OTC Trading Strategies and Technologies to Succeed in Over-the-Counter Markets
Aug 12, 2025
In a world where speed, privacy, and precision matter more than ever, OTC trading has become the go-to path for financial institutions and sophisticated investors.
Unlike traditional trading on centralized exchanges, the OTC market thrives behind closed doors, built on relationships, custom deals, and advanced strategies that most retail traders never see.
This article breaks down how OTC trading works, its primary advantages, and how cutting-edge technology is reshaping this opaque but powerful corner of the financial world.
Key Takeaways
- OTC trading strategies are customised and designed for discretion, large trade sizes, and complex financial instruments.
- New platforms, AI tools, and APIs are revolutionising OTC deal-making, reducing counterparty risk and improving price transparency.
- From arbitrage to agency-based execution, strategy choice depends on risk appetite, asset type, and market liquidity needs.
How OTC Trading Is Done?
OTC trading is not like normal trading on a centralized exchange, where everyone can see what’s happening. In OTC trading activities, it’s all private and less about a public list of orders. People talk directly, agree on special deal terms, and deal in secret.
Main Players
OTC trading has big players—often big groups, rich folks, or big companies—wanting to buy or sell a lot without others noticing. Since these are big deals, they are done quietly so they don’t shift the market price.
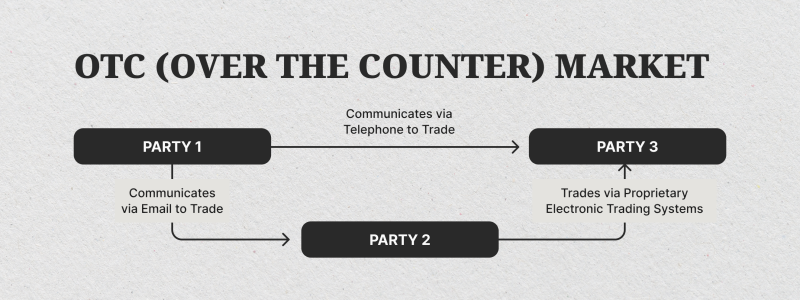
Brokers come in to help these players, connecting buyers and sellers, talking about deal terms, and helping with the deal’s end and middle jobs. Sometimes, specialized firms or finance houses give out prices and fill big orders to keep everything running smoothly in this hidden area.
Pricing
Here, unlike an exchange with the public, instantly changing prices, OTC trading is where prices are negotiated in private. One side asks for a price, and the other gives their offer. Prices can change a lot based on how big the trade is, when it is, and if the market is shaky.
This way of setting prices is good for big groups. They can trade a lot without messing up the price or alerting everyone.

Tools Used
Some OTC trades still happen on the phone or encrypted chats, but more and more use digital methods. Many OTC desks have tools that let traders talk in real-time, check prices, and finish trades all through one digital platform.
For instance, with RFQ tools, traders can ask many for their best price transparency. Many desks now have secure pages where trades are verified, settled, and even take care of legal stuff, all together.
Even with new tech, talking directly still matters, especially for big or tricky trades.

Finishing and Sorting Trades
In OTC, finishing trades is more about direct agreements than automated clearing. Usually, the two sides sort out when and how to swap money and assets.
Depending on what’s being traded and where, this might be done in a day or two. For more safety, some big trades use a trusted third-party who holds the underlying assets until everyone agrees all terms are met.
No central clearinghouse means more risk of the other side not following through, so trust, a good name, and strong legal deals are key in OTC markets.
Fast Fact
The OTC market is larger than most major exchanges combined, with some trades exceeding $1 billion, all negotiated without public visibility.
Main OTC Trading Strategies
When you dive into the hard world of over-the-counter (OTC) trading, the way you pick can really change your win or loss, big time, when in big deals or with special money tools outside the main stock markets.
Not like markets on central exchanges, OTC securities trades happen just between two people, often without a major exchange or set places like the New York Stock Exchange watching them.
So, what are the top OTC trading strategies for the ones in the venture market now? Let’s go over the most used ones in the OTC area and how pros handle the risk from others while they keep their trades smooth.
Principal Trading
In principal trading, the OTC desk or the one giving the liquidity takes the other end of your deal. This way is big with firms that trade with their own money and people who set the market, who don’t mind some risk.
They not only help but also join the market, and they might gain (or lose) depending on how the market or costs change.
This way often does well when the trader can access their own deep information or is working with assets that not many people want, like penny stocks or new market names.
Since these trades are not open to price checks in real time, these spots need a good look to match the fair market value and current market conditions.
Agency-Based Action
Agency-based trading is less risky as the broker does not take on market risks but looks for the best price for a client. This is often the path for big money investors who need help with OTC deals or tools, not wanting to face price risks straight on.
These brokers work with wide nets and RFQ systems to ask for prices from many liquid givers, keeping prices good while cutting worries about market tricks. This kind of action is also more common in places with strong laws after the big money mess.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage is still one of the most innovative OTC trading strategies in both OTC groups and exchange-traded markets. In the OTC area, it often means spotting price gaps between OTC and leading exchanges. For example, if an asset costs less in an OTC deal than on a big exchange, it could mean good money for a quick trader.
Another type is cross-border arbitrage, commonly used in complex financial markets where time zones, liquidity, and rules change by area. When done with care and backed by solid risk and hedging strategies, arbitrage faces fairly low risk from market manipulation and shifts.
Smart Trading and Hidden Pools
One of the more advanced OTC trading strategies today uses smart trading and hidden pool settings. Smart systems help set and better order operations across chopped up liquid spots, bringing in both OTC areas and exchange platforms.
