What Are Digital Dollars, and How Can They Be Used?
Mar 18, 2024

The creation and development of the digital form of the US dollar as the world reserve currency has become a catalyst for the transformation of both the country’s banking sector and the economic system worldwide, opening up a number of opportunities for the practical use of the beneficial aspects of distributed ledger technology, which became the basis for the formation of the principles and provisions laid down in the digital currency concept, known as digital dollars, or CBDCs.
This article will tell you what the digital dollar is, its features, and the prospects it can give to the global financial system.
Key Takeaways:
- The digital dollar is an electronic form of physical (paper) currency, the principles of which are based on the use of distributed ledger technology on behalf of the U.S. central bank.
- The digital dollar is the next evolution of the U.S. banking system, helping to support the private banking sector and providing many of the benefits of digital payments.
What Is a Digital Dollar?
The concept of a digital dollar entails the introduction of a virtual currency that holds the status of legal tender within the United States. This digital form of currency would possess the ability to be utilised for the purchase of goods and services, as well as the settlement of any outstanding debts.
Nonetheless, it would solely exist in a virtual realm devoid of any physical manifestation in the form of paper banknotes. Instead, it would be stored and exchanged exclusively through computer networks.
While Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) share certain similarities with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, fundamental differences set them apart. Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of numerous participants, whereas CBDCs are centralized assets managed by governments and central banks. This centralized approach ensures that the control and management of CBDCs remain within the purview of authorized entities.
The prevalence of digital transactions, facilitated by credit cards, debit cards, and payment applications, has led to a gradual decline in the use of physical cash.
Nevertheless, using digital dollars would diverge significantly from these existing digital transaction methods. This is primarily due to the fact that a digital dollar would be directly backed by the Federal Reserve, serving as a liability of this central banking institution rather than being associated with a commercial bank or any other financial entity.
Fast Fact:
Until recently, in the U.S., the development of the concept of the digital dollar and the basics of the CBDC was handled by the Hamilton project, which is now closed.
How Does the Digital Dollar’s Technology Operate?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT), similar to blockchain, is the driving force behind the potential implementation of a digital dollar in the United States. DLT enables the recording and sharing of digital information across a network of interconnected computers operating in a peer-to-peer manner.
Unlike the traditional approach, where a central authority, such as a bank, maintains a centralized record of transactions, the ledger in DLT is synchronized across the entire network. Each participant possesses their own copy of the ledger, ensuring decentralization. Transactions are organized in blocks and chronologically linked, forming an immutable chain.
By distributing the ledger across the network, DLT ensures high security and transparency for the digital dollar. No single point of failure exists, and any modifications made to the ledger are immediately visible to all participants. Additionally, to minimize volatility, the digital dollar may be designed as a stablecoin, backed by an equivalent amount of U.S. dollars.
The Federal Reserve could issue digital dollars to approved entities like banks, who would then distribute them to individuals and businesses. These digital dollars could be facilitated through mobile wallets, enabling instant payments to other wallet holders.
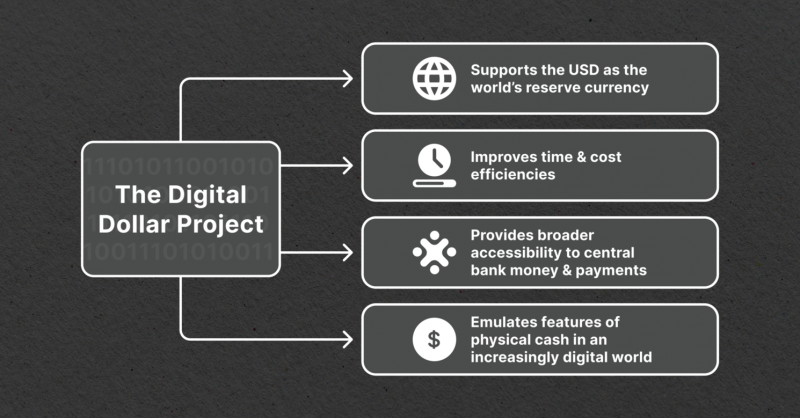
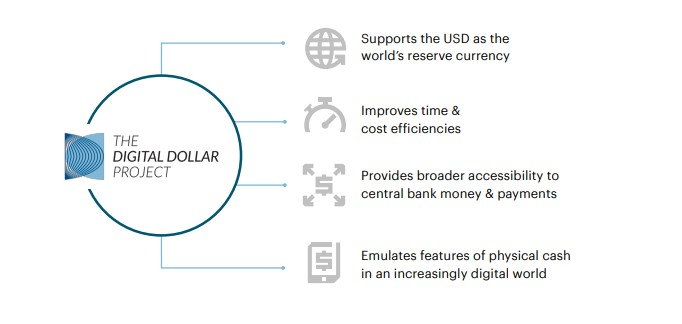
Digital Dollar Project — The Future of U.S. Banking System?
The Digital Dollar Project is a collaborative effort between the Digital Dollar Foundation, a non-profit organization, and Accenture (NYSE: ACN) to advance the study of a central bank digital currency (CBDC), commonly referred to as a “digital dollar.”
The project’s primary objective is to stimulate research and public discourse regarding the potential benefits of a tokenized form of the US dollar. Additionally, it aims to bring together influential figures and entities from the private sector to propose potential models that can assist the public sector in developing, testing, and adopting a CBDC.
By focusing on the interests of the general public, the project aims to safeguard the future relevance of the US dollar for both individuals and institutions within domestic and international economies.
Considering the US dollar’s prominent role as the world’s primary reserve currency and the growing interest in CBDCs by other governments and organizations, the Digital Dollar Project recognizes the importance of piloting a digital version of the US dollar across various use cases.
