Warren Buffett’s Investment Strategy: How to Master
Feb 27, 2023
Today, we will talk about a person whose name is well-known to anyone working in the field of investing. Warren Buffett, the legendary investor and chairman of Berkshire Hathaway, is renowned for his remarkable success in the world of investing.
Often welcomed as one of the greatest investors of all time, Buffett’s investment strategy has become a subject of intense study and admiration.
Warren Buffett rules of investing stand as a beacon of success in the financial world, offering invaluable lessons for investors seeking stable prosperity.
In this article, we delve into the fundamental principles, strategies, and wisdom behind Buffett’s legendary approach to wealth creation.
Key Takeaways:
- Warren Buffett rules for investing are founded on timeless principles such as value investing, patience, and discipline.
- Buffett emphasises quality over quantity, seeking companies with enduring competitive advantages and sustainable business models.
- Despite challenges and criticisms, Buffett’s track record of success reaffirms the effectiveness of his approach, inspiring investors worldwide.
Background on Warren Buffett

Born in 1930 in Omaha, Nebraska, Warren Buffett displayed an early talent for business and investing. He began his journey by purchasing his first stock at the age of 11 and filed his first tax return at 13.
Buffett’s fascination with investing led him to study under the guidance of Benjamin Graham, the father of value investing, at Columbia Business School.
Buffett’s investment philosophy was heavily influenced by Graham’s principles of buying undervalued stocks and holding them for the long term.
Fundamental Principles of Buffett’s Investment Strategy

At the heart of Buffett’s strategy lies the essence of value investing, summarised by his committed adherence to time-tested principles.
Buffett believes that “price is what you pay, value is what you get,” emphasising the importance of investing in companies with strong fundamentals and durable competitive advantages.
At the core of Warren Buffett’s investment rules lie a few fundamental principles:
Value Investing: Buffett is a loyal advocate of value investing, which involves identifying undervalued stocks that have the potential for long-term growth. He looks for companies with solid fundamentals, including a competitive advantage, sustainable business model, and competent management.
Margin of Safety: Buffett emphasises the importance of having a margin of safety when making investment decisions. This means buying stocks at a significant discount to their intrinsic value to protect against downside risk.
Long-Term Perspective: Buffett is known for his patient approach to investing. He believes in holding onto quality companies for the long term and allowing the power of compounding to work in his favour.
Focus on Quality: Buffett prioritises quality over quantity when selecting investments. He looks for companies with durable competitive advantage, known as economic moats, which enable them to maintain profit margins and avoid competition.
Fast Fact:
Warren Buffett spends nearly 80% of his workdays reading. He has invested around $15 billion in wind and solar energy.

