Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) Explained
Nov 22, 2024

Our modern world depends on extensive physical infrastructure, including cell towers, power lines, roads, railways, and data centers. However, traditional management methods for this infrastructure often lack efficiency. It tends to be overly centralized, with limited public access and an uneven distribution of resources.
That’s where this new idea of “decentralized physical infrastructure networks” or DePINs comes in. The basic premise is to use blockchain technology and financial incentives to create a more user-driven, efficient way to build and maintain physical infrastructure.
The thinking is that by decentralizing control and empowering more people to participate, we can address some of the shortcomings of the current model.
Key Takeaways:
- DePINs are a paradigm shift in infrastructure management that connects physical resources with blockchain technology, enabling direct peer-to-peer sharing of resources.
- These networks solve critical infrastructure challenges by removing centralized control, reducing costs, and improving efficiency through blockchain-powered smart contracts and tokenized incentive systems.
- Despite the promising potential, DePINs face challenges, including regulatory uncertainty, security concerns, and the complexity of managing physical infrastructure integration with blockchain systems.
What is DePIN?

Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs) bridge the physical and digital worlds, utilizing blockchain technology to create decentralized networks for sharing tangible resources. Think of DePIN as a public library where anyone can contribute or borrow resources freely, with blockchain serving as a transparent, always-accessible catalog of all transactions and activities.
These networks enable direct sharing of physical infrastructure resources like WiFi, data storage, and energy without intermediaries. While services like WiFi signals may seem intangible, they rely on physical components such as antennas, routers, and servers – the foundational elements of DePINs.
Built on blockchain technology, DePINs use cryptocurrencies for transactions and reward participants who share their resources. The blockchain acts as a digital manager and record keeper, creating an open system where anyone can provide services without special permissions while maintaining transparent public records of all network activities.
Traditional infrastructure systems often face limitations due to centralized control. DePINs address these challenges by:
- Making infrastructure more accessible, efficient, and resilient
- Distributing control among network participants rather than concentrated entities
- Ensuring continuous service availability during disruptions
- Reducing entry barriers and bureaucratic overhead
- Enabling faster deployment and adaptation to local needs
- Creating opportunities for smaller businesses and entrepreneurs
Key Components of DePIN
Blockchain and Smart Contracts: DePIN uses blockchain for transparency and trust, allowing participants to contribute resources with clear, immutable records. Smart contracts automate and enforce rules within DePIN systems, from resource allocation to token rewards.
Decentralized Governance: Unlike centralized systems, DePIN networks employ decentralized governance, where network participants influence the network’s development and resource distribution through voting and consensus. This decentralized approach ensures that decisions are transparent and aligned with the community’s interests.
Token Rewards: Participants in decentralized physical infrastructure networks earn tokens for their contributions, such as sharing excess energy in an energy grid or offering unused storage space for decentralized storage solutions. These tokens incentivize participation and create a decentralized economy around resource sharing.
How Exactly Does DePIN Work?
DePINs operate on a core principle of distributed ownership and participation. Here’s a breakdown of how they function:
- Individuals and organizations contribute physical resources like WiFi hotspots, data storage devices, solar panels, or electric vehicles to the DePIN network.
- Smart contracts on the blockchain automate resource allocation and service delivery. When a user utilizes a network resource (e.g., accessing WiFi), a smart contract automatically triggers a payment in the form of DePIN tokens to the resource provider.
- DePIN projects issue unique tokens that act as incentives for network participants. Users earn these tokens by contributing resources and providing services, which can be traded or used to access other services within the DePIN ecosystem.
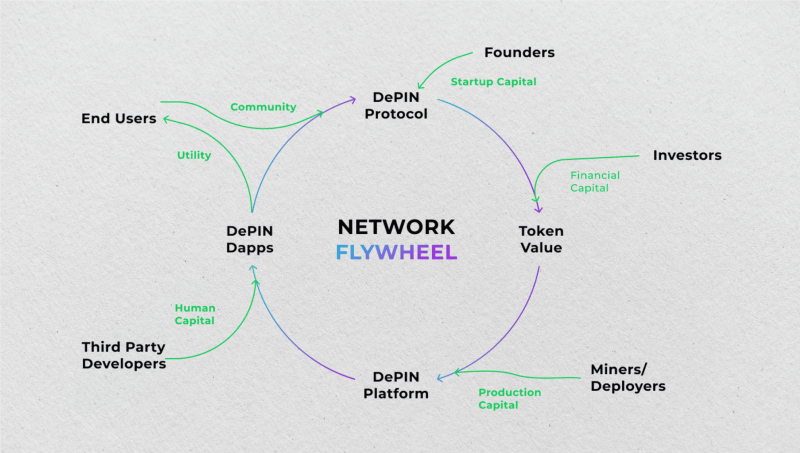
DePINs function on a self-reinforcing cycle known as the DePIN flywheel. Here’s how it works:
- More users contributing physical and digital resources expand the network’s capacity and service offerings.
