SEC Crypto Regulations: What Financial Advisors Need to Know

The crypto world is at the intersection of innovation and regulation, and the SEC plays a pivotal role in shaping its future. As blockchain technology evolves, so do the challenges of maintaining market integrity while fostering innovation.
From enforcing compliance to launching proactive measures like a dedicated crypto task force, the SEC’s approach to crypto regulation signals a shift toward building a transparent and balanced framework.
Whether you’re an investor, advisor, or entrepreneur, understanding the SEC’s evolving stance on crypto is essential to navigating this dynamic space.
Key Takeaways
- The SEC has shifted from an enforcement-first strategy to proactive regulation, which was highlighted by the creation of a crypto task force in 2025.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges, stablecoins, and initial coin offerings (ICOs) remain critical areas of regulatory focus to ensure compliance and transparency.
- High-profile enforcement actions against Binance, Coinbase, and others emphasize the importance of adhering to U.S. securities laws in the rapidly evolving crypto sector.
The Essence and Goals of Crypto Regulation
Crypto ordinances play a critical role in shaping the landscape of digital assets and their integration into the financial system. These regulations aim to balance innovation with consumer protection, ensuring that the benefits of blockchain technology are realized while mitigating risks such as fraud, money laundering, and market manipulation.

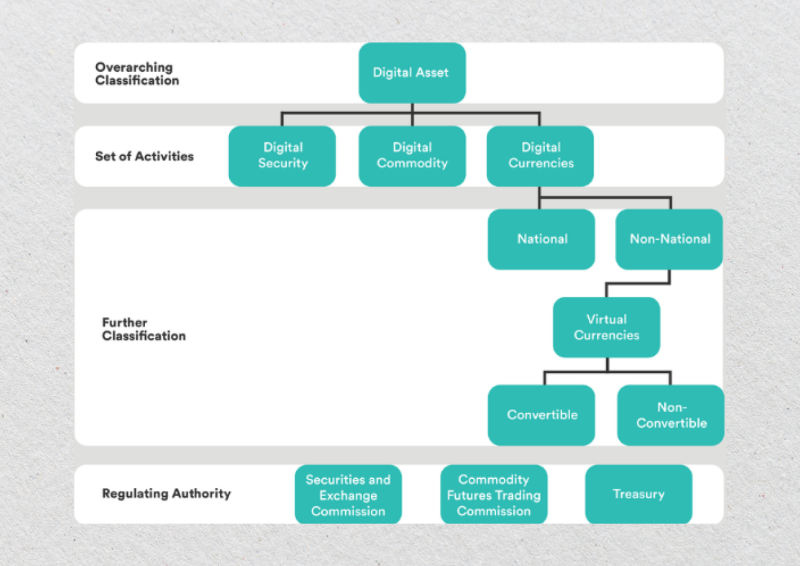
One key challenge in crypto regulation is classifying digital assets. Different jurisdictions and regulatory bodies have varying definitions for cryptocurrencies, tokens, and blockchain-based financial instruments. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) classifies many cryptocurrencies as securities, subjecting them to strict regulatory oversight under securities laws.
Meanwhile, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) considers Bitcoin and Ethereum commodities that fall under its purview. This dual classification highlights the complexity of the regulatory framework, making it essential for stakeholders to stay updated on the evolving guidance from regulators.

Fast Fact
In 2023, Binance and its founder, Changpeng Zhao, faced the largest financial penalty in SEC history, amounting to $4.3 billion, for crypto-related violations.
SEC’s Role in Crypto Regulations
The U.S. SEC is key in regulating cryptocurrencies to ensure this fast-growing market follows established securities laws. The SEC primarily aims to protect investors, promote fair and efficient markets, and support capital formation. To address the unique nature of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, the SEC has adapted its approach to meet the challenges and opportunities of digital assets.
The SEC focuses on maintaining the integrity of cryptocurrency trading platforms. Exchanges that handle cryptocurrencies considered securities must either register with the SEC or qualify for exemptions. This helps preserve transparency, prevent fraud, and promote fair trading practices. The SEC also requires financial institutions and advisors to follow strict guidelines for safely holding digital assets on behalf of their clients.
