How Forex Brokers Make Money? – A-Book vs. B-Book Model
Oct 14, 2022
A foreign exchange (Forex) broker is a firm whose purpose is to connect traders and investors to a specialized platform where foreign currency can be bought and sold.
All transactions in Forex are conducted between two foreign currencies, also known as fiat money.
There are two types of brokers in the Forex market: A-Book and B-Book. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of both of them, as well as to describe what an FX broker is all about. We will also discuss how Forex brokers make money.
What is an FX broker?
The foreign currency market is a continuously operating marketplace, open 24 hours per day, 5 days a week. Retail traders can use these markets to bet on the movement of currency prices through services provided by Forex brokerages. Bigger players in the Forex market include corporations, banks, and financial service providers — which makes this marketplace an integral piece of today's global economy.
It is estimated that more than 6 trillion US dollars are traded on the foreign exchange market every day. In fact, Forex brokers manage only a small percentage of this industry.
The majority of Forex trades take place between currency pairs from the G10 nations, which are the most economically developed countries. The most common currency pairs traded are the US dollar, euro, pound sterling, Japanese yen, and Swiss franc. Most of these currencies are also known as "safe havens."
The trading process involves a trader purchasing a currency pair and selling it back to close the order. For example, if a trader wants to swap euros for US dollars, they would buy the EUR/USD pair. This means that they are effectively purchasing euros using US dollars. By selling the pair back at a later date, the trader can then cash in on any changes in the exchange rate.
The main risk of trading currencies is brokers who might not be regulated, which is rather rare nowadays, yet still a concern. Every broker must undergo procedures and meet financial regulations that impose obligations, limits, and recommendations on financial firms.
Foreign exchange market regulations refer to the regulations and legislation that a Forex business must adhere to. However, regulation is more than just putting rules in place; consistent monitoring and compliance with the standards are also required.

The goal of regulation is to keep all parties safe from potential financial risks or fraud.
Now, let's take a look at how Forex brokers make money and compare A-Book vs. B-Book.
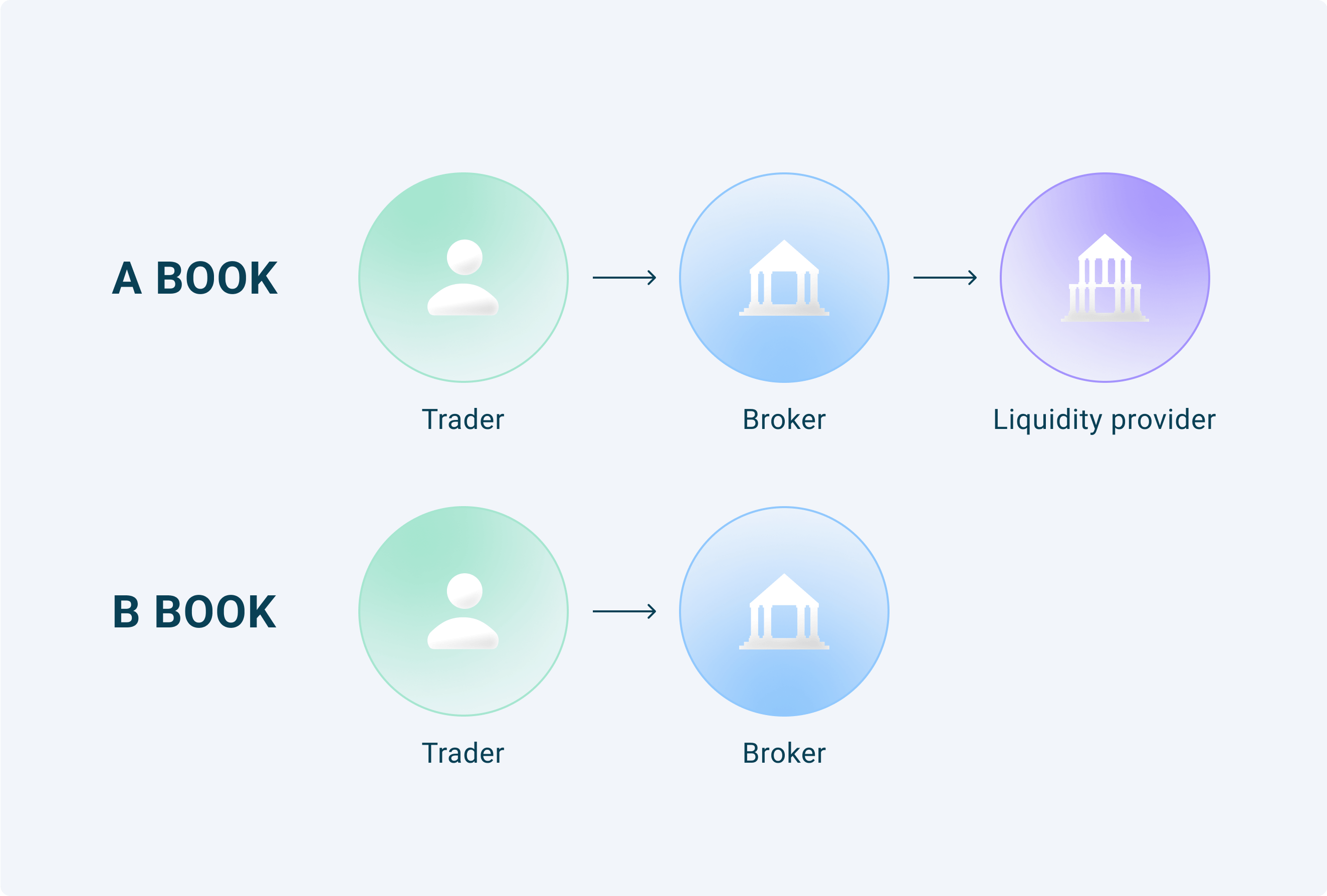
As of now, there are two basic business models in the Forex trading world: A-Book (non-dealing desk) and B-Book (market maker). Both describe how brokers will offer liquidity for customer interactions on the trading platform. Each broker must determine if they want to act as an intermediary or a counterparty for their clients.
A-Book model
A-Book is a kind of FX execution model, referred to as a non-dealing desk broker or an STP (Straight Through Processing) broker. These brokers make money by charging commissions or by profiting from spreads.
An A-Book broker works as a bridge that links a trader's terminals to a liquidity provider, or LP. Thus, the A-Book approach implies that orders are sent directly to the interbank market, where these orders are filled by liquidity providers.
A-Book brokers profit by raising the spread or collecting fees based on the number of orders placed. Due to the fact that they profit the same amount from successful as well as unsuccessful traders, and there are no conflicts of interest. They do not take many risks, yet they may make less revenue since they solely gain on margins/commissions.
That said, this concept acts as a go-between for the investor and markets. By interacting with an A-Book FX broker, the trader avoids both the market maker and their trading desk. As a result, the entities that might otherwise benefit from their trades are eliminated.
The key benefit of utilizing an A-Book broker is that they face fewer conflicts of interest because their customers' profits do not negatively influence their operations.
Typically, prices in this model are obtained from several market players rather than from a single liquidity source, which may result in more accurate quotations, narrower trading spreads, and improved fills, especially in contrast to Forex brokers, which obtain their prices from a single source.
It is important to note, however, that A-Book brokers are not without disadvantages. Orders are sent straight to the liquidity pool, resulting in adjustable spreads for traders. These spreads can be relatively narrow when liquidity is strong, but they can differ wildly during low-volume intervals.
Furthermore, it is essential to remember that spreads on these currency pairings might shrink around standard market sessions. But, during off-market periods, you will likely see the reverse, meaning that spreads will enlarge.
What about B-Book?
A market maker is often a synonym for the B-Book Forex broker. This scenario involves a broker trading against his customers. The broker does not use an external liquidity pool to carry out deals; instead, the business serves as a counterparty to the trader's transactions.
Essentially, a broker will sell to a trader who makes a buy order and vice versa. It is apparent that this kind of approach leads to conflicts of interest between B-Book brokers and their customers.
However, trading using a B-Book broker may turn out to be advantageous for traders. For instance, traders might obtain full guarantees for their deals. Additionally, since the broker serves as the market maker, investors typically receive decent processing of their orders even during periods of low liquidity.
A B-Book model provides constant spreads regardless of whether you trade during busy market hours or off-market hours, which is yet another solid reason to use a B-Book broker. When using the B-Book Forex model, you usually pay a predetermined spread each time you initiate or exit a transaction.
There is no doubt that constant spreads make trading during market volatility simpler. However, you will also need to adjust your trading approach to take into account these fixed spreads.
B-Book brokers lose money when clients make profitable transactions, and vice versa. Basically, the more losses traders suffer, the more profits brokers get. It is often questioned if it is illegal. Authorities, however, generally encourage this method since it enables clients' trades to execute at a better price due to the order being filled without delays.
Both A-Book and B-book Forex brokers that are regulated have a "market maker license". Typically, brokers are regulated by ASIC, FCA, or the NFA.
Many major Forex brokers use a hybrid methodology that involves entering transactions into either the A-Book or B-Book based on trader characteristics. This allows these brokers to better manage their risk while still providing their clients with access to the market.
Bottom line
To sum it up, none of the solutions is ideal, and none of them will avoid potential losses. If you are a broker, it would be best for you to decide which model is appropriate for your company's specific goals and strategy. A similar recommendation could be made for investors selecting a brokerage firm.
It is a widely known fact that the Forex brokerage market may provide numerous opportunities for success if you handle money management and emotions responsibly. Thus, apply a model that suits your requirements and prepare for a long yet exciting trading journey.




