How to Start a Prop Firm in 2024?
Sep 12, 2024

The development of capital management methods within the framework of investment activities in the capital markets has formed several fundamentally new concepts of trading, which are based on the creation of specialized companies using an approach to management that differs them from traditional investment firms and brokerage companies, independent evaluation, control and making investment decisions and the use of own capital for work. Such companies operate on the prop trading model.
This article will explain to you what prop firms are and their characteristics. You will also learn about how to start a prop firm and how it makes money for you.
Key Takeaways:
- In prop trading, trading is conducted exclusively on the firm’s own funds and not on the money of clients attracted under management.
- Firms whose core business is proprietary trading may utilize various trading strategies, including scalping, volatility trading, various types of arbitrage, pair trading, etc.
What is a Prop Firm?
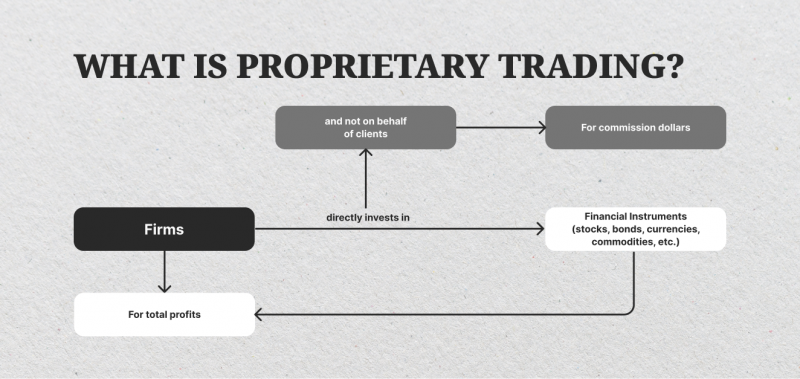
A proprietary trading firm, often referred to as a prop firm, is a financial institution or private company that engages in trading financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and other derivatives, using its own capital instead of managing funds on behalf of clients.
This approach distinguishes prop firms from traditional investment firms and brokerages, as they operate independently and solely focus on generating profits through their trading activities.
By trading their own capital, prop firms maintain complete control over their trading decisions, enabling them to adapt quickly to market conditions and pursue aggressive strategies without external constraints.
The primary objective of a prop firm is to capitalize on market movements by employing various trading strategies. These strategies can range from short-term day trading and swing trading, which aim to exploit price fluctuations over a few hours or days, to more sophisticated methods like algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading (HFT).
Algorithmic trading uses complex mathematical models to automate trading decisions, while HFT involves executing a large number of trades at incredibly high speeds to capture tiny price inefficiencies. Both strategies rely heavily on advanced technology and data analytics to identify and exploit market opportunities.
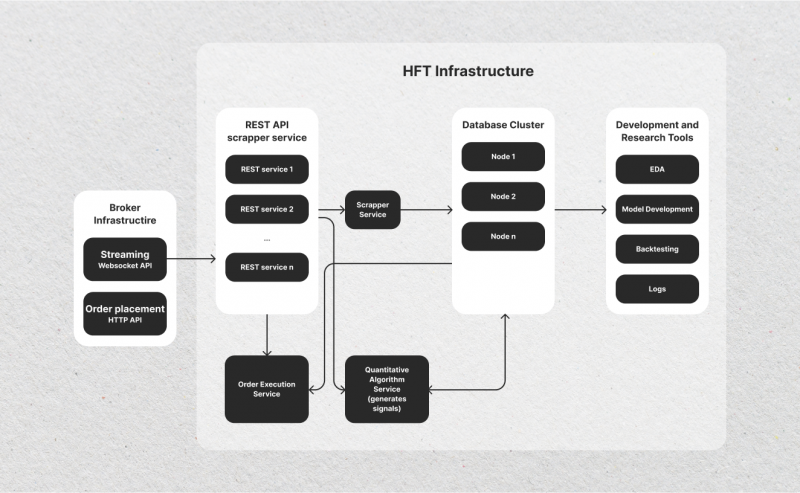
Prop firms are known for their emphasis on advanced technology and infrastructure. They invest heavily in state-of-the-art trading platforms, high-speed data feeds, and low-latency networks to gain a competitive edge in the market.

