
Food and Water
Food and water are essential for providing nourishment and hydration to the body. Food supplies essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that the body needs to function correctly.
Shelter
A shelter is essential for protecting against elements such as rain, wind, and extreme temperatures and offering security from potential threats.
Clothing
Clothing serves multiple purposes, including providing warmth, protection from the elements, and ensuring modesty.
Healthcare
Healthcare is crucial for promoting and maintaining overall well-being and diagnosing and managing various medical conditions and diseases.
Basic Education
Basic education is essential for developing literacy skills and gaining a fundamental understanding of the world around us. It provides individuals with the knowledge and tools to navigate everyday life, make informed decisions, and contribute to their communities.
Sanitation
This category includes clean water and proper waste disposal, which are crucial for health.
The category of needs reflects the need to maintain optimal conditions for the human body’s functioning and the degree of comfort in life. The following characteristics determine these needs.
Essential for Survival
The fulfillment of needs is essential for sustaining life and ensuring fundamental well-being.
Limited and Finite
The list of essential requirements is concise and remains consistent over time.
Non-Negotiable
Meeting one’s needs is essential to maintaining a state of well-being and ensuring one leads a productive and fulfilling life.
Priority
When making decisions, it’s important to prioritize needs over wants. This means that essential requirements should precede desires when considering options and making choices.
Fast Fact:
To plan a budget for needs and wants, many follow the 50/30/20 rule.
The Wants — Definition, Characteristics, Examples
The concept of wants refers to non-essential items or desires that contribute to improving the quality of life. These are not necessary for basic survival but are driven by individual preferences, tastes, and aspirations. Wants can encompass various goods, services, experiences, and other elements individuals seek to enhance their lives and fulfill their desires.
The category wants, as well as needs, includes an extensive list of more luxurious lifestyles corresponding to a higher level of well-being. It includes:
Luxury Goods
Luxury designer apparel, state-of-the-art electronic gadgets, and sleek, high-performance automobiles.
Entertainment
Entertainment options encompass a wide range of activities, such as attending concerts, purchasing video games, and going to the movies.
Travel
This category includes vacations and leisure trips.
Gourmet Food
Dining at fancy restaurants or purchasing exotic foods.
Home Upgrades
Non-essential home improvements like swimming pools or advanced home automation systems.
Wants also have certain characteristics that describe their difference from wants. These include:
Enhance Quality of Life
Wants contribute to comfort, pleasure, and satisfaction.
Variable and Infinite
Wants are numerous and can change over time based on trends, personal growth, and societal influences.
Optional
Unlike needs, wants are not essential for survival and can be deferred or sacrificed if necessary.
Secondary Priority
Wants are considered after needs have been met.
What Is the Difference Between Needs and Wants?
Needs are the essential, fundamental requirements for a person to live and function properly. They are the basic things that a person must have in order to survive and maintain a decent quality of life. These include physiological needs (food, water, shelter, etc.), safety needs (security, stability, etc.), social needs (belonging, love, relationships, etc.), and esteem needs (self-worth, recognition, etc.).

In contrast, wants are the non-essential, desired items or experiences that an individual would like to have, but are not absolutely necessary for their survival or basic well-being. Wants are often based on personal preferences, social influences, or aspirations, rather than fundamental requirements. Examples of wants to include luxury goods, recreational activities, status symbols, and personal interests.
While wants can enhance an individual’s quality of life and provide a sense of satisfaction, they are not as critical as needs for maintaining a person’s overall health and functioning. The distinction between needs and wants is crucial in personal financial planning, budgeting, and decision-making, as it helps individuals prioritize their spending and allocate resources in a way that ensures their fundamental requirements are met first before pursuing non-essential desires.
Budgeting for Needs and Wants
When it comes to budgeting, the distinction between needs and wants is crucial for effectively managing one’s financial resources. Here’s a closer look at how to budget for needs and wants:
Budgeting for Needs
- Identify your essential, non-negotiable requirements. These include your physiological needs (food, water, shelter, clothing, etc.), safety needs (housing, transportation, healthcare, etc.), and basic social and esteem needs.
- Prioritize these needs and allocate a significant portion of your budget to ensure they are fully covered. This should be your top priority when creating a budget.
- Estimate the costs for each need and make sure to account for any recurring or essential expenses.
- Aim to have a buffer or emergency fund to handle unexpected needs that may arise.
Budgeting for Wants
- Once your needs are covered, you can allocate a portion of your budget toward your wants or discretionary spending.
- Wants are the non-essential items or experiences you desire, such as entertainment, hobbies, travel, dining out, or luxury goods.
- Determine how much you can realistically afford to spend on wants without compromising your ability to meet your needs.
- Consider setting a specific budget or limit for your wants to ensure they don’t consume too much of your overall financial resources.
- Prioritize your wants and be mindful of impulse purchases or unnecessary spending.
Striking a Balance
- Achieving a healthy balance between needs and wants is crucial for maintaining financial stability and well-being.
- Avoid allocating too much of your budget towards wants at the expense of your needs.
- Periodically review and adjust your budget to ensure it reflects your evolving needs and priorities.
- Seek to find creative ways to satisfy your wants without compromising your ability to meet your essential needs.
Conclusion
Needs and wants are two opposites that comprise a set of certain criteria that determine the degree of comfort of life and normal life activity. Each of these categories is an integral element of life, determining the priority and importance of those or other life benefits of a person, depending on his or her financial opportunities and personal preferences.




