The Dollar Milkshake Theory: Could the US Dollar Become Even Stronger?
Oct 12, 2023

The Dollar Milkshake Theory is receiving a great deal of attention in the financial world due to its unique perspective on the US dollar’s future. This theory, proposed by Brent Johnson, challenges conventional wisdom by suggesting that the USD will continue to gain strength and dominate the global currency landscape despite current economic uncertainties.
In this article, we will delve into the Dollar Milkshake Theory, exploring its key concepts, implications, and possible implications on the cryptocurrency market.
Key Takeaways:
- The U.S. dollar has long held the position of the world’s reserve currency.
- The domination of USD allows the Fed to manipulate monetary policy and maintain the stability of the U.S. financial system, which impacts the global economy.
- There are many critics of the Dollar Milkshake Theory, which point to the lack of published research and clear time frames for the predictions.
The Dollar’s Prevailing Dominance
To comprehend the Dollar Milkshake Theory, let’s first examine the role of the U.S. dollar in the global financial system.
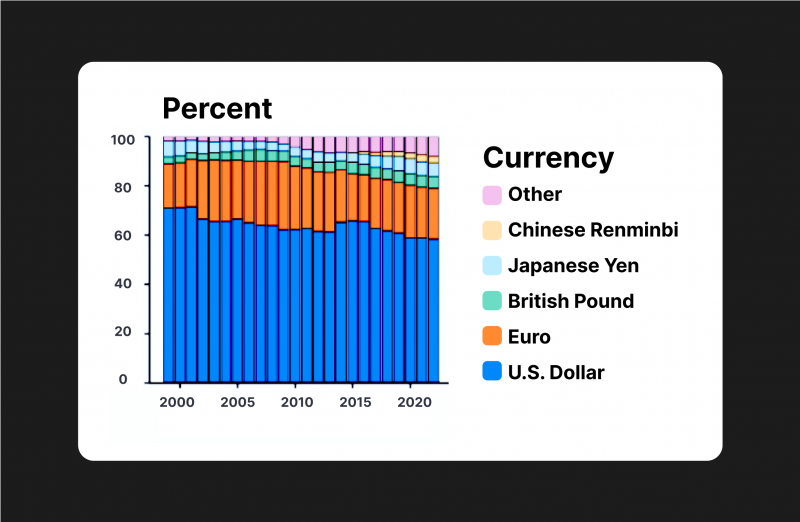
The U.S. dollar has long held the position of the world’s reserve currency. Since the end of World War 2 and until today, it has served as a primary medium of exchange in global trade and is widely accepted as a store of value. According to the Federal Reserve figures, the dollar accounted for 58% of disclosed global official foreign reserves in 2022, greatly surpassing all other currencies.
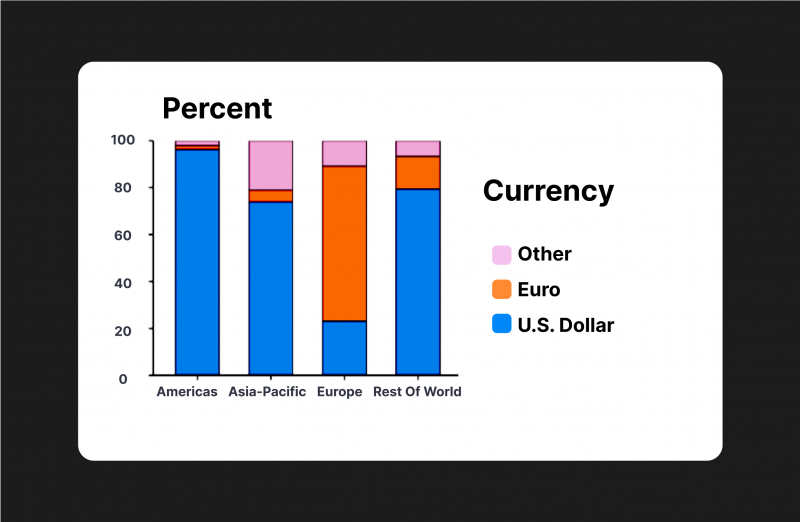
Furthermore, the dollar accounted for 96% of trade invoicing in the Americas, 74% in Asia-Pacific, and 79% worldwide between 1999 and 2019. The only exception is Europe, where 66% of the market is dominated by the euro.