This technological advantage allows prop firms to execute trades faster than their competitors, which is crucial in high-frequency and algorithmic trading environments. Meanwhile, prop firms often develop proprietary software and algorithms tailored to their specific trading strategies, further enhancing their ability to generate profits.
Fast Fact:
Prop trading is a concept that replaced the traditional approach to trading and money management.
Fundamental Characteristics of a Proprietary Trading Firm
Taking into account the peculiarities of work laid down in the concept of prop trading firm, it is a new form used within the framework of trading activity with different classes of assets and implies the use of own capital, providing total control and management of investment decisions.
At the same time, such companies have a number of distinctive characteristics that determine the concept of work laid down in the firms of this format. Among them, the following can be emphasized:
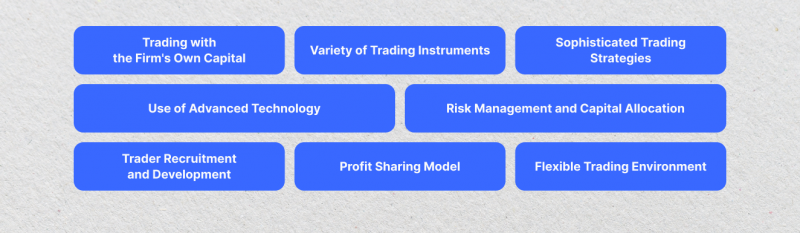
Trading with the Firm’s Own Capital
Proprietary trading firms, also known as prop firms, distinguish themselves from traditional brokers and asset managers by using their own capital to trade rather than trading on behalf of clients.
This distinct approach grants them complete autonomy over trading decisions, free from external client influences. As a result, prop firms possess significant flexibility and agility in their operations, as the interests of external clients do not constrain them.
Variety of Trading Instruments
Proprietary trading firms, also known as prop firms, are financial institutions that buy and sell a diverse range of financial instruments. These include stocks, options, futures contracts, foreign exchange, and cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
By operating across such a wide spectrum of markets, prop firms can identify and capitalize on many market opportunities while mitigating risk through strategic asset allocation and diversification.
Sophisticated Trading Strategies
Proprietary trading firms utilize diverse trading techniques such as day trading, swing trading, algorithmic trading, market making, and arbitrage. These strategies are carefully crafted to leverage market irregularities and fluctuations to achieve steady and sustainable profits.
Use of Advanced Technology
Proprietary trading firms are known for extensively using advanced trading technology and incorporating highly sophisticated software, trading platforms, and algorithms to maintain a competitive advantage. These firms frequently utilize high-frequency trading (HFT) and low-latency trading systems, which allow them to execute trades at incredibly rapid speeds, giving them a significant edge in the market.
Risk Management and Capital Allocation
Implementing effective risk management practices is a crucial factor in the success of proprietary trading firms. These firms meticulously establish and enforce stringent risk controls encompassing position limits, stop-loss orders, and thorough monitoring systems to mitigate potential losses effectively. Additionally, they carefully manage the allocation of capital to ensure optimal utilization of resources across various trading teams and strategies.
Trader Recruitment and Development
Proprietary trading firms frequently seek out experienced traders and furnish them with the necessary capital, tools, and technology for success. Additionally, they typically extend comprehensive training and mentoring initiatives to enhance traders’ abilities, ensuring that their team is well-prepared to navigate the intricacies of the market.
Profit Sharing Model
In numerous proprietary trading firms, traders receive compensation through a profit-sharing model, where they are entitled to a percentage of the profits they generate. This arrangement serves to align the traders’ interests with those of the firm, fostering a high level of motivation and incentivizing peak performance.
Flexible Trading Environment
Proprietary trading firms frequently provide traders with the flexibility of working from various locations, including the option to conduct remote trading. Additionally, traders at these firms have access to global markets 24/7, enabling them to capitalize on trading opportunities anytime. This flexible work environment appeals to a diverse group of traders, from seasoned professionals to up-and-coming talent.
