Blockchain for Business. Pros & Cons
Nov 25, 2022
We wouldn't exaggerate if we said that blockchain technology ranks among the most praised technologies of today. Blockchain, initially mainly used to support Bitcoin payments and usage of other cryptocurrencies, now powers countless other digital assets, and engineers are seeking to integrate the technology into industries such as health, entertainment, banking, and other commercial businesses.
In this article, we will explain what blockchain is, how blockchain works, why it has value, and what distinguishes it from other internet technologies. Moreover, we will share the significant upsides and downsides of blockchain and how people found ways to implement blockchain for business.
First things first, let's talk about the definition of blockchain.
What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain refers to a distributed database or ledger across a computer network of so-called nodes. You can think of it as a database which saves data in digital format only. Blockchain-based crypto assets don't represent any tangible objects. As one of the most critical functions of blockchain technology, which is mainly used in cryptocurrency systems, it provides a reliable and decentralized database of all transactions. The blockchain's uniqueness is that it ensures the reliability and security of data records and delivers credibility without the necessity for a third party.
The way data is organized differs significantly between a traditional database and a blockchain. A blockchain accumulates information in units called blocks, which store sets of data. When a block's storage capacity is reached, it is locked and connected to the preceding block, producing a data chain = blockchain. All new evidence accompanying that recently introduced block is assembled into a newly formed block, which is then uploaded to the chain once this block is completed.
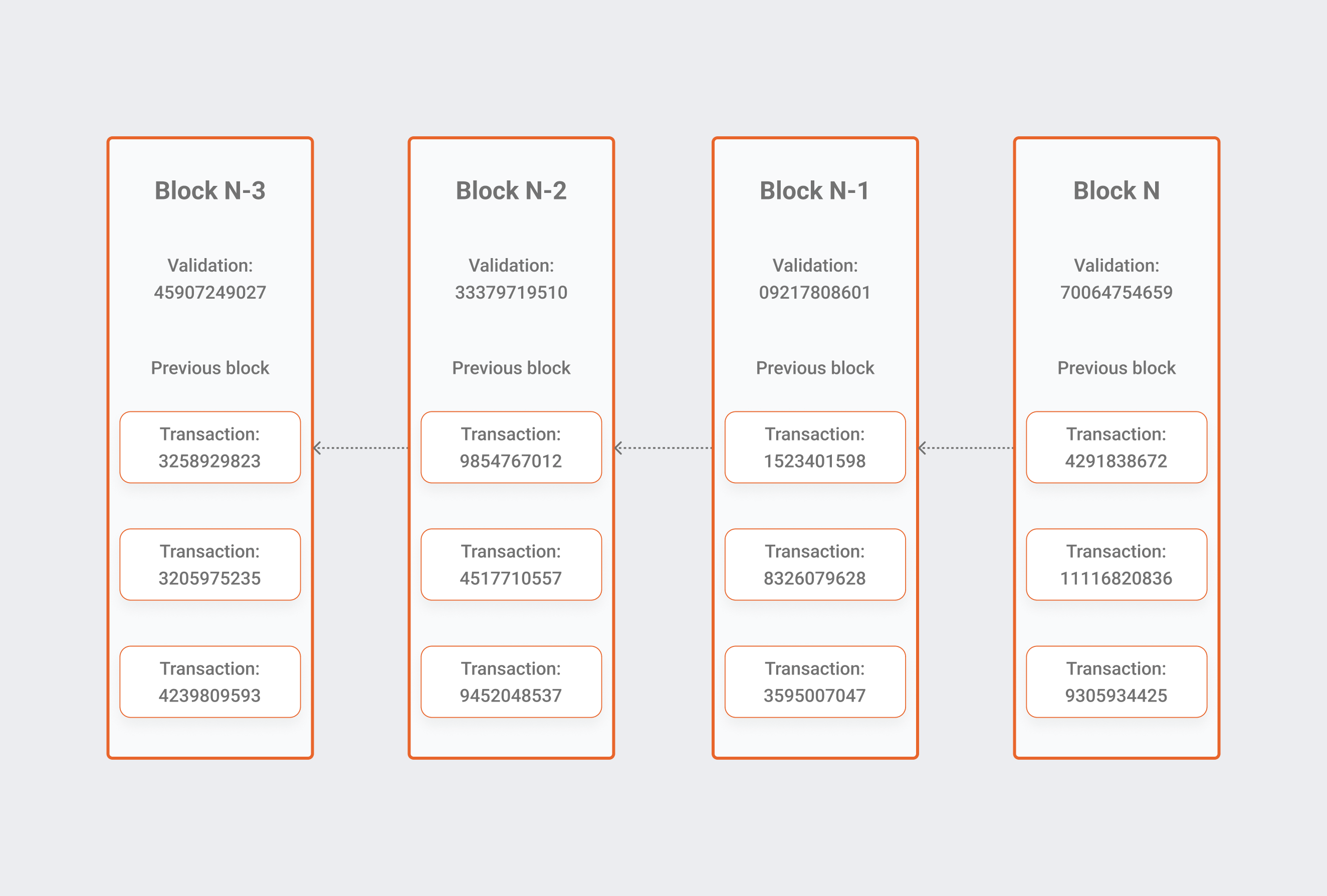
A database typically organizes information in tables and columns, but a blockchain, as the name suggests, organizes its data into blocks that are linked together. In a decentralized system, this database model creates an unchangeable data timeline. Remember, when a block is completed, it becomes permanent and is a component of this history. Once a block is included in the chain, it is assigned a specific timestamp.
If the theory is clearer now, let's look at how the blockchain works in practice.
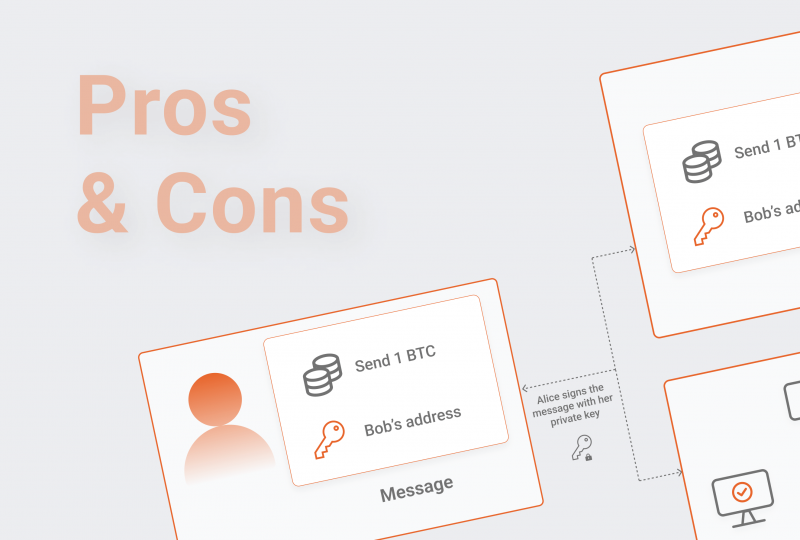
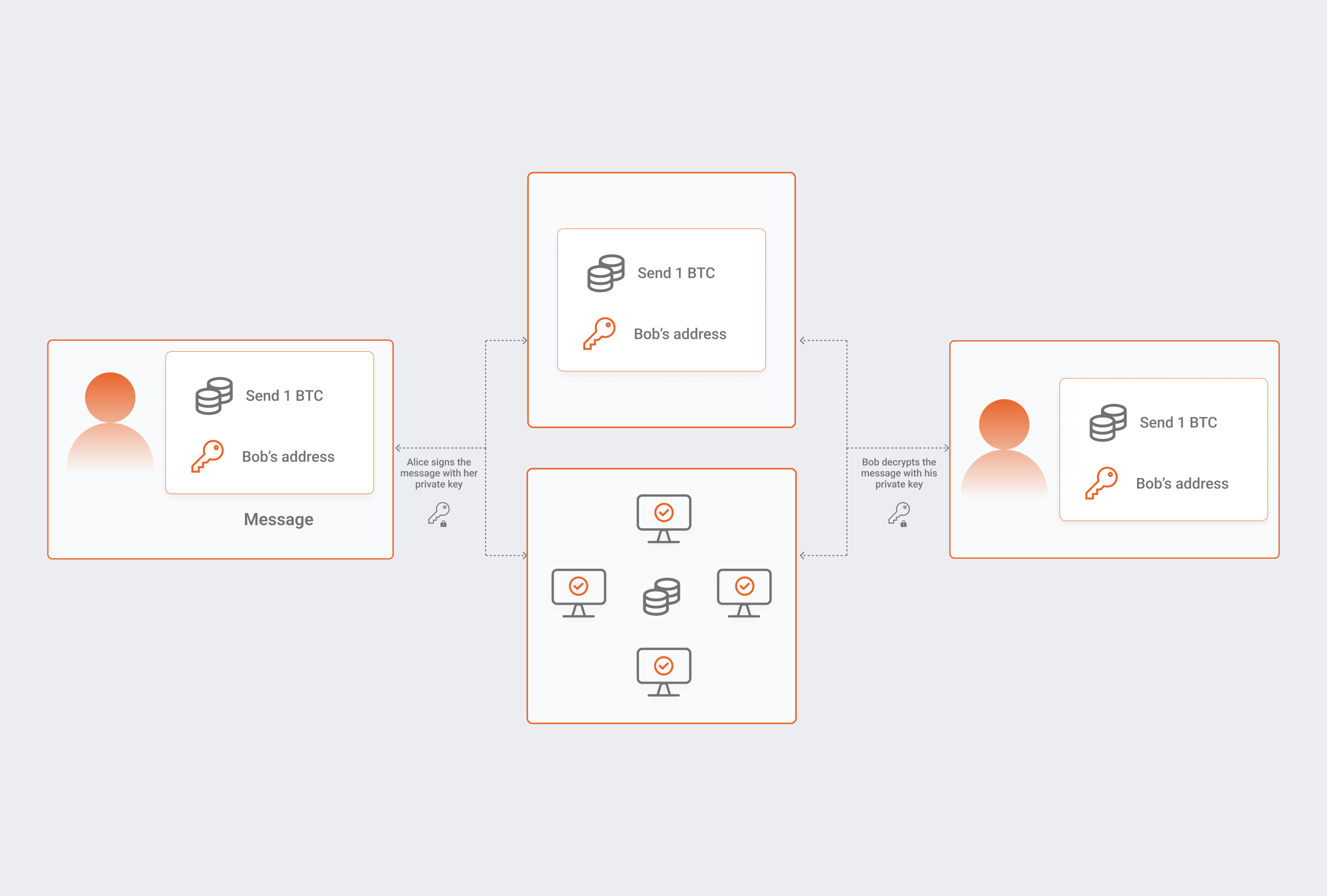
Below we will show an example of how a blockchain can be employed to authenticate and store transactions.
First, a particular user decides to buy some cryptocurrency. Say he bought Litecoin. Once the user buys some amount of LTC, the data processed is sent through Litecoin decentralized nodes network, whose main job is to validate every single transaction that takes place. Following approval, the payment is linked with others to generate a block, which is then put into a continuously expanding chain of operations. The finished block is encrypted, and the transaction record is irreversible on the blockchain; it cannot be erased or modified, making it highly secure.
If we take a look at the most significant blockchain out there, the Bitcoin blockchain, it is transparent, which means that anybody who holds BTC may examine the transaction history. Tracing the identity of a specific account might be challenging and near impossible for the public, as the ledger only displays individual addresses that interact on the blockchain. Public blockchains also enable any user with the necessary computing capacity to contribute as a node in authorizing and recording transactions into the blockchain.
However, not all blockchains are open. A blockchain can be configured as a private ledger, making it possible for the owner to restrict the people who can edit or add to the blockchain. While the pool of users on a private blockchain may be limited, it remains decentralized between those who are engaged. Private blockchains utilize the same encryption mechanisms as public blockchains to ensure the confidentiality of all data kept within the network.
The concept of a safe, decentralized permanent record of data has caught the attention of many businesses, and blockchain transactions may offer solutions to many of today's security challenges, recordkeeping methods, and data ownership difficulties.
Now, let's look at the advantages people can receive from implementing and using blockchain.