Key Components of Buffett’s Investment Process
Buffett’s investment process is marked by meticulous research, identifying companies with enduring competitive advantages and robust growth prospects. By prioritising quality over quantity and maintaining a diverse portfolio, Buffett mitigates risks while maximising returns for his shareholders. Buffett’s investment process can be broken down into several key components:
#1 Research and Analysis
Buffett and his team meticulously researched companies before making investment decisions. They analyse financial statements, evaluate business models, assess competitive positioning, and scrutinise management quality.
#2 Circle of Competence
Buffett stays within his circle of competence by investing in industries and businesses that he understands well. He avoids complex financial instruments and speculative schemes.
#3 Patience and Discipline
Buffett exercises patience and discipline in his investment approach. He is willing to wait for the right opportunities to arise and does not succumb to market fluctuations or short-term trends.
#4 Contrarian Mindset
Buffett is not swayed by popular opinion or market sentiment. He is willing to go against the crowd and buy when others are fearful, provided that the fundamentals of the business remain strong.
His famous advice to “be fearful when others are greedy and greedy when others are fearful” underscores the importance of contrarian thinking in investing.
Portfolio Management Strategies
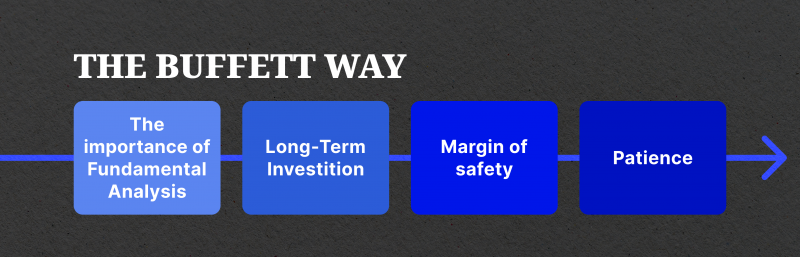
Buffett’s portfolio management ethos embodies the ethos of patience and persistence, avoiding short-term speculation in favour of long-term investments.
Through strategic allocation and smart decision-making, Buffett cultivates a portfolio composed of sustainable growth. Buffett’s portfolio management strategies mainly revolve around concentration and diversification:
- Concentration: Buffett believes in concentrating his investments on several high-quality companies. He prefers to have a deep understanding of each business in his portfolio rather than spreading his investments thinly across numerous holdings.
- Diversification: While Buffett advocates for concentration, he also emphasises the importance of diversification within his circle of competence. He diversifies across different industries and sectors to mitigate risk and capture opportunities.
He famously stated, “Our favourite holding period is forever,” highlighting his commitment to long-term value creation.
Behavioural Aspects of Buffett’s Strategy
Buffett’s approach exceeds simple numbers, emphasising the importance of temperament and rationality in investing. By remaining disciplined amidst stock market volatility and adhering to contrarian principles, Buffett strengthens his position as a wise investor.
Warren Buffett’s investment rules are not only based on financial analysis but also incorporates behavioural aspects:
- Emotional Control: Buffett maintains emotional control and avoids making impulsive investment decisions based on fear or greed. He remains rational and level-headed, even during periods of market volatility.
- Long-Term Focus: Buffett’s long-term perspective helps him ignore short-term fluctuations in stock prices and focus on the underlying fundamentals of the businesses he invests in.
He advises investors to “never lose money” and to “invest in what you understand,” underlining the significance of prudence and comprehension in decision-making.
Criticisms and Challenges
While Buffett’s strategy has gathered widespread approval, it is not immune to criticism and scrutiny. Critics question its adaptability in the face of evolving stock market dynamics, highlighting potential challenges in identifying underrated opportunities in a digital age. The main challenges of his strategy are:
- Underperformance in Certain Periods: Buffett’s intrinsic value investing approach has faced periods of underperformance, particularly during bull markets or when growth stocks outperform value stocks.
- Size Limitations: Berkshire Hathaway’s immense size has made it increasingly challenging for Buffett to find attractive investment opportunities that can generate significant returns.
However, Buffett’s track record of success speaks volumes, reaffirming the resilience and effectiveness of his investment philosophy.
Warren Buffett’s Winners and Losers
Warren Buffett has made numerous outstanding investments throughout his career. Some of his most notable investments include:
Coca-Cola (KO)
Buffett began buying shares of Coca-Cola in the late 1980s and continued to accumulate them over the years. Coca-Cola has proven to be one of Buffett’s most lucrative investments, providing substantial returns through both capital appreciation and dividends.
American Express (AXP)
Buffett first invested in American Express in the 1960s after the company faced a crisis due to a financial scandal. Buffett saw an opportunity in the company’s strong brand and loyal customer base. His investment has paid off handsomely over the years.
Apple (AAPL)
Buffett began buying shares of Apple in 2016, and his investment in the tech giant has been highly successful. Apple’s strong fundamentals, including its dominant position in the smartphone market and robust ecosystem of products and services, have contributed to its impressive performance.
Gillette
Berkshire Hathaway acquired Gillette in 1989, adding another strong consumer brand to its portfolio. Gillette’s razors and other grooming products have continued to generate steady profit margins for Berkshire Hathaway over the years.
These are just a few examples of Warren Buffett’s successful investments. His investment philosophy, characterised by a focus on buying high-quality companies at reasonable prices and holding them for the long term, has guided him to generate substantial wealth for himself and Berkshire Hathaway shareholders over many decades.
While Warren Buffett is known for his many successful investments, he has also experienced losses and made some investments that did not perform as well as expected. Some of Buffett’s notable losers include:
Berkshire Hathaway’s textile business
Buffett’s initial investment in Berkshire Hathaway was in the textile industry. However, the textile business faced significant challenges due to competition from cheaper imports, eventually leading Buffett to close the textile operations. This experience taught Buffett the importance of investing in companies with durable competitive advantages.
Dexter Shoe Company
In 1993, Berkshire Hathaway acquired the Dexter Shoe Company for around $400 million, primarily using Berkshire stock. However, the shoe business faced difficulties, and Buffett later acknowledged that the acquisition was a mistake. He exchanged Berkshire stock to buy back Dexter Shoe Company’s shares, leading to a loss for Berkshire Hathaway’s portfolio.
Energy Future Holdings (formerly TXU)
Berkshire Hathaway invested $2 billion in Energy Future Holdings, a Texas-based energy company, through high-yield bonds. However, Energy Future Holdings filed for bankruptcy in 2014 due to a heavy debt burden and declining natural gas prices, resulting in significant losses for Berkshire Hathaway.
Despite these investment setbacks, Buffett’s overall track record remains exceptional, emphasising his ability to learn from mistakes and adapt his investment approach over time.
Conclusion
Warren Buffett’s investment strategy is built on timeless principles of value investing, patience, and discipline. His emphasis on quality, long-term perspective, and rational decision-making have enabled him to achieve remarkable success in the world of investing.
While Buffett’s approach may not be immune to criticisms and challenges, his enduring legacy as a legendary investor continues to inspire and guide value investors around the globe.
FAQs:
Why is Warren Buffett so rich?
A lot of Buffett’s wealth can be explained by this simple mathematical concept — compound interest over a very long period of time. Buffett was also never a big spender. Instead of spending, he invested and compounded his money.
What is Warren Buffett’s golden rule?
Warren Buffett once said, “The first rule of an investment is don’t lose [money]. And the second rule of an investment is don’t forget the first rule.”
What is Warren Buffett 70 30 rule?
The 70/30 rule is a guideline for managing money that says you should invest 70% of your money and save 30%. This rule is also known as the Warren Buffett Rule of Budgeting, and it’s a good way to keep your finances in order.