How Proprietary Trading Firms Make Money

Proprietary trading firms, or prop firms, primarily make money by trading their own capital in the financial markets. They employ a variety of strategies and methods to capitalize on market opportunities, leveraging their expertise, advanced technology, and risk management skills. Here are the main ways prop firms make money:
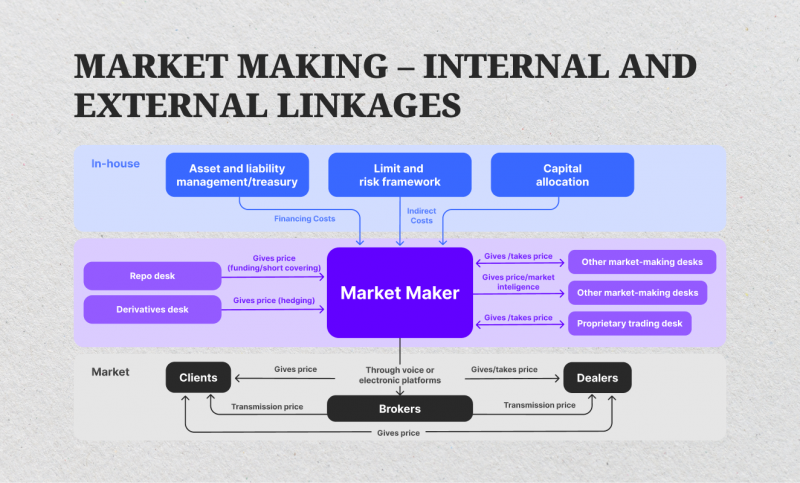
Market Making
Prop firms act as market makers, providing liquidity by quoting both buy and sell prices in a security or derivative. By continuously buying and selling, they profit from the bid-ask spread—the difference between the buying and selling prices.
Market-making requires advanced technology and quick execution to manage risks and capitalize on narrow spreads.
Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage trading involves taking advantage of price discrepancies between different markets or instruments. Prop firms use sophisticated algorithms to identify and exploit these minor price differences. This strategy can include statistical arbitrage, merger arbitrage, or cross-exchange arbitrage, allowing the firm to make risk-free or low-risk profits.
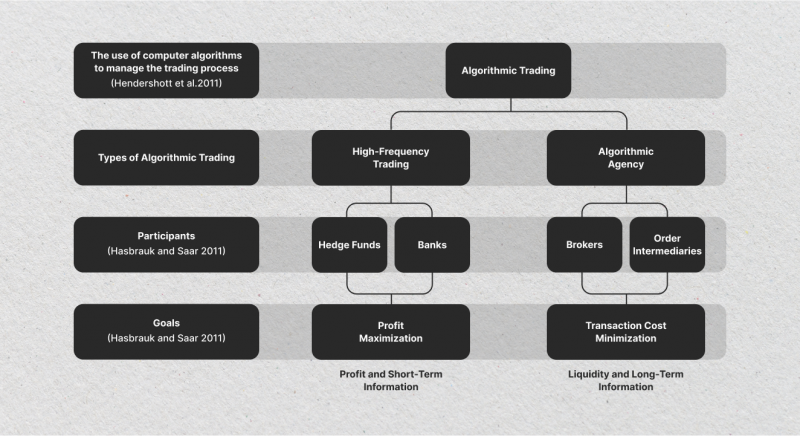
Algorithmic and High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
Prop firms often engage in algorithmic trading, where computer programs execute trades based on pre-set conditions, and high-frequency trading, which involves implementing many trades in fractions of a second. These strategies capitalize on rapid market movements and inefficiencies, requiring significant investment in technology and data infrastructure to maintain a competitive edge.
Directional Trading
In directional trading, firms take positions based on anticipated market movements, speculating on price increases (going long) or decreases (going short) of stocks, commodities, currencies, or other financial instruments. This strategy relies on market research, technical analysis, and trading insight to predict and profit from market trends.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage is a form of quantitative trading that uses statistical models to identify trading opportunities based on historical price relationships and patterns. By identifying pairs or groups of securities that are mispriced relative to each other, prop firms can enter offsetting positions to capture mean reversion when prices are correct.
Event-Driven Trading
Event-driven trading focuses on capitalizing on market movements triggered by significant events such as mergers, earnings announcements, regulatory changes, or geopolitical developments. Prop firms analyze how these events impact specific stocks or sectors and take positions accordingly, aiming to profit from the resulting price volatility.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders aim to make numerous small profits from minor price changes throughout the trading day. Prop firms use scalping by executing trades quickly and managing very tight risk parameters, often leveraging high-speed trading platforms to maximize the volume of profitable trades.
Options Trading and Hedging
Prop firms trade options to profit from market volatility and price direction or as a hedging tool to manage other positions. Strategies like straddles, strangles, and spreads allow prop firms to capitalize on expected price movements or volatility without owning the underlying asset.
Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading involves using complex mathematical models, algorithms, and statistical analysis to identify trading opportunities. Prop firms employ quants (quantitative analysts) who develop and refine trading models to systematically exploit inefficiencies in the market, often trading in large volumes to generate substantial profits.
Trading Derivatives
Derivatives trading, such as futures and CFDs (contracts for difference), allows prop firms to speculate on the future price movements of an underlying asset without owning it. This approach enables leveraged trading, enhancing profit potential while managing exposure through hedging strategies.
Risk Arbitrage
Risk arbitrage, often used in merger and acquisition scenarios, involves buying the target company’s stock while shorting the acquiring company’s stock. This strategy profits from the spread between the current trading price and the acquisition price, assuming the deal will go through as expected.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks to capitalize on expected price swings. Prop firms use technical analysis to identify market trends, reversals, and price patterns, allowing them to time entries and exits to maximize profit potential over the medium term.
Pairs Trading
Pairs trading involves taking offsetting long and short positions in correlated securities. When the relationship between the pairs diverges from historical norms, the firm profits from the expected convergence. This strategy is market-neutral and can generate profits regardless of broader market direction.
Trading in Volatility Markets
Volatility trading strategies capitalize on market uncertainty and rapid price movements, often using instruments like VIX futures, volatility ETFs, or options. Prop firms use these strategies to profit from market conditions where prices fluctuate sharply, regardless of the direction.
How to Start a Prop Trading Firm

Starting a proprietary trading firm is a complex process that requires the effective resolution of a number of key issues and consideration of the main aspects of doing business in the provision of services on financial markets. As a type of brokerage business, starting your own brokerage firm covers a full range of legal, technical, financial, and other elements, including a detailed analysis that determines the legitimacy, stability, and reliability of such a structure.
Among the main nuances to consider in the process of starting a prop firm are the following:
1. Determining the Way of Starting Prop Trading Firm
The current conditions of the brokerage solutions market environment and the level of financial support for startups have led to the creation and development of a number of methods that provide a quick and convenient way of starting a brokerage firm of any kind.
For example, when starting a prop trading firm, it is possible to take all obligations and develop a product from scratch or use specialized services within the framework of a modern white-label solution, allowing a quick entry into the required market. On the other hand, many people also prefer the turnkey development model, where a vendor company creates the required product on its own and brings it to the market.
2. Market Research and Planning
Conducting market research and strategic planning is essential for any business aiming to succeed. Start by pinpointing your target audience, which involves understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Following this, it is crucial to evaluate your competitors and stay informed about industry trends to identify opportunities and threats in the market. Establishing a clear niche and articulating your unique selling proposition (USP) will help differentiate your business from others in the field.
Developing a comprehensive business plan is a vital step in this process. This plan should encompass your vision and mission statements, which outline the core purpose and values of your business. Additionally, it should include both short-term and long-term objectives to guide your growth. Finally, financial projections and an assessment of funding requirements will provide a roadmap for your financial strategy, ensuring that you are prepared for the challenges ahead.
3. Legal Structure and Compliance
It is paramount to determine the appropriate legal structure for your business, whether it be a Limited Liability Company (LLC), a corporation, or another form. Following this, you must register your business name and secure any required licenses to operate legally. A thorough understanding of the regulatory landscape ensures your business adheres to all relevant laws and regulations.
Beyond that, it is imperative to create legal contracts and agreements tailored for traders to protect your interests and clarify expectations. Establishing compliance protocols and risk management procedures will further safeguard your business, ensuring you are prepared to navigate any potential legal challenges while maintaining operational integrity.
4. Secure Funding and Capital
Acquiring financial resources and capital is essential for any business endeavor. This can be achieved through various avenues, including personal savings, attracting investors, or obtaining loans. Each funding source has advantages and considerations, which must be carefully evaluated to align with the business’s goals and financial strategy.
It is necessary to accurately assess the capital needs of the business to ensure sufficient funding for operations and growth. Establishing dedicated bank accounts and implementing robust financial management systems are vital to maintaining financial health and transparency. These measures facilitate effective tracking of income and expenses and support informed decision-making as the business evolves.
5. Technology Infrastructure
Establishing a solid technology infrastructure is essential for any trading operation. This begins with selecting an appropriate trading platform, such as cTrader or MetaTrader, which will serve as the foundation for executing trades. Additionally, it is crucial to develop or integrate a comprehensive trader’s room, also known as a client portal, to facilitate seamless interactions between the traders and the platform.