To establish its authority, the SEC has taken significant enforcement actions in the crypto space. Cases involving companies like Ripple Labs and Telegram highlight its stance on unregistered securities offerings.
The SEC has also increased oversight of crypto exchanges, requiring those dealing with securities-like assets to comply with registration rules. As the crypto market continues to evolve, the SEC’s role remains critical in protecting investors while encouraging innovation.
Major Areas of SEC Regulation in Crypto Landscape
The SEC has developed a multi-faceted regulatory approach to address the complexities of the cryptocurrency market. These regulations aim to protect investors, ensure market integrity, and foster compliance in a rapidly evolving sector.
Below are the key areas where the SEC focuses its efforts in the cryptocurrency space:
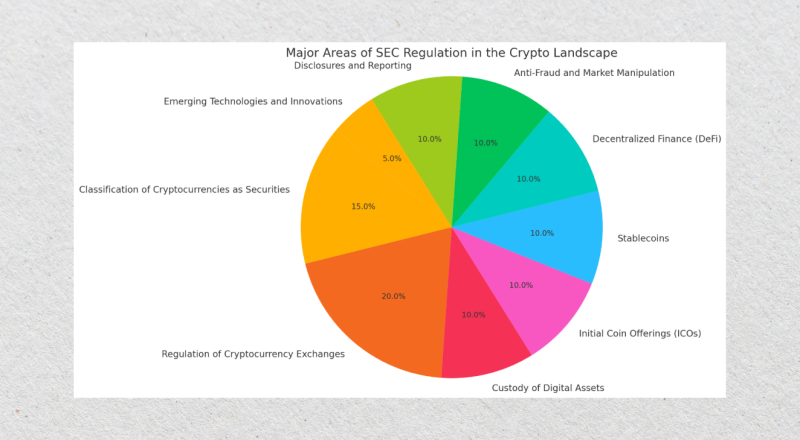
Classification of Cryptocurrencies as Securities
The SEC’s primary focus is determining whether a cryptocurrency qualifies as a security. This is done using the Howey Test, which evaluates whether an asset involves an investment of money in a common enterprise with an expectation of profit derived from the efforts of others. If a cryptocurrency meets these criteria, it is classified as a security and falls under the SEC’s jurisdiction.
Issuers of such cryptocurrencies must comply with registration requirements, provide accurate disclosures, and adhere to anti-fraud provisions. This classification is especially relevant for tokens sold during initial coin offerings (ICOs), many of which have been identified as unregistered securities offerings.
Regulation of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Another critical focus for the SEC is cryptocurrency exchanges that facilitate the buying and selling securities, such as digital assets. Such platforms must either register as national securities exchanges or operate under specific exemptions.
These regulations ensure that exchanges comply with federal securities laws, provide fair and efficient trading environments, reduce the risk of fraud, and enhance market integrity.
Custody of Digital Assets
The SEC has specific guidelines for the custody of digital assets, particularly for registered investment advisors (RIAs). These rules require financial advisors and institutions managing crypto assets on behalf of clients to use secure custody solutions, such as insured or qualified custodians.
They must maintain accurate asset ownership records, provide transparency in reporting, and safeguard client assets against theft or misuse. These regulations aim to minimize risks associated with cybersecurity breaches and operational failures.
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
ICOs, a popular way for startups to raise capital, have been a significant area of SEC enforcement. Many ICOs involve the sale of tokens that qualify as securities but fail to comply with registration requirements.
The SEC requires ICO issuers to register their offerings unless they qualify for an exemption, provide full and accurate disclosures to investors, and adhere to anti-fraud laws to prevent misleading or deceptive practices. High-profile cases like Ripple (XRP) and Telegram (Gram tokens) highlight the SEC’s stance on unregistered ICOs.
Stablecoins
The SEC closely monitors stablecoins, which are cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies or other assets. Depending on their structure and use case, stablecoins may function like securities or money market funds. If classified as securities, stablecoins are subject to SEC oversight, including registration and reporting requirements.