Many countries price their commodities, including oil, in U.S. dollars, which further solidifies its dominance in international transactions.
Fast Fact:
The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 officially made the dollar the world’s reserve currency, a status it maintains to this day.
Understanding the Dollar Milkshake Theory
So, what is the Dollar Milkshake Theory?
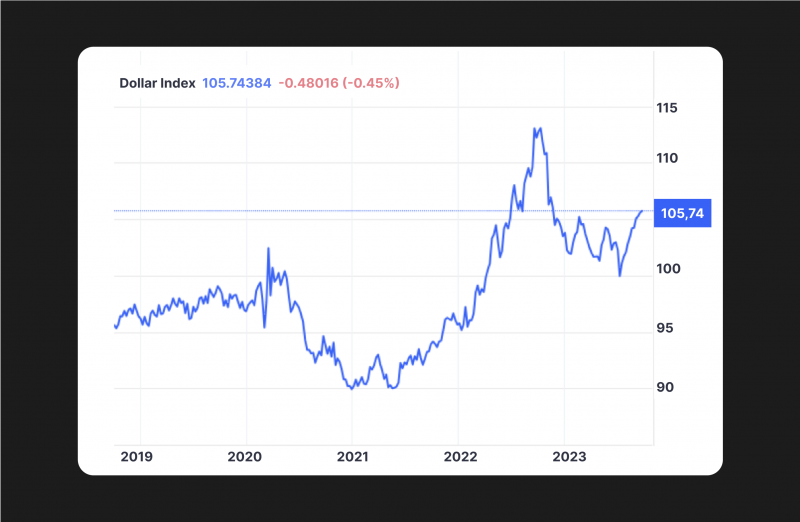
The Dollar Milkshake Theory, coined by Brent Johnson, the CEO of Santiago Capital, predicts that the U.S. dollar will continue to rise and maintain its dominance over other currencies.
To explain the U.S.’s actions during times of global economic distress, Brent Johnson used this analogy:
Imagine a glass filled with a milkshake, where the froth and toppings represent various asset classes. Ingredients such as milk, cream, sugar, and straw represent the flow of cash into and out of the markets, while the straw represents the U.S. Fed’s monetary policies.
When the Fed implements monetary easing by lowering interest rates, it can be likened to adding milk and sugar to a milkshake, creating froth and raising the level of liquidity in the global market. However, when the Fed tightens its policies, it is comparable to using a straw to suck out the liquidity from the market, just as one would with a milkshake.
How Does the Dollar Milkshake Theory Work?
The Milkshake Dollar Theory suggests that as central banks around the world “mix” their economies with easy monetary policies (as if they were blending milkshakes from several different flavours), the US dollar will be the one to absorb the global capital, similar to sucking up a blended milkshake with a straw.
Essentially, because U.S. interest rates are higher than those in other developed countries, and foreign dollars are needed to repay dollar-denominated debts, foreign money will migrate into the U.S., causing the dollar to strengthen.
While the U.S. economy has certain weaknesses today, distinct monetary policies still give the USD an advantage over other currencies. The proponents of the theory believe that the US dollar will only strengthen as a global safe haven. However, a stronger dollar could have significant consequences for the valuation and acceptance of certain assets, most notably cryptocurrencies.
How Monetary Policies Impact the Money Supply
Monetary policies play a crucial role in regulating the money supply and maintaining price stability. The U.S. Federal Reserve employs various tools for its monetary policies, including changing short-term interest rates, open-market operations (OMO), and reserve requirements.
Interest Rate Hikes
When inflation is high, the Federal Reserve implements tightening policies by raising interest rates, making it more difficult for banks and institutions to borrow, thereby reducing the money supply. The conventional view among economists is that higher interest rates lead to lower inflation.
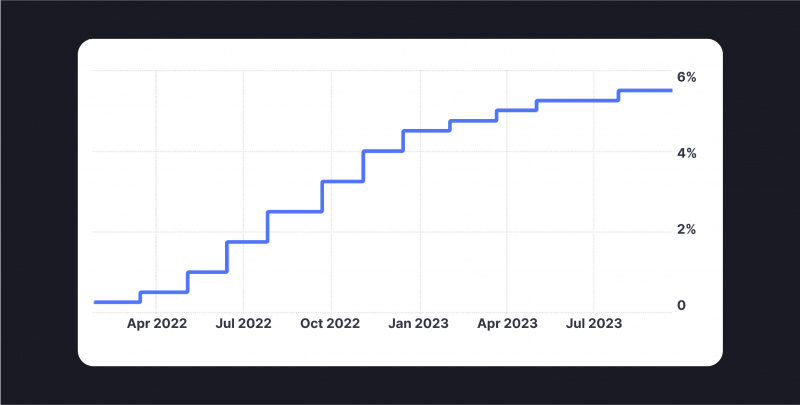
As an illustration, from 2022 to 2023, the Federal Reserve implemented a series of rate increases in order to combat rising inflation, raising the interest from just a few percentage points to almost 6%.