Traders can set by code when to make trades, how much to show, and where to send orders—really useful in OTC trading strategies where price info is short.
Hidden pools—trading spots out of the public eye—are commonly used in OTC to prevent market clues and changing prices. These tools are big for large trades in money tools, not on the main exchanges.
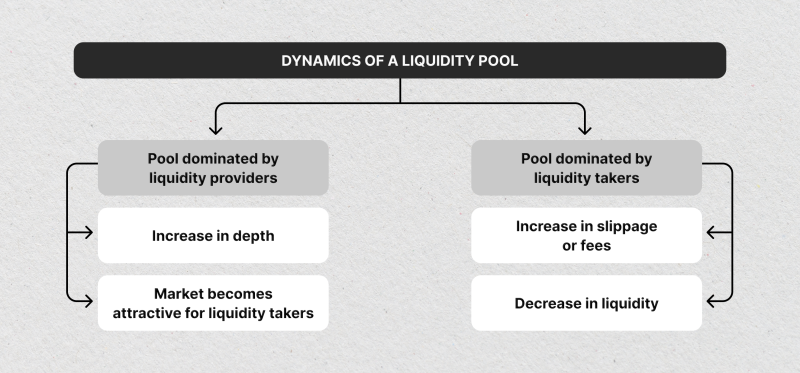
Getting Liquidity and Keeping it In
In today’s digital money markets, many OTC desks work as small markets themselves. They bring together market makers and trade limits inside to do client orders without needing outside spaces.
This prevents slips and makes trades faster, which is particularly beneficial when dealing with direct transactions in complex instruments that are not traded much.
This approach needs a broker or OTC desk that is well-linked and works best when the place has many counterparties and receives market updates in real time.
Technology in OTC Trading
In the past few years, tech has changed how over-the-counter (OTC) trade is done. Where once we used phones and emails, now it’s all about fast, safe, smart tech in a fancy market.
Big old stock places use open order books, but OTC markets have gone with new ways. They now cover up the clear view gap and cut down the risk of dealing with others. This is key when the money stuff gets hard and the deals are big.
The Rise of Electronic OTC Platforms
The times are gone when OTC trading was slow and had lower liquidity. Now, places like Paradigm, Tradeweb, and TP ICAP have changed the game by giving all-digital ways to do OTC transactions.
These places mix things up—sitting halfway between big trade spots and old broker groups—where traders can ask for prices, talk over deals, implement various OTC trading strategies, and lock in trades fast.
Not like markets where all trade, OTC places let people make deals their own way in things like OTC stocks to OTC futures, with much more room to move than any one big trade spot can give.
For high-net-worth individuals looking to leverage smart OTC trading strategies, these places let them access large amounts of money, better price plans, and smooth ways to wrap up trades—all while keeping the market liquidity risk low.
APIs, AI-Based Pricing & Smart Negotiation Tools
At the heart of top OTC trade plans today are smart tools that work in secret to make trades better. One big change has been the mix of tools that let systems talk fast with others who give money, make markets, and check risks.
With these tools, firms can set up fast quotes, see live prices, and even handle trade sizes fast. Add AI for prices, and you set a new way to do OTC securities.
These smart tools check live market information, past prices, and market trends to give better quotes that show the true market price, not just a guess.
Also, AI bots that help in talks are popping up in both over-the-counter and dark pool trade spots. They help traders get good deals quietly in areas where not much is traded, like penny stocks, new market items, or securities that don’t move much.
Compliance, KYC & Risk Management Integration
As regulatory oversight has tightened since the global financial crisis, modern OTC platforms have adapted by deeply embedding compliance frameworks into their core systems. Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and audit trail features are no longer optional—they’re essential.
These platforms now integrate seamlessly with risk management strategies, compliance dashboards, and even sanction screening tools, allowing market participants to execute trades with confidence.
In some jurisdictions, this tech-driven transparency has helped position OTC contracts as safer, more compliant alternatives to lightly regulated exchange markets.
By automating checks and storing transaction records, firms can reduce operational risk in their OTC trading strategies while staying aligned with global financial markets standards. The result is a more transparent environment, even in an industry long known for its private, bespoke nature.
Strategy Meets Technology
The most successful traders in today’s OTC markets group know that a strong tech stack can amplify even the best OTC trading strategies. Whether you’re using algorithmic trading to execute across fragmented venues, tapping into dark pool trading for stealth execution, or working through APIs to price OTC derivatives contracts, the message is clear: technology isn’t just helpful—it’s foundational.
As the boundary between exchange-traded and over-the-counter assets continues to blur, the firms that win will be the ones who embrace automation, intelligence, and compliance-first infrastructure. In a market built on discretion, having the right digital tools might be the sharpest edge a trader can have.
Conclusion
OTC trading is no longer just about whispered deals and handshake agreements. It’s now a sophisticated arena where strategy meets innovation, driven by smart systems, deep liquidity, and strict compliance.
As over-the-counter trading continues to grow in importance, mastering its strategies, risks, and tech tools isn’t just smart—it’s essential for success in modern financial markets.
FAQ
What is the difference between OTC and exchange trading?
OTC trades happen privately between parties involved, while formal exchange trades are public and go through centralized platforms.
Is OTC trading legal and regulated?
Yes, but regulation varies by country and asset. Compliance tools like KYC and AML are essential in OTC.
Can retail customers access OTC markets?
Generally, OTC trading is limited to institutional investors and high-net-worth players due to size and complexity.