Pros
Robust security
The main advantage of this developing technology is the robust security of blockchain-enabled applications. The improved security provided by blockchain arises from how the system functions: With end-to-end encryption, blockchain generates an immutable record of transactions that prevents fraud and illicit behavior. Furthermore, data on the blockchain is distributed across a large number of computers, making hacking it extremely difficult. If we compare it to standard computer systems that keep all crucial data in one place on a single server, it should be evident that blockchain, which can be stored on any device globally, is more secure and less vulnerable. Moreover, by encrypting data and demanding permits to restrict exposure, blockchain can solve privacy concerns more effectively than conventional computer systems, which are constantly potential targets of cyber attackers.
High speed of transactions
Blockchain was designed to process every transaction substantially quicker than traditional techniques since it eliminates middlemen and replaces other human procedures when it comes to payments. In some circumstances, blockchain can process a transfer in minutes or even less. Nevertheless, these intervals can range; how rapidly a blockchain-based system can execute transactions is determined by various factors, including the size of each block of data and network activity. Also, researchers have discovered that blockchain often outperforms traditional procedures and technology in terms of efficiency. There are, and certainly will be numerous cases when a particular company utilizes blockchain technology to reduce work procedures from days to hours or even seconds.
Considerably more affordable solution
The blockchain network can indeed help enterprises save a notable amount of money because it improves payment system throughput. It also eliminates mechanical responsibilities like data aggregation and editing, as well as reporting or auditing procedures. Experts emphasize the advantages that financial institutions realize when implementing blockchain, stating that the potential of blockchain to speed clearing and settlement translates directly into operational cost reductions. In general, blockchain allows organizations to save money by automatically removing intermediaries that have previously performed the operations that blockchain can handle in a matter of minutes.
Users can be confident of the participants
One of the advantages of the blockchain network is that it encourages trustworthiness among entities where trust is either inefficient. By participating in blockchain transactions and data sharing, companies can take advantage of opportunities that they would not have access to otherwise. This trustless system allows businesses to interact with each other directly, without the need for a third party mediator. In early days, blockchain eased transactions between companies that did not have personal contact but needed to exchange information or capital. Bitcoin and other altcoins serve as excellent examples of how blockchain can foster trust between two parties who have never even met.
Clearly, blockchain is a promising technology that can benefit businesses in numerous ways, making it a worthwhile investment for most organizations. However, we can not proceed further without looking at the downsides of what blockchain can bring to the business.
Cons
Utilizing blockchain can eventually turn out to be costly
One of the advantages of the blockchain can quickly turn out to be one of the main downsides.
Every activity must undergo consensus processes to confirm its validity. Naturally, the consensus process necessitates a substantial amount of energy to complete each node. Besides that, every node must interact with one another to confirm that the payment is legitimate.
Consensus techniques, on the other hand, such as proof of work, demand a lot of processing power, which raises the total power requirements. But remember that different consensus procedures now require significantly less energy.
Blockchain can be an expensive option. Essentially, the cost is determined by the sort of feature needed together with your requirements. Besides that, developing a solution from scratch will also involve a significant investment.
Regulatory and controlling issues
Another significant disadvantage of blockchains is that blockchain solutions don't provide the necessary network regulations. As a result, many people have lost faith in the system. Moreover, the absence of oversight increases the risk of ICO scammers, which occurred many times in the history of crypto.
Since cryptocurrencies are not regulated, many people have been tricked by ICO scams. Government entities are also having difficulty adopting it since this industry is not governed by any legislation or centralized institution.
Once private keys are lost, your funds are gone
The private key is a necessary component of trading on the network. Although other users could see your public key, a private key is far more critical, and it should be appropriately hidden since it serves as a security code to access your funds. Each blockchain address will have its own unique private key. If you don't want anyone to steal your crypto funds, you must keep your secret keys safe at all costs. But remember, if you lose your private key, you will also lose access to your funds that are kept on the network. Ensure you keep them safe since there is no way of getting them back.
Large storage space is required
What is also important to take into account is that blockchain ledgers can grow fairly large in the future. The Bitcoin blockchain presently requires more than 200 GB of storage space. The current rise in blockchain size looks to be outpacing the expansion in hