The Future of Fintech in 2024: Forecast, Trends & Risks
Aug, 21, 2024

Fintech is a contraction of finance and technology and means the use of technology in the delivery of financial services. The fintech industry has expanded significantly over the last ten years due to the development of AI, blockchain, big data, and smartphone use.
Today, fintech is at the dawn of the new wave of disruption and innovation that will redefine the ways consumers and businesses approach their finances. This article presents the outlook of the major fintech trends in 2024 and identifies the threats that may be encountered in the field.
Growth Forecasts
Fintech has become one of the fastest-growing sectors globally. According to McKinsey’s research, between 2023 and 2028, revenues in the fintech sector are predicted to grow at a rate nearly three times faster than those in the traditional banking industry. Investment is expected to grow to over $15 billion globally by 2024 as new technologies and changing consumer behaviors continue to shape the financial services ecosystem.
In 2024, the largest fintech hubs will continue to be centered in technology epicenters like Silicon Valley and Shanghai. However, emerging markets in Latin America, Africa and Southeast Asia will also present major growth opportunities.
Key Fintech Categories
Fintech encompasses a diverse range of subsectors serving both consumer and business financial needs. Below is an overview of the key fintech categories that will drive most of the sector growth towards 2024:
Digital Payments
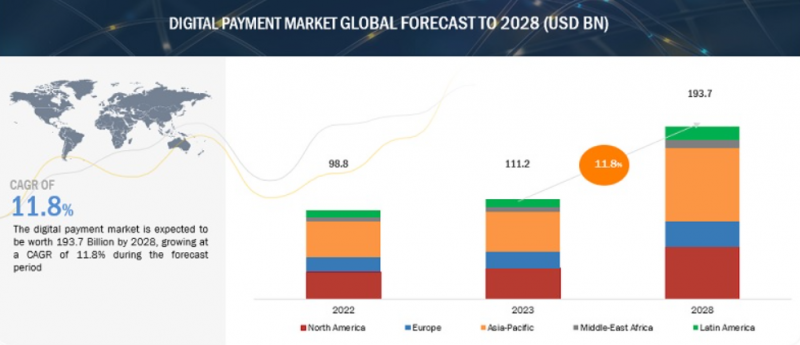
Digital payments can be described as the utilization of technology in the payment process that does not involve the use of cash or checks. This includes online transactions, mobile money, person-to-person transactions and POS systems. Market and Markets estimated that the total value of the digital payment market in revenues in 2023 exceeded $111.2 billion. The digital payments market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8% between 2023 and 2028, reaching a valuation of approximately $193.7 billion by the end of the projection period.
Growth drivers:
- Surging ecommerce and mcommerce transactions
- Government support for cashless initiatives
- Enhanced payment infrastructure in developing countries
RegTech
Regulatory technology (RegTech) refers to the use of technology to help businesses more efficiently comply with regulations and lower compliance costs. The global RegTech market is expected to grow from $12.82 billion in 2022 to 85.92 billion by 2032 according to Fortune Business Insights.
Growth drivers:
- Increasing regulatory requirements globally
- Rising need to automate compliance processes
- Emergence of technologies like AI and blockchain for regulatory compliance
InsurTech
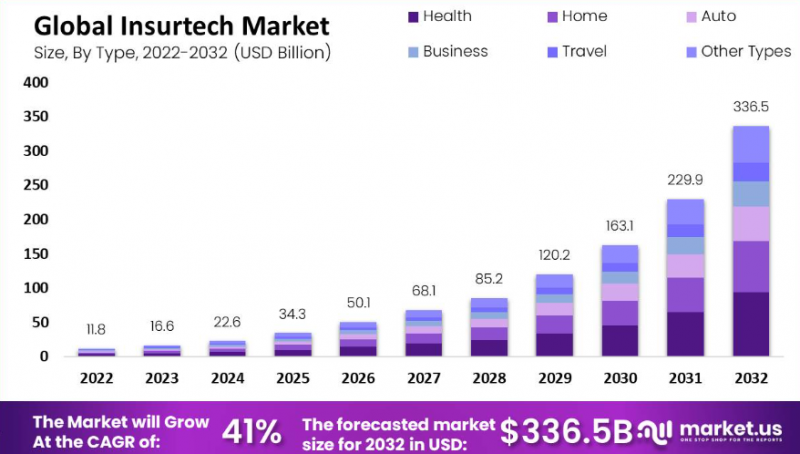
Insurtech refers to the use of technology innovations designed to squeeze efficiency and savings from the current insurance industry model. Market.US estimates the insurtech market will grow from 16.6 Billion billion in 2023 to 336.5 billion in 2032. According to estimates, this market will grow at the fastest rate – 41.0% – between 2023 and 2032!
Growth drivers:
- New data sources providing insight into customer behavior and risk models
- Increasing Internet and smartphone penetration in emerging markets
- Need for personalized and on-demand insurance
WealthTech
Wealth tech refers to the use of technology to improve and automate financial advice capabilities as well as investment management and trading processes. According to FMI, the global wealthtech market is expected to grow from $5.42 billion in 2023 to $26.1 billion by 2033.
Growth drivers:
- Rising robo-advisory services powered by AI and ML
- Increasing high net worth individuals globally
- Growing demand for personalized wealth management
Key Fintech Trends in 2024
Underpinning the growth across fintech sectors are several dominant technology trends that are shaping innovation and disruption in 2024:
Test Automation in Fintech
In the context of fintech innovation towards 2024, test automation services play an instrumental role in accelerating development cycles and mitigating business risks from rapid changes.
As mentioned in the legacy barriers section, incumbent financial institutions often rely on complex, outdated systems that require extensive testing with any upgrades to ensure stability and compliance. Manual testing alone cannot match today’s deployment velocities.
Likewise, fintech disruptors leveraging modern cloud-native stacks still require reliability and safeguards before pushing updates to production.
Test automation is the technology practice of scripting tests that simulate user flows across software to automatically validate functionality and catch regressions. This is accomplished by leveraging frameworks like Selenium, Cypress and proprietary testing tools.
Test automation will become a mandatory discipline for both established institutions and emerging disruptors to efficiently build reliable solutions while staying ahead of customer demands and competitor offerings.
AI-Powered Solutions
The capabilities of AI technologies like machine learning, neural networks and natural language processing will improve significantly by 2024. These advancements will allow fintech providers to deliver highly personalized and predictive services catered to each customer’s specific financial needs and behaviors.
Use cases include:
- Predictive analytics for wealth management
- Intelligent chatbots for customer service
- Automated fraud monitoring and risk assessment
- AI-powered credit underwriting models
According to Allied Market Research, global AI in fintech market revenue will grow from 8.23 billion in 2021 to 61.30 billion by 2031.
Embedded Finance
Embedded finance involves the integration of financial services like payments, lending and insurance directly into non-financial environments. For example, rideshare platforms or retailer checkout flows can be enabled to facilitate financial transactions natively.
By eliminating friction across user journeys, embedded finance will be instrumental in driving higher conversion and engagement across various industries.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology will move past the hype phase into more mainstream enterprise adoption across fintech. According to Gartner, blockchain business value is forecast to surpass $176 billion billion by 2025. Companies will leverage blockchain solutions to enable:
Faster cross-border payments
- More efficient KYC/AML verification
- Peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries
- Tokenization of assets
Open Banking Ecosystems
Open banking refers to the secure sharing of user financial data between banks, fintechs and third-party providers through APIs. By linking into banking data, fintechs can build innovative products and services.
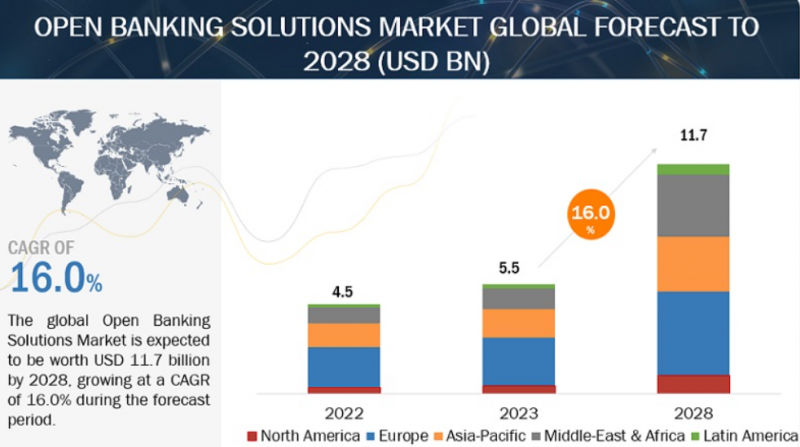
According to Markets and Markets estimates, open banking platform revenues will grow from $5.5 billion in 2023 to $11.7 billion by 2028 globally as more markets implement open banking legislation and adoption accelerates.
Key Risks and Challenges
While the fintech sector outlook appears overwhelmingly positive towards 2024, there are still several risks and challenges that could impact the pace of innovation.
Cybersecurity Threats
As digital banking and cashless payments grow, cyberattacks aimed at financial institutions and fintech infrastructure will increase in frequency and sophistication. Attackers will leverage more advanced techniques like AI and quantum computing to carry out fraud, ransomware campaigns or critical infrastructure disruption.
To counter these threats, fintech players will need to prioritize cybersecurity investments and resiliency measures across their systems.
Data Privacy Regulations
With regulators responding to high-profile cases of user data misuse, new privacy laws are emerging globally, giving customers more control over their personal data. These include “Right to be Forgotten” requests and restrictions on using customer data for marketing or analytical purposes without explicit consent.
Navigating this complex regulatory environment poses technological and operational challenges for fintechs that rely extensively on customer data to deliver personalized offerings.
Legacy Technology Barriers
Banks and insurers looking to innovate within their existing systems face barriers to integrating with modern solutions because of outdated, complex legacy infrastructures. Rip-and-replace overhauls carry execution risks and heavy costs. Upgrading core banking or policy admin systems can take years to implement due to extensive integrations.
To overcome these constraints, incumbent institutions will lean more on IT services partners over the next few years to help bridge legacy platforms with the agility required to collaborate with fintech disruptors.
Talent Shortages
The fintech sector faces immense competition for high-skill technology talents like software engineers, data scientists and designers. The pandemic accelerated demand for these scarce digital skills across most industries.
As a result, fintech hiring managers battle rising salary expectations and attrition rates in order to attract and retain the top talent necessary to compete and foster innovation cycles.
Final Thoughts
Fintech companies are set for further development in both the application of core technologies and the added financial value by 2024. Traditional financial services are evolving from AI for tailored banking to blockchain for secure global trading. This shift is also creating related trends such as embedded finance to integrate transactions into other sectors that have not been connected before.
However, there are challenges such as cybersecurity, data privacy, legacy constraints and talent scarcity that could slow down the pace of new fintech solutions coming to the market. Those companies that are able to address these challenges early on while at the same time taking advantage of the enablers such as test automation will be in a vantage position to capture the market share in the periods up to and including 2024.
The role of fintech in the future still holds great promise for enhancing financial performance around the world. Financial services are still central to the overall economy, which means that the trends in the advancement of fintech in 2024 will be of much broader impact as innovation brings efficiency, productivity and growth to various industries.