The SEC has raised concerns about the transparency and stability of some stablecoin projects, particularly those involving reserve backing or redemption mechanisms.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi presents unique challenges for the SEC. DeFi platforms, which operate without traditional intermediaries, often facilitate activities like lending, borrowing, and trading. If these platforms involve securities transactions, they fall under the SEC’s jurisdiction.
Key concerns include the lack of investor protection, the potential for fraud and manipulation, and compliance with securities laws by developers and operators of DeFi platforms.
Anti-Fraud and Market Manipulation
The SEC enforces anti-fraud and anti-manipulation provisions to protect investors from deceptive practices in the crypto market. These include misrepresentation of token utility or value, insider trading on material non-public information, and pump-and-dump schemes where bad actors artificially inflate token prices before profiting and leaving other investors with losses. The SEC actively monitors the market for these activities and takes enforcement actions when necessary.
Disclosures and Reporting
Transparency is a cornerstone of SEC regulations. Issuers of crypto assets classified as securities must provide full and accurate disclosures to investors, including information about the business model and purpose of the cryptocurrency, risks associated with the token, how raised funds will be used, and details about the management team. These disclosures help investors make informed decisions and reduce risks.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The SEC is expanding oversight to cover emerging technologies in the crypto space. This includes NFTs, which may fall under SEC regulation if they are fractionalized or tokenized to resemble investment contracts.
Security tokens, designed to represent ownership or investment rights, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which issue tokens meeting the Howey Test criteria, are also areas of focus.
Collaboration with Other Regulatory Agencies
The SEC collaborates with other U.S. regulators to ensure cohesive crypto oversight. This includes the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), which oversees cryptocurrencies classified as commodities like Bitcoin and Ether, as well as derivatives trading.
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) enforces anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements. The Federal Reserve and Treasury Department address issues related to stablecoins and broader financial system risks.
Key Laws Used to Regulate Crypto by the SEC
The SEC uses several existing federal laws to regulate the cryptocurrency industry. These laws were originally designed to govern traditional securities markets but have been adapted to apply to digital assets like cryptocurrencies, ICOs, and decentralized platforms.
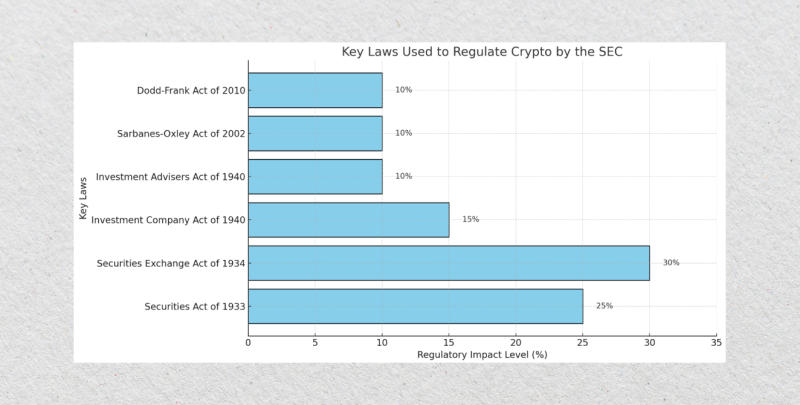
Below is a detailed explanation of these foundational laws and their relevance to the crypto industry.
Securities Act of 1933
This law governs the issuance and sale of securities to the public, promoting transparency, protecting investors, and preventing fraud. The SEC applies this act to cryptocurrencies classified as securities, requiring them to be registered before being offered to the public.
Initial coin offerings often fall under this law if their tokens meet the Howey Test criteria for securities. The act also mandates detailed disclosures about the crypto project, including its purpose, financial health, risks, and team credentials, ensuring investors can make informed decisions.
Securities Exchange Act of 1934
This act regulates securities trading on exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) markets to ensure fair practices and prevent fraud, insider trading, and market manipulation. Cryptocurrency exchanges facilitating the trading of digital assets classified as securities must register as national securities exchanges or operate under exemptions.