On the other hand, during periods of economic slowdown, the Federal Reserve eases its policies and lowers interest rates to encourage more lending and stimulate economic growth.
OMO
Open-market operations are the Federal Reserve’s primary tool for regulating the money supply and controlling short-term interest rates.
It involves the buying and selling of government securities, such as Treasury bills and bonds, in order to adjust the level of reserve balances in the market. The goal is to influence the availability of money and credit in the economy, thereby influencing the price level and economic activity.
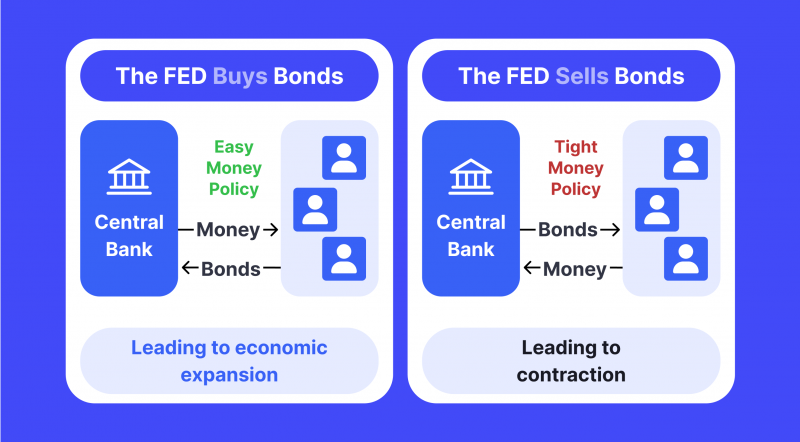
OMO can be used to either increase or decrease the money supply, depending on the desired outcome. For instance, when the Federal Reserve wishes to increase the money supply, it will buy government securities, thus increasing the reserve balances in the market. Conversely, if the Federal Reserve wants to reduce the money supply, it will sell government securities, causing the market reserve balances to decrease.
Reserve Requirements
Reserve requirements are funds that banks must hold against their deposits, and the Federal Reserve can manipulate this amount to encourage or discourage lending.
By increasing reserve requirements, the Federal Reserve can discourage lending, which in turn reduces the amount of money available to borrow and invest. On the other hand, reducing reserve requirements encourages lending, increasing borrowing and investment opportunities.
Evaluating the Implications
The Dollar Milkshake Theory presents several implications regarding various factors affecting the global markets.
The Potential of the Liquidity Crisis
One significant implication is the potential liquidity crisis caused by the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies. As the U.S. central bank, the Fed plays a crucial role in controlling inflation and managing interest rates. The monetary policies implemented by the Federal Reserve can significantly affect global market liquidity, impacting investments in the financial markets and international trade.
Inflation Risk
Another significant aspect to be aware of is the risk of inflation during quantitative easing (QE), a form of monetary policy used to stimulate economic growth.
Quantitative easing is used at a time when interest rates are near zero, and it involves the central bank purchasing assets, such as government bonds, to increase the money supply and stimulate economic activity. For example, QE was actively used by the Fed during the COVID-19 pandemic – at that time, in 2020, the Fed planned to purchase $700 billion in assets to boost the economy.
However, in 2022, the central bank changed its course and started to hike interest rates and reduce its portfolio of assets instead because of the rising inflation and many problems for the economy caused by the QE policy.
So, through the QE, the central bank can lower interest rates, which makes it cheaper to borrow money and stimulates businesses to invest and hire more people. However, the increase in the money supply through QE can also lead to inflation, which needs to be carefully managed by the Federal Reserve.
Fast Fact:
A decade ago, 45% of global cross-border holdings of corporate debt were denominated in dollars, while 35% were denominated in the euro. In 2018, the dollar share exceeded 60% and the euro share fell below 20%.
