Best Decentralized Crypto Exchanges In 2023
Apr 07, 2023

Today, we have countless opportunities to convert our fiat currency to cryptocurrencies and vice versa, but in the beginning, when these digital assets were still unfamiliar and strange for the masses, purchasing cryptos or exchanging them was not so simple.
Quick fact: the first ever transaction of purchasing crypto assets with fiat occurred on October 12, 2009, when New Liberty Standard bought a total of 5050 BTC from Sirius for an amount of $5.02 through PayPal.
This operation established that approximately 1010 BTC was equivalent to $1, which actually caused the first price increase of Bitcoin and gave birth to crypto investments.
Today, from so many options of centralized or decentralized crypto exchanges, it’s even getting challenging to pick the right place to purchase cryptos, swap them, or trade with them. However, that’s why we’re here.
This article will give you a detailed analysis of DEXs and name the top decentralized exchanges to perform your crypto-related operations.
Key Takeaways
- Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are a type of cryptocurrency exchange that allows users to trade digital assets without a central authority or intermediary.
- There are three main categories of DEXs: automated market makers (AMMs), order book-based exchanges, and DEX aggregators that combine liquidity from multiple sources.
- Compared to centralized exchanges, DEXs typically offer low trading fees and safer transactions since users retain control of their assets.
- Popular DEXs include Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance, and dYdX, among others.
- While DEXs have grown in popularity, they still face challenges such as liquidity fragmentation and slower transaction time.
What Is A Decentralized Crypto Exchange?
First, let’s discuss what a decentralized crypto exchange itself is. Officially, a decentralized exchange (DEX) is a P2P marketplace that facilitates users’ direct exchange of crypto assets. DEXs use smart contracts or pieces of code that may run autonomously, to finalize trades.
Private keys for each party’s wallet remain securely in the hands of the respective parties, meaning no personal information is exchanged. There are several types of decentralized exchanges, so let’s break them down first.
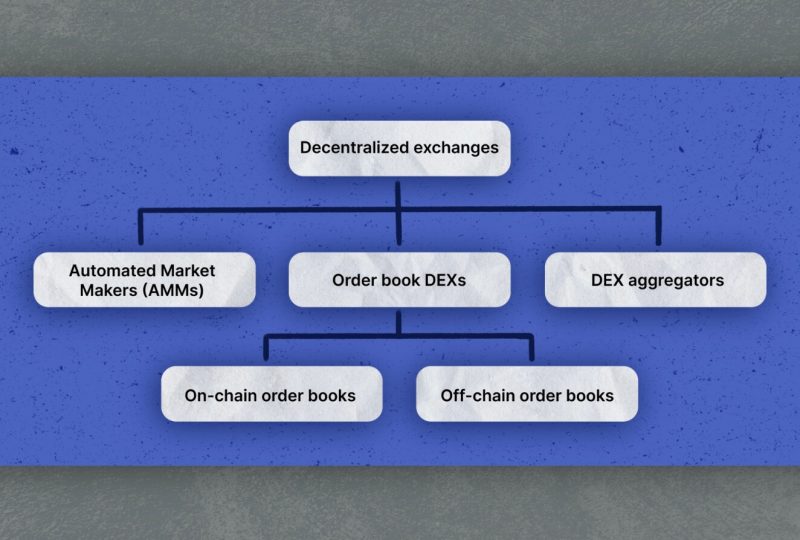
Types Of Decentralized Exchanges
DEXs for trading cryptocurrencies are plentiful. However, they may be broken down into three broad categories: automated market makers, order book DEXs, and DEX aggregators. Each DEX variant facilitates direct crypto trading, but they vary significantly in vital points.
- Automated Market Makers
AMMs, or automated market makers, tackle the crucial issue of DEX liquidity head-on. In other markets, the matching process facilitates trades between buyers and sellers. However, AMMs can make instantaneous trades because they use liquidity pools. The liquidity provider receives compensation, typically in the form of transaction fees, for their participation in the pool.
One major drawback of AMMs is slippage, which occurs when the liquidity pool is insufficient to handle the trades. Slippage may result in increased fees for purchasers, and uneven trading between two trading pairs might also cause temporary loss for a liquidity provider.