The act also enforces anti-fraud provisions and prohibits manipulative practices. Platforms accused of enabling the trading of unregistered securities, such as Coinbase and Binance, are often scrutinized under this law.
Investment Company Act of 1940
This act regulates investment companies like mutual funds, hedge funds, and ETFs by enforcing transparency, accurate valuations, and investor protection measures. Crypto investment funds or projects pooling investor money to invest in cryptocurrencies may fall under this law.
These funds are required to register with the SEC, provide periodic reports, and adhere to disclosure requirements. This law is particularly relevant for firms creating crypto ETFs or similar financial products offering exposure to digital assets.
Investment Advisers Act of 1940
This law governs investment advisers managing portfolios for clients, imposing fiduciary duties, registration requirements, and anti-fraud provisions. Registered investment advisers managing crypto portfolios must comply with this act, ensuring they act in their clients’ best interests.
Advisors must provide transparent information about fees, investment strategies, and cryptocurrency risks. The SEC has proposed stricter rules for advisors managing digital assets, including requiring the use of qualified custodians for client funds.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
This law focuses on corporate governance, financial reporting, auditor independence, and improving transparency and accountability for publicly traded companies. Crypto firms offering securities or seeking public investment must comply with financial reporting standards under this act.
Publicly traded crypto companies are also subject to audits and must ensure accurate financial performance reporting to reduce risks of fraud or mismanagement. These requirements extend to cryptocurrency exchanges and projects that are publicly listed.
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010
Enacted after the 2008 financial crisis, this law increased regulatory oversight of financial institutions, implemented consumer protections, and established rules for derivatives markets. The act gives the SEC and other regulators’ authority over complex financial instruments, including crypto derivatives.
It enforces consumer protection measures for crypto platforms offering services like lending and staking, which can expose users to significant risks. The SEC has also used this act to scrutinize stablecoins, particularly those tied to derivatives or complex financial structures.
Recent SEC Crypto Case Precedents
The U.S. SEC has recently increased its regulatory scrutiny of the cryptocurrency sector, placing a significant emphasis on enforcement actions directed at prominent exchanges and platforms. A comprehensive overview of significant SEC recent cases related to cryptocurrency is provided below.
Binance
In June 2023, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Binance, the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, and its founder, Changpeng Zhao. The SEC accused Binance of mishandling customer funds, operating without proper registration, and misleading investors.
In November 2023, Zhao agreed to resign from Binance and pleaded guilty to violating the American Bank Secrecy Act. He was sentenced to four months in prison in April 2024. Binance also pleaded guilty to related charges and agreed to pay $4.3 billion in fines.
This case marked one of the most significant enforcement actions in the crypto industry, highlighting the SEC’s commitment to enforcing compliance among major crypto exchanges and their executives.
Coinbase
In June 2023, the SEC sued Coinbase, alleging it operated as an unregistered securities exchange, broker, and clearing agency. The SEC identified several tokens traded on Coinbase as securities and criticized its staking-as-a-service program.
As of January 2025, the case remains ongoing, with Coinbase contesting the SEC’s allegations and advocating for clearer regulatory guidelines. This case has sparked industry-wide debates about the clarity of U.S. crypto regulations. The outcome could define the regulatory obligations of crypto exchanges in the U.S.
Kraken
In February 2023, the SEC charged Kraken for failing to register the offer and sale of its crypto asset staking-as-a-service program. The SEC alleged that Kraken’s staking program was an unregistered securities offering.
Kraken agreed to cease its staking services for U.S. customers and paid a $30 million settlement without admitting or denying the allegations. This enforcement action underscored the SEC’s focus on staking programs and set a precedent for regulating such services.
Bittrex
In April 2023, the SEC charged Bittrex, a U.S.-based crypto exchange, with operating an unregistered securities exchange, broker, and clearing agency. The SEC alleged that Bittrex facilitated the trading of digital assets that were offered and sold as securities without registering.