World’s Central Banks Reactions
One more aspect of the theory is that central banks of other countries will adjust their monetary strategy according to the situation caused by the Fed.
When the Fed raises interest rates, other countries that took out loans will have to pay higher interest rates. The strengthening dollar puts more pressure on central banks as they struggle to repay dollar-denominated debts. To pay off the old debts, they may borrow more loans but can’t keep up with the strengthening dollar.
Eventually, other global economies have to follow the Fed’s lead and inflate their currencies in the same way. Nevertheless, dollar demand continues to rise as the U.S. drains global liquidity. Debt becomes more expensive, causing the local currencies to lose value in comparison with USD.
The Impact of Fed’s Actions on Global Economy
The Dollar Milkshake Theory suggests that due to the dollar’s dominance in the global market, any significant actions taken by the Federal Reserve could potentially have a negative impact on the macroeconomy, especially for developing nations heavily reliant on dollar-denominated debts.
If the currency strengthens, it will become more challenging for these countries to repay their loans, leading to an increase in debt distress. Given that approximately half of the world’s debt is in dollars, such a scenario would create an imbalance in the global economic landscape.
Moreover, as the United States continues to attract capital from the international market, countries with weaker currencies may face additional challenges.
Dollar as a Safe Haven Asset
A safe haven asset is an asset that is expected to retain or increase its value in times of market volatility or global economic uncertainty. These assets are seen as reliable investments and are often used as a hedge against inflation and market downturns.
The U.S. dollar is considered to be one of the most popular safe-haven assets worldwide today. When markets are unstable, investors sell their assets and exchange them for dollars, while the dollar rises at the same time.
Other safe-haven assets include gold, silver, and certain government bonds. These assets are seen as more reliable investments in times of market volatility or economic uncertainty.
What Does the Theory Mean for the Crypto Community?
Cryptocurrencies are not specifically mentioned in Brent Johnson’s dollar milkshake theory; however, many experts have been speculating about how the theory could impact the crypto market.
One of the key points is the comparison of cryptocurrencies as a store of value against a stronger USD. Traditionally, cryptocurrencies have been viewed as a hedge against depreciating fiat currencies. However, if the USD strengthens, it could challenge this narrative and make cryptocurrencies less attractive for those seeking to preserve their wealth.
Another implication is the potential for a liquidity boost in the cryptocurrency market. As the USD becomes more dominant, it can enhance its role as a primary trading pair for cryptocurrencies. This could lead to increased liquidity in the market, making it easier for traders and investors to buy and sell digital assets.
Furthermore, as the USD strengthens, countries may implement measures to prevent capital flight. This could include imposing fees or restrictions on cross-border transactions involving USD. In such a scenario, cryptocurrencies could become an alternative option for individuals and businesses looking to conduct cross-border transactions without facing these limitations.
Arguments Against the Theory
The Dollar Milkshake Theory has faced its fair share of criticism and counter-arguments. Some experts question the validity of the theory, pointing out the lack of published research and clear time frames for the predictions. The theory’s reliance on the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies is also a point of contention, as the effectiveness of these policies can vary depending on various factors and the actions of other central banks.
Contrasting perspectives, such as the Bretton Woods III Theory proposed by economist Zoltan Pozsar, suggest a different future for the global monetary order. These perspectives argue that a new world monetary order may emerge, with commodity-based currencies playing a central role and potentially weakening the Eurodollar system.
Conclusion
The Dollar Milkshake Theory offers a unique perspective on the future of the U.S. dollar and its impact on the global economy. While it faces criticisms and potential limitations, the theory’s core ideas and implications provide valuable insights into the evolving financial landscape. As the financial market experiences fluctuation and uncertainty, understanding the Dollar Milkshake Theory contributes to a comprehensive analysis of the factors shaping its future.
FAQs
What is the Dollar Milkshake Theory’s explanation for the dollar’s future?
The Dollar Milkshake Theory suggests that as the USD becomes more dominant, its role as a primary trading pair for cryptocurrencies will increase, leading to increased liquidity in the market.
What can we learn from the Dollar Milkshake Theory by using the milkshake analogy?
The milkshake analogy is used to illustrate how the Federal Reserve’s tightening policies can be seen as a way to “suck out” liquidity from the market, as one would do with a milkshake.