- Order Book DEXs
Order book DEXs keep track of all active orders in a booking system, as the name suggests. These orders specify the maximum and minimum prices a buyer or seller is ready to pay and accept, respectively, for a certain item.
Order book DEXs can be either off-chain or on-chain. Keeping assets in wallets while placing open orders on the blockchain is made possible by on-chain order books.
Orders are stored in off-chain order books, and the blockchain is only used for transaction settlement. The order books that exist off-chain are typically more efficient and cheaper to use. However, when dealing with high numbers of trades, order book DEXs frequently experience liquidity issues.
- DEX Aggregators
DEX aggregators utilize several protocols and strategies to solve the problem of low liquidity. By relying on a few DEXs for their liquidity, businesses can keep their swap fees low, improve the quality of their token products, and lessen the likelihood of slippage.
Some of these DEXs incorporate assets from centralized platforms to their liquidity pools to further solve price and transaction failure issues. Yet, they are still noncustodial through having various integrations with different CEXs.
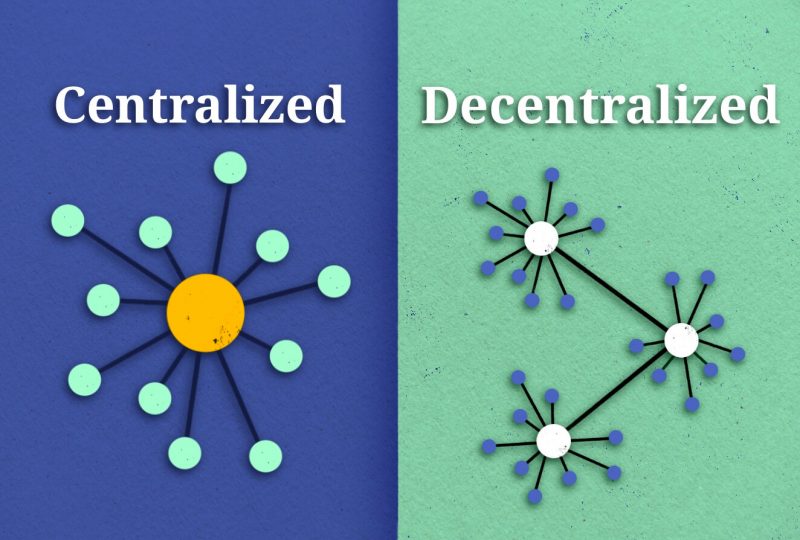
Centralized VS Decentralized crypto exchanges
To fully acknowledge the importance of decentralized exchanges, it’s essential to compare them to their primary opponent – centralized crypto exchange. What’s the difference?
- Safety
While centralized crypto exchange systems comply with stringent security measures, decentralized exchanges are safer since they do not need users to transfer funds into intermediary accounts, which are prime targets for cybercriminals. A crypto trader’s funds and all transactions are entirely under his control while using a self-custody wallet.
- Trading Fees
DEXs do not have transaction fees like centralized exchanges because they do not use third-party exchange services. Due to the absence of middlemen, transactions conducted via decentralized exchanges are less expensive than those conducted via centralized platforms.
- Adoption
Although centralized exchanges have a larger user base due to their earlier market entry, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are quickly gaining traction among crypto traders. They are having a significant impact on the cryptocurrency exchange industry.
- Control
Peer-to-peer systems used by decentralized exchanges allow users greater agency than those of controlled exchanges. The popularity of DEXs can be attributed to their offering more user privacy than centralized exchanges. Therefore, the vast majority of crypto traders prefer trading on DEXs.
To sum up, the choice between a centralized and decentralized exchange comes down to two factors: convenience and security. A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a great option for traders who want reduced costs and more autonomy over their money.
Top 10 Decentralized Exchanges
Now, let’s talk about the 10 top decentralized exchanges and discuss their pros and cons.