Bittrex settled with the SEC, agreeing to pay a $24 million fine and cease operations in the U.S. This case highlighted the SEC’s enforcement actions against exchanges operating without proper registration and emphasized the need for compliance with securities laws.
Ripple Labs (XRP)
In December 2020, the SEC sued Ripple Labs, alleging that its sale of XRP tokens constituted an unregistered securities offering. In July 2023, a court ruled that XRP sales to institutional investors violated securities laws, while secondary sales on exchanges and programmatic sales to retail investors were not considered securities transactions.
Ripple was ordered to pay a civil penalty of over $125 million. This case provided a nuanced perspective on how different types of token sales are treated under securities laws and underscored the importance of compliance for crypto issuers.
Terraform Labs (Terra LUNA)
The SEC sued Terraform Labs and its co-founder Do Kwon in February 2023, alleging securities fraud. The SEC claimed Terraform Labs misled investors about the stability of its algorithmic stablecoin, TerraUSD (UST), and the broader utility of its blockchain platform.
The lawsuit highlighted unregistered securities offerings, fraudulent claims about UST’s ability to maintain its dollar peg, and market manipulation to inflate token demand.
In March 2023, Do Kwon was arrested in Montenegro for using falsified documents. He faced extradition requests from the U.S. and South Korea. The SEC aimed to hold Terraform Labs accountable for violating securities laws. It sought to recover investor losses caused by the collapse of UST and LUNA, which wiped out over $40 billion in market value in May 2022.
The Future of SEC Crypto Regulations
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies in the United States is undergoing significant changes as of January 2025. The U.S. SEC has initiated new efforts to create a clearer framework for digital assets, moving beyond its traditional enforcement-focused approach to a more proactive regulatory stance.
Formation of the SEC Crypto Task Force
On January 21, 2025, Acting SEC Chairman Mark T. Uyeda announced the establishment of a dedicated cryptocurrency task force. This task force, led by Commissioner Hester Peirce — known for her pro-crypto stance — aims to address the growing need for regulatory clarity in the digital asset space.

The primary objectives of the task force include providing clear and comprehensive guidelines for crypto regulation, ensuring investor protection while fostering market innovation, and collaborating with other regulatory bodies, including federal agencies, state regulators, and international counterparts. This initiative signifies a notable shift from the SEC’s enforcement-centric approach, aiming to proactively address the evolving crypto landscape.
Industry Developments
The SEC reviews applications for exchange-traded funds (ETFs) linked to “memecoins,” such as those associated with figures like former President Donald Trump and Elon Musk. While these ETFs could potentially bring new investors into the market, they have sparked debates over whether they might encourage speculative trading behaviors.
At the same time, regulatory oversight has heightened in other areas of the crypto industry, with increased scrutiny of stablecoins and DeFi platforms. These developments are likely to shape the broader regulatory environment for digital assets.
Final Remarks
The SEC’s role in crypto legislation is more critical than ever as it seeks to balance fostering technological innovation and protecting investors. With new task forces, proposed regulations, and high-profile enforcement actions, the regulatory landscape is becoming more apparent yet complex.
As the U.S. moves towards a cohesive framework, staying informed and compliant is not just an option but a necessity for all stakeholders in the crypto ecosystem.
FAQ
What is the SEC’s role in crypto regulation?
The SEC regulates cryptocurrencies classified as securities to assure transparency, prevent fraud, and protect investors under existing securities laws.
What is the SEC Crypto Task Force?
The task force, announced in January 2025, aims to create clear regulatory guidelines for digital assets and address challenges in the cryptocurrency market.
Are all cryptocurrencies regulated by the SEC?
No, the SEC regulates cryptocurrencies classified as securities. Bitcoin and Ethereum, for example, are considered commodities and fall under the jurisdiction of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
What are the SEC’s key enforcement areas in crypto?
The SEC focuses on unregistered securities offerings, fraudulent practices, crypto exchange compliance, and custody of digital assets.
What is the future of SEC crypto standards?
The SEC is moving towards proactive regulations with more precise guidelines for innovation, investor protection, and collaboration with other agencies.