Such a proactive approach is seen as a crucial and responsible step for the United States to take at present. The project perceives the underlying infrastructure of the US dollar as a vital public asset and believes that upgrading this infrastructure will offer improved flexibility, options, stability, and prosperity for present and future generations.
The initiative aims to investigate the potential advantages of a tokenized US dollar while acknowledging the obstacles and benefits of other possible models. The proposed model involves a tokenized version of the US dollar that coexists with traditional currencies, distributed mainly through commercial banks and regulated money transmitters and recorded on a new transactional infrastructure, possibly utilizing distributed ledger technology.
Basic Principles of Digital Dollar
The Digital Dollar Project stands out from existing electronic payment systems by adopting a token-based approach instead of an account-based model. This unique nature allows it to possess characteristics similar to physical cash while incorporating the advantages of traditional account-based payment mechanisms. These principles form the foundation of the digital dollar’s design.
1. Tokenization
The US dollar in digital form will be represented by a token because using a tokenized digital dollar is advantageous because there is no superior and secure settlement medium to the US central bank money. This fact must be incorporated to ensure that it remains relevant and available.
The DDP believes that a digital dollar has the potential to modernize the money infrastructure, which is a vital public resource. Additionally, it can make the US dollar more viable in the digital age.
2. Continued Private Sector Innovation
Implementing a digital dollar will serve as a powerful driver for innovation, fostering an environment that encourages the growth of private sector initiatives. Rather than hindering their development, the digital dollar will complement and support the advancement of these initiatives, creating a synergistic relationship between the public and private sectors.
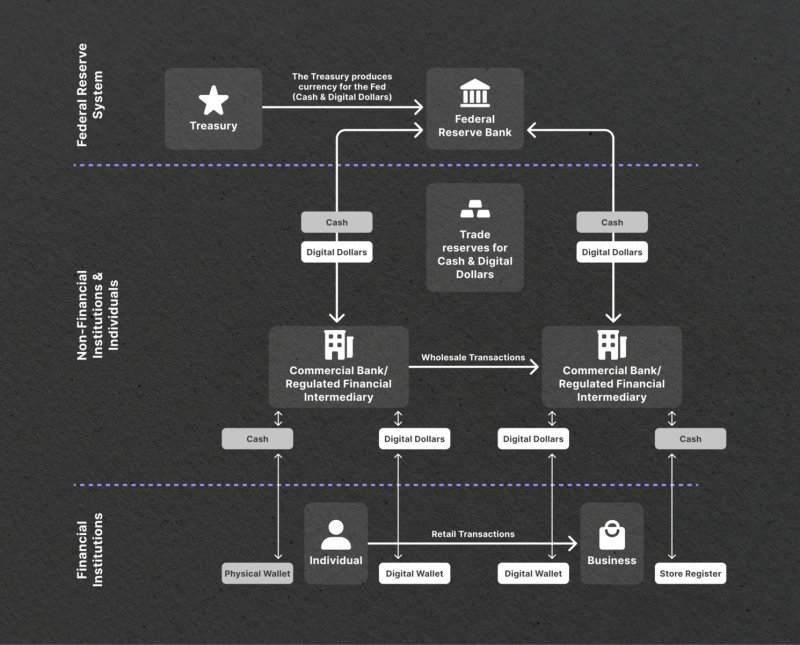
3. Maintenance of The Two-Tiered Banking System
The distribution of a digital coin will occur using the current two-tiered structure of commercial banks and regulated intermediaries, which involves multiple steps and processes to ensure efficient and secure transactions.
Firstly, the central bank, responsible for issuing and regulating the digital dollar, will create the necessary infrastructure and protocols for its distribution. This may involve developing a digital currency platform or utilizing existing financial infrastructure to facilitate distribution.
Commercial banks, as the primary intermediaries between the central bank and the general public, will play a crucial role in the distribution of the digital dollar. They will act as custodians of the electronic currency, holding and managing the digital dollar balances on behalf of their customers.
4. Privacy
Policymakers will determine the delicate equilibrium between safeguarding individual privacy rights and ensuring compliance with regulations through the implementation of the digital dollar. This decision-making process will be guided by the principles established in the Fourth Amendment, reflecting the evolving legal landscape.
5. Third Format of Currency
The introduction of a digital dollar will function in conjunction with traditional fiat currency and commercial bank money. It will replicate numerous characteristics of physical money, enabling it to integrate with existing account-based systems seamlessly.
6. Monetary Policy Neutral
The introduction of a dollar electronic cash is unlikely to have any adverse effects on the Federal Reserve’s capacity to influence monetary policy and manage inflation. On the contrary, a digital dollar has the potential to serve as a novel policy instrument, offering additional flexibility and options for the Federal Reserve to navigate economic conditions effectively.
7. Technology and Design Considerations
If the primary goal of the digital dollar is to increase financial inclusion and accessibility, the design may prioritize user-friendly interfaces and accessibility features to ensure that individuals of all backgrounds can easily access and use the currency. On the other hand, if the main objective is to enhance security and prevent fraud, the technology used may focus on implementing robust encryption and authentication measures.
Additionally, the policy considerations surrounding the dollar digital cash, such as privacy concerns, regulatory compliance, and monetary policy implications, will also heavily influence the technological and design decisions.
Conclusion
The digital dollar holds immense potential to revolutionize the financial landscape, offering numerous benefits such as increased efficiency, enhanced security, and improved accessibility. Yet, its implementation requires a comprehensive understanding of the intricate workings of the monetary system, as well as the potential risks and challenges associated with digital currencies.
To achieve the desired outcomes, the government must align its essential monetary and public policy objectives with the private sector’s expertise, creativity, and agility. Collaboration between these two entities is vital to leverage their strengths and capabilities, ensuring a well-rounded and robust digital dollar ecosystem.