1. dYdX
dYdX is a DEX where users may buy, sell, and trade over 35 different cryptocurrencies in perpetuity, including Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Dogecoin (DOGE), and Cardano (ADA). In terms of trading volume and market share, it is among the largest decentralized exchanges in the world.
While dYdX’s DEX is similar to Uniswap or SushiSwap, it was built with perpetual trading in mind. Perpetuals, an abbreviation for “perpetual swap trading contract,” are derivative or financial instruments derived from another asset’s value. Like futures and options, perpetual allows investors to wager on an asset’s potential growth in value. Unlike futures and options, the term “perpetual” describes swaps since they never end.
dYdX does not use an AMM to power its exchange. Instead, a classic order book + matching approach is used to fulfill the needs of large-scale traders. Despite dYdX’s specialized trading model, it has become one of the industry’s leading exchanges thanks to its accessibility to both institutional and retail traders.

2. Uniswap
Uniswap is an ERC20 token exchange system built on the Ethereum blockchain. Uniswap is a community service that aims to eliminate the need for platform fees and intermediaries when trading tokens. Another difference between Uniswap and other exchanges is that instead of matching buyers and sellers to set prices and complete trades, a simple arithmetic equation and pools of tokens and ETH are used.
Uniswap was the first to adopt the Automatic Market Maker model, wherein users deposit Ethereum tokens into “liquidity pools,” and prices are determined by algorithms (unlike order books, which match bids and offers on a centralized exchange like Coinbase) based on supply and demand.
Users can earn prizes and facilitate peer-to-peer trading by contributing tokens to Uniswap’s liquidity pools. Tokens (using Ethereum’s ERC-20 protocol) can be created and listed by anybody, anywhere in the world, and tokens can be supplied to liquidity pools by anyone.
3. Curve Finance
The Curve Finance protocol was developed with stablecoin liquidity in mind to offer more consistent interest rates without requiring investors to keep a highly speculative asset. Since its debut, Curve has provided traders with high volumes of liquidity at reasonable costs and with minimal slippage. Over 33 distinct liquidity pools are currently available on Curve, each offering returns that can fluctuate according to the types and amounts of assets included in the pool.
The CurveDAO is a vital component of the Curve ecosystem. Curve Finance is managed by the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Curve, headquartered in Aragon. All votes are counted, although those cast earlier in the voting period are given more weight.

4. PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap is an Ethereum-based decentralized cryptocurrency exchange built on the BSC Chain. Users can freely trade tokens that adhere to the BEP-20 standard.
PancakeSwap also uses an automated market maker (AMM) methodology, meaning market participants in the AMM framework transact in digital assets via permissionless liquidity pools.
Depositors receive LP (liquidity provider) tokens for their contributions to these liquidity pools. They are compensated monetarily for using their assets in the loan process. However, there is a cost associated with accessing this liquidity through the DeFi platform. The contributors to the pool are eventually reimbursed for this fee. A small portion of these funds is set aside in the PancakeSwap treasury for future platform upkeep.
You can make money by exchanging LP tokens. Moreover, CAKE, PancakeSwap’s native BEP-20 token, can be farmed in an alternative liquidity pool for rewards. Plus, PancakeSwap features SYRUP pools where staking rewards are even higher.

5. Kine Protocol
Kine Protocol is an open-source, Ethereum-based platform for decentralized derivatives trading. Its ultimate goal is to facilitate fast, transparent, and easy derivatives transactions for its users while also creating a market with infinite liquidity.
The cutting-edge peer-to-peer pool engine of the industry facilitates all transactions by optimizing leverage and cross-margin to achieve maximum capital efficiency. Kine is now the best user-experienced decentralized derivatives trading platform since it has established a multi-chain configuration to accommodate a wide range of user requirements.

6. 1inch
The 1inch decentralized application is a DEX aggregator that looks over several DEXs and hundreds or thousands of liquidity providers to find the lowest price for a trade. The dApp facilitates the exchange between two parties after they identify the cryptocurrencies they wish to purchase and sell. It’s similar to services that search many airlines and lenders to find you the best price on a car loan or plane ticket.
Initially, 1inch’s dApp only looked at a few DEXs for available bargains. Today, 1inch searches liquidity providers on the Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon blockchains with a Pathfinder algorithm to find the best price. The dApp is backed by the 1inch Network’s liquidity solution, which lets you stake cryptocurrency for transaction fees.
When purchasing or selling cryptocurrency, customers can establish a limit order price of 1inch. The deal is put on hold until the target price is reached, at which point it is automatically completed. With 1inch’s limit order solution, you can stipulate various non-price constraints for the order’s execution.
7. Covo Finance
Users of Covo Finance, a fully decentralized spot and perpetual swap exchange, can buy and sell Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other favored digital currencies without the need for a third party to hold their funds in a cold storage wallet. Covo’s dedication to user security, coupled with its provision of trading solutions, including low-fee swaps and leveraged trading up to 50x, distinguishes it from its rivals.
The COVO Token, issued by Covo Finance, is a utility token for use in governance. Matic tokens, esCOVO tokens (which can be staked or vested to earn COVO Tokens), and Multiplier Points (which increase yield without contributing to token inflation) are all ways in which stakers are compensated for their participation in the Network. By boosting the yield as if the user were staking the same number of COVO tokens, Multiplier Points boost the returns and rewards for long-term holders without causing token inflation.
Covo prioritizes user safety so they can have a frictionless experience by guaranteeing that their cryptocurrency is always safe.

8. Sushiswap
In September 2020, two unknown programmers, Chef Nomi, and 0xMaki, released a service called SushiSwap. It’s a very well-liked DApp on the Ethereum network. For its decentralized exchange system, SushiSwap uses an AMM model. The SushiSwap platform does not provide a traditional order book, meaning smart contracts facilitate the buying and selling of cryptocurrency, with the price set by an algorithm.
SushiSwap was originally a fork of Uniswap, its base was built on Uniswap’s code.
SUSHI, the native token of the SushiSwap protocol, is both a reward and a voting token for liquidity providers on the platform and if you own one, you can earn rewards even if you stop supplying liquidity.
When SushiSwap first started, it enticed liquidity providers to invest LP tokens on Uniswap by rewarding them with a high yearly interest rate on their SUSHI stakes.

9. QuickSwap
QuickSwap operates as an AMM and decentralized exchange over the Polygon network at the Layer 2 level. Like Uniswap, it allows users to contribute to liquidity pools and profit from transaction fees while exchanging tokens.
Because it is a DEX, KYC isn’t required. You only need a wallet to use the platform and MATIC tokens to cover the cost of any transactions.
QuickSwap makes connecting the Ethereum blockchain with Polygon possible, where users can freely trade and swap ERC-20 tokens.
QuickSwap’s in-house digital currency is known as QUICK. You can stake it for dQUICK or other participating tokens or exchange it on QuickSwap for another trading pair.

10. KyberSwap
KyberSwap is an aggregator for DEXs that works with numerous blockchains, such as Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, Cronos, Arbitrum, Velas, and Aurora.
Token trading and liquidity mining are both possible on KyberSwap. With KyberSwap, users can safely and quickly exchange tokens through a streamlined interface and a protected environment.
Users that deposit DAI into the KyberSwap protocol are eligible to receive interest from the Dai Savings Rate (DSR). Fees are earned when users sell their tokens in the liquidity pools, the most effective way to liquidate them. Ultimately, the native token KNC that powers KyberSwap motivates liquidity providers and compensates KyberSwap users.
How Do I Trade On DEX?
Having learned what a DEX is and why it exists, we can now move on to discussing how to make a cryptocurrency purchase on a DEX. To help you get going, below is a detailed manual.
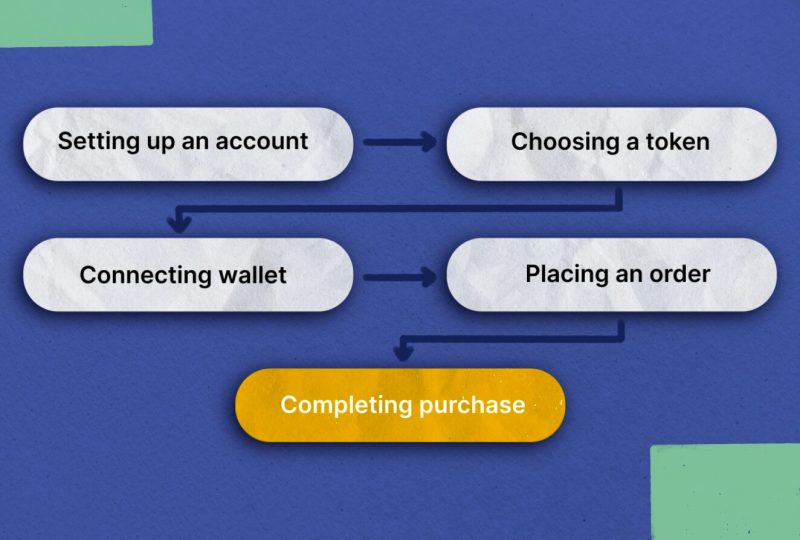
- Set Up An Account
First, you’ll need to create an account before you can buy cryptocurrency on a DEX. The majority of DEXs will necessitate registration before you can use their services. In most cases, you’ll need to enter your name, email address, and password. To begin trading on some DEXs, you may also be asked to provide identity verification.
- Choose A Token To Buy
After signing up, you can begin browsing for the token you wish to purchase. You shouldn’t have any trouble locating the token you seek from the many offered by most DEXs. Before putting down any money, you should do your homework and research well on the token.
- Connect Your Wallet
Before you can make a crypto purchase, you will need to connect your wallet to the DEX. This is important so the exchange knows where to send the funds after your purchase is complete. Hardware, software, and mobile crypto wallets are only some wallet types that DEXs typically support.
- Place An Order
Once you’ve linked your wallet, you can make an order to acquire the token of your choice. On most DEXs, you can set your buying limit and asking price for the token you want to receive. Automated orders can be set up to make sure you always get the cheapest pricing.
- Complete Your Purchase
The DEX will connect you with a seller who possesses the token you want to purchase after you place your order. The money will be deposited into your account once the deal goes through. Depending on the DEX, this could take anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours.
Closing Thoughts
To sum up, DEXs are undoubtedly an essential element of the cryptocurrency world, allowing for the peer-to-peer exchange of digital assets without intermediaries. They have gained popularity in recent years for various reasons, including instant liquidity for new tokens, easy onboarding experience, and democratized access to trading and liquidity provision.
While it’s unclear whether DEXs will become the primary venue for trading or whether their current design can sustain long-term growth, they are expected to remain crucial for the crypto ecosystem. Furthermore, ongoing improvements in transaction scalability, smart contract security, governance infrastructure, and user experience will help to enhance their capabilities and institutional adoption.