Furthermore, setting up effective risk management and reporting systems is vital to monitor and mitigate potential risks associated with trading activities. Implementing back-office and compliance software will ensure that all operations adhere to regulatory standards and maintain operational efficiency. Lastly, prioritizing robust cybersecurity measures is imperative to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the trading environment.
6. Recruitment and Onboarding of Traders
Attracting and integrating traders into an organization involves several vital components. Initially, it is essential to establish precise profiles for traders, outlining the necessary skills and qualifications that align with the company’s objectives. Following this, effective recruitment strategies must be devised, utilizing channels such as online advertisements and referral programs to reach potential candidates.
Once suitable candidates are identified, implementing comprehensive onboarding and training initiatives is crucial to equip new traders with the knowledge and tools they need to succeed. Additionally, designing competitive compensation structures, including profit-sharing arrangements and salary packages, will help to motivate and retain top talent within the trading team.
7. Marketing and Client Acquisition
Establishing a proprietary trading firm requires a comprehensive marketing and client acquisition approach. This involves developing effective branding and positioning strategies that resonate with the target audience. Implementing digital marketing techniques, such as search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and leveraging social media platforms, is essential for enhancing visibility and attracting potential clients.
In addition to digital efforts, fostering networking opportunities and forming strategic partnerships can bolster client acquisition. Creating a vibrant community of traders and investors enhances engagement and builds trust and loyalty among clients. This multifaceted strategy is crucial for a proprietary trading firm’s long-term success and growth.
8. Developing Trading Strategies and Risk Management
Effective trading strategies and robust risk management practices are essential to successful trading operations. Defining and approving specific trading strategies that align with market conditions and organizational goals is crucial. Additionally, establishing clear risk management guidelines and limits will help mitigate potential losses and ensure that trading activities remain within acceptable risk parameters.
Monitoring trader performance is also vital to uphold compliance with established strategies and risk management rules. This involves tracking individual trader outcomes and enforcing adherence to the defined protocols. Furthermore, developing a comprehensive performance evaluation and feedback mechanism will facilitate ongoing improvement and adaptation, ensuring traders receive constructive insights to enhance their skills and decision-making processes.
9. Ongoing Operations and Growth Strategies
Day-to-day management and operational activities are essential for maintaining organizational efficiency and effectiveness. This includes the routine oversight of business functions and the implementation of strategies to enhance overall performance.
The company is focused on entering new markets and diversifying its range of trading instruments to foster growth. Additionally, a commitment to ongoing improvement is evident through investments in technology upgrades and the professional development of traders, ensuring that the organization remains competitive and responsive to market changes.
Conclusion
Forming a proprietary trading firm is a complex yet rewarding endeavor that requires meticulous planning, strategic analysis, and a thorough understanding of the financial markets. Each step is critical in setting up a successful prop firm, from defining your business model and securing capital to navigating regulatory landscapes and implementing advanced trading technologies.
Launching a prop firm is about capitalizing on market opportunities and building a solid foundation supporting growth and resilience. With the right approach, you can create a prop trading business that thrives in the dynamic world of financial trading, offering both traders and the firm a pathway to success.
FAQs:
What is a proprietary trading firm?
A proprietary trading firm, or prop firm, is a financial institution or private company that trades various financial instruments using its capital rather than client funds.
What capital do I need to start a prop firm?
The required capital varies widely depending on your business model, trading strategies, and operational scale. A small prop firm can start with a few hundred thousand dollars, while larger firms may require millions to support more complex trading strategies and attract top traders.
Do I need regulatory approval to start a prop firm?
Yes, regulatory approval might be required depending on your location and the types of financial instruments you trade. Research your jurisdiction’s licensing requirements and consult legal experts to ensure compliance with local financial regulations.
What technology do I need to set up a prop firm?
You’ll need a robust trading platform, risk management tools, market data feeds, and high-speed internet connections. Additionally, investing in algorithmic trading software and backtesting tools is essential for firms relying on automated or high-frequency trading strategies.
How do prop firms make money?
Prop firms make money by executing profitable trades using their own capital. They employ various trading strategies, such as day trading, swing trading, arbitrage, algorithmic trading, and high-frequency trading, to capitalize on market opportunities.