Roth IRA Guide: What It Is and What You Need to Know.
Sep 13, 2023

Are you looking to invest in a way that will help you save for retirement? A Roth IRA account may be the answer.
This guide provides an overview of what a Roth IRA is and how it works, as well as guidelines for making contributions and understanding income limits and withdrawal rules. We’ll also compare the advantages of a Roth versus a traditional IRA so you can make an informed decision about which type of IRA is best for you.
Key Takeaways:
- A Roth IRA allows users to save money on a tax-deferred basis.
- With a Roth IRA, savers have the option to open an account with an online brokerage or robo-advisor, a bank or credit union, or opt for a self-directed IRA if they prefer more control over their investments.
- The main eligibility requirement for Roth IRAs is earning an income, which can come from working or other sources such as untaxed combat pay and alimony.
- The choice of a particular IRA depends on the individual’s income level, age, and expectations for future income growth.
What Is a Roth IRA?
A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account available for US citizens that allows them to save money on a tax-deferred basis. Contributions to your Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning they don’t qualify as pre-tax deduction.
The funds you contribute to a Roth IRA grows tax-free, so when you reach retirement age, you won’t owe any income taxes or penalties when withdrawing. This makes a Roth IRA ideal for those who expect their income taxes to be higher in retirement.
When you invest in a Roth account, you can choose from a diverse range of securities, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs. The choices available to you will vary based on your unique investing approach, inclinations, and the options provided by the financial institution with which you opened your account.
How Does a Roth IRA Work?
Roth IRAs are funded with post-tax dollars, meaning that there is no tax break or other immediate benefit for contributing. However, the advantage comes later on: withdrawals taken from the account after age 59½ are not taxed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Furthermore, because taxes have already been paid on contributions to a Roth IRA, those funds can be withdrawn at any time without incurring any additional taxes or penalties. This means that all of the investment growth earned on the account is tax-free, a major advantage over accounts funded with pre-tax money.
The funds within the account can be used to purchase various types of investments, such as stocks and bonds, allowing you to diversify your portfolio. Additionally, you can also use a Roth IRA to purchase real estate or other types of alternative investments like cryptocurrency. Whichever investment route you choose, the tax-free growth within the account will help give you a head start on building wealth for retirement.
What Are The Eligibility Requirements for Roth IRAs?
To contribute to a Roth IRA, the primary requirement is having earned income.
- Have an earned income.
Earned income can be obtained in two ways.
- Firstly, you can work for someone else who compensates you, which includes commissions, tips, bonuses, and taxable fringe benefits. This applies to both W-2 employees and 1099 contractors.
- Secondly, if you run your own business or farm or have certain other types of income, they can also be treated as earned income for the purpose of contributing to a Roth IRA. These additional types of income include untaxed combat pay, military differential pay, and taxed alimony.
What is Unearned Income?
Any type of passive investment income from securities, rental property, or other assets counts as unearned income. This includes income generated from dividends, interest, and capital gains. It’s important to note that unearned income cannot be contributed to a Roth IRA due to tax regulations.
In addition to passive investment income, there are several other common types of income that do not count towards certain financial considerations. These types of income include alimony (which is nontaxable), child support, Social Security retirement benefits, unemployment benefits, and wages earned by penal institution inmates. It’s crucial to be aware of these exclusions when planning your financial strategies and contributions.
What Are the Age Restrictions for a Roth IRA?
There are no age restrictions or limitations when it comes to making contributions to a Roth IRA. For instance, even a teenager who has a part-time job can open and fund a Roth IRA, possibly as a custodial account if they are underage. On the other hand, an employed individual in their 70s can also continue contributing to a Roth IRA.
Roth IRA Rules
When it comes to the tax-free retirement income from a Roth IRA, there are a few important considerations to keep in mind. Before you decide to invest, it’s essential to understand three key topics: contribution limits, income limits, and withdrawal limits.
These factors play a crucial role in determining how much you can contribute, how much income you can earn, and when and how you can withdraw funds from your Roth IRA.
Rules for Contributions
When it comes to contribution limits in 2023, both Roth IRAs and traditional IRAs appear to be on equal footing.
The annual contribution limit remains at $6,500 for individuals under 50 or $7,500 for those over 50. However, it’s important to note that your annual earnings may have an impact on your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA, potentially reducing or even eliminating your capacity to meet the maximum limit. It’s crucial to consider this factor while planning your retirement savings strategy.
Rules for Income Limits
The IRS has established income limits for Roth IRA contributions. In other words, individuals who earn a certain amount of money within their tax year are not eligible to contribute more than the specified limit:
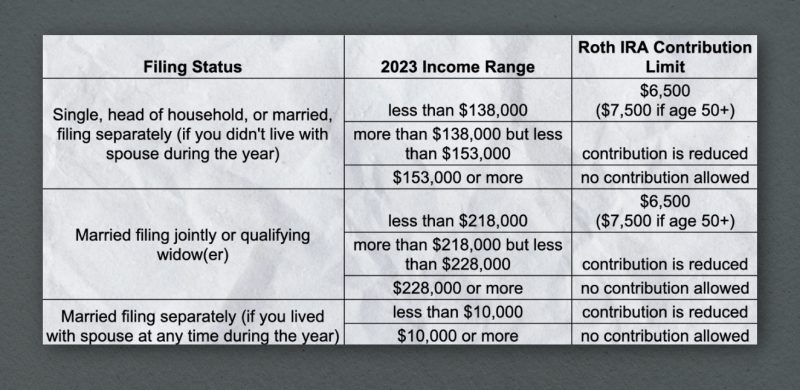
It is also important to be aware that the contribution limits for IRAs are the same regardless of whether you have a traditional or Roth IRA. This means that when calculating your total annual contributions across multiple accounts, you must take into consideration the maximum limit and not exceed it. This means that if you own both types of IRAs, the total contributions for all of them combined must not surpass the maximum limit.
For example, if your income allows only a partial Roth IRA contribution, you can make up for the difference by utilising a traditional IRA. This option allows you to contribute more towards your retirement savings while ensuring that your total contributions do not exceed the overall IRA contribution limit for the year. By strategically combining both types of IRAs, you can optimise your retirement planning and maximise your potential savings.
If you’re ineligible for a Roth IRA, you can consider contributing to a traditional IRA instead. Later, you can convert it to a Roth IRA using a technique called the backdoor Roth (also known as a Roth IRA conversion). This conversion enables you to transfer funds from your traditional IRA to a Roth IRA but remember that you’ll be required to pay taxes on the amount beforehand.
Withdrawal Rules
Roth IRAs are unique in that these accounts offer you tax free withdrawals. You can access your contributions without owing any taxes or facing penalties for essentially whatever purpose.
However, withdrawals on earnings work differently and depend on the account holder’s age as well as whether they meet the five-year rule.
If you meet the five-year requirement:
- Under 59 1⁄2 – Earnings may be subject to taxes and a 10% penalty, however, these can be avoided by using the money for a purchase of a first place of residence or permanent disability.
- Over 59 ½ – Earnings are not subject to taxes or penalties.
If you don’t meet the five-year requirement:
- Under 59 1⁄2 – Earnings are subject to taxes and potentially a 10% penalty, although this can be avoided if the money is used for a specific purpose, such as a purchase of a first place of residence or education expenses.
- Over 59 ½ – Earnings are subject to taxes but not penalties.
Do I Have the Option of Withdrawing Without Penalties?
There are certain cases when you may be able to take out money from your retirement account without incurring a penalty. These include using the funds for college tuition, up to $5,000 to cover adoption costs, paying medical bills and health insurance premiums during joblessness, as well as buying a first home with a maximum of $10,000. It is important to note that the money withdrawn is still subject to income taxes if it has yet to be taxed.
Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA
When deciding between different IRA accounts, it’s important to remember that the Roth is based on post-tax income. This means that you won’t have to worry about paying taxes on withdrawals during retirement, whereas with a traditional IRA, your contributions are tax-deductible, but withdrawals are taxed at ordinary income tax rates.

The choice between the two ultimately comes down to your individual circumstances, such as income level and whether you’re expecting a significant increase in your future income. In general, Roth IRAs tend to be better for younger individuals who expect their incomes to rise significantly over time and would benefit from having tax-free retirement savings. For those with lower income levels or near retirement age, traditional IRAs may provide more tax savings in the short term but could also result in hefty taxes when withdrawals are made.
It’s important to consider both options carefully before making a decision. Consulting with an experienced financial planner or tax professional can help you determine which option is best for your unique situation.
Where Can I Open a Roth IRA Account?
When it comes to opening a Roth IRA, you have multiple options available. One option is to open an account with an online brokerage, which usually offers a convenient wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs.
Another option is to choose a robo-advisor, which utilises automated algorithms to manage your investments. This can be a great choice if you prefer a hands-off approach to investing. Robo-advisors typically offer diversified portfolios tailored to your risk tolerance and investment goals.
If you prefer a more traditional approach, you can open a Roth IRA with a bank or a credit union. With these institutions, you have the option to place your Roth contributions in a savings account or a certificate of deposit (CD). This can be a good choice if you prioritise safety and stability.
For those looking for more flexibility and control over their investments, a self-directed IRA is an option to consider. With it, you have the freedom to invest in alternative assets such as cryptocurrencies, gold, and real estate. This can be appealing if you have a deep understanding of these markets and believe in their potential for growth.
Overall, the key is to choose the option that aligns with your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferences. Each option comes with its own set of advantages and considerations, so it’s important to do research and talk to an investment professional if needed.
Last Words
The tax benefits of a Roth IRA are undeniable, but it’s important to understand the requirements before making any decisions. Every investor’s situation is unique, so it’s essential to weigh up your options and consider the long-term implications before deciding which account works best. Being aware of contribution limits, income limits, and withdrawal rules will help you make an informed decision about how to best manage your retirement savings.
In addition to being used for retirement, Roth IRAs offer an opportunity for younger investors to start investing early and benefit from tax-free growth of their money over time. For those in a high tax bracket, Roth IRAs are a great way to save money on taxes while still investing in their retirement.
Taking full advantage of the benefits a Roth IRA offers is an excellent way to set yourself up for a secure financial future.
FAQs
What are the requirements for opening and contributing to a Roth IRA?
To be eligible to open and contribute to a Roth IRA, you must have taxable earned income (including wages, salaries, bonuses, tips and commissions) or net earnings from self-employment. Additionally, your modified adjusted gross income must not exceed the imposed limit as determined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and you cannot be older than 70 1⁄2 years of age.
What happens if I exceed the Roth IRA contribution limit?
If you exceed the contribution limit for your Roth IRA account, you will be subject to a 6% excise tax on the excess amount. You can avoid this penalty by withdrawing any contributions in excess of the allowable amount before filing your taxes. To do so, contact your financial institution and request a distribution of funds from your Roth IRA. The withdrawal should be made before April 15th of the tax year in which you made the contribution.
Can you tell me how to set up a Roth IRA?
To start investing in a Roth IRA, you will need to open an account with a financial institution or brokerage firm. When opening the account, be sure to specify that it is a Roth IRA, as there are different types of accounts available. You can then fund your Roth IRA with after-tax contributions and begin investing in different types of investment instruments. You can also work with a financial advisor to develop customised investment strategies to meet your specific goals.