- A larger, more diverse network provides greater value to users, attracting further participation.
- As the network grows, the utility of DePIN tokens increases, potentially leading to a rise in their market value.
This flywheel effect creates a sustainable ecosystem where the network grows, users benefit, and token values are appreciated.
Fast Fact:
One of the simplest ways to earn passive income with DePIN projects is by renting out unused storage space for decentralized data storage. Businesses and individuals are increasingly seeking secure, decentralized storage solutions, and by offering your spare capacity, you can earn DePIN tokens in return.
DePIN Use Cases
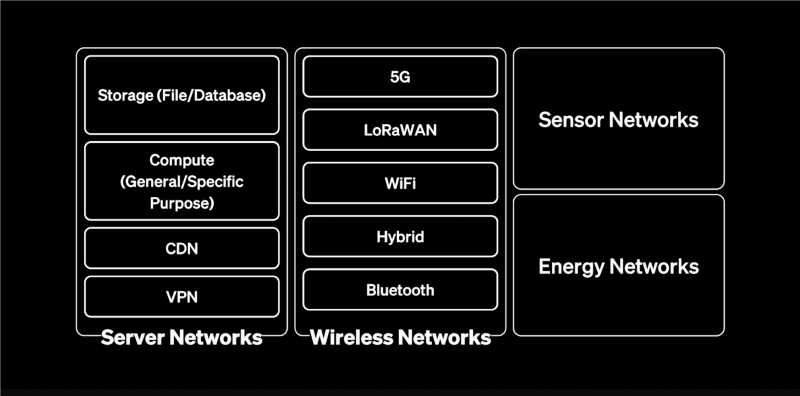
DePIN projects span a variety of sectors, each using a unique combination of decentralized technologies and resource networks. Below are some popular applications of digital resource networks:
1. Decentralized Wireless Networks
Decentralized networks have gained traction in the telecommunications sector, where decentralized wireless networks provide an alternative to traditional carriers.
In this model, individuals and businesses can contribute their bandwidth and network infrastructure to the community, earning tokens in return. This setup particularly benefits rural or underserved areas with limited centralized wireless connectivity.
2. Decentralized Energy Grid and Renewable Energy
Decentralized energy grids enable individuals to share excess energy from renewable sources like solar panels with their communities. Participants support a more efficient energy distribution system by contributing unused energy and promoting renewable energy adoption.
DePIN networks in energy grids offer token rewards for energy trading, fostering a decentralized economy within the renewable energy sector.
3. Decentralized Data Storage Solutions
In data storage, a decentralized network addresses the growing demand for secure, decentralized storage solutions by allowing participants to contribute unused storage space. This creates a distributed storage facility network where data is stored across multiple locations, enhancing data integrity and security.
Unlike traditional centralized storage services, decentralized storage solutions are resilient to single points of failure.
4. Supply Chain and Transportation Networks
Supply chain management is another sector where DePIN networks are innovating. By leveraging blockchain for transparency, DePIN projects in transportation networks and logistics track goods and ensure data accuracy across each stage of the supply chain. This transparency improves efficiency and reliability, helping to build trust among all parties involved.
Examples of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network Projects
Several DePIN projects are already making waves across different infrastructure sectors:
Helium: Focuses on creating a decentralized wireless network. Users can share their WiFi hotspots and earn HNT tokens in return, while others can access a more extensive and potentially lower-cost wireless network.
Filecoin: Offers decentralized data storage solutions. Users can rent out their unused storage space and earn FIL tokens, while others can access secure and reliable data storage at potentially lower costs compared to centralized cloud services.
Hivemapper: Utilizes drones and other aerial vehicles to capture and share geospatial data. Network participants earn HONEY tokens for contributing data, while businesses and individuals can access high-resolution aerial imagery for various applications.
Challenges DePINs Face
While DePIN networks present exciting opportunities, they face several challenges:
Regulatory Hurdles
DePIN projects often operate in regulatory gray areas, especially in the energy trading and telecommunications sectors. Governments may impose restrictions on decentralized networks, particularly if they threaten traditional institutions.
Scalability and Technical Limitations
Scaling decentralized networks for mass adoption can be challenging. Managing physical resources in a decentralized manner requires significant infrastructure, computing power, and seamless connectivity between nodes, which can be costly and technically complex.
Resource Allocation and Coordination
In DePIN systems, efficient resource allocation is essential. Participants may need guidance or incentives to optimize resource contribution, especially in networks that rely on variable resources like renewable energy. Managing these resources across a decentralized infrastructure requires advanced consensus mechanisms and coordination tools.
Conclusion
DePINs represent a significant advancement in infrastructure management, offering decentralized alternatives to traditional systems. While challenges exist, their potential to revolutionize resource sharing and management makes them a promising technology for future infrastructure development.
As DePIN networks evolve, they can redefine how society manages and utilizes its most critical resources, building a future where infrastructure is decentralized and owned and operated by the people who rely on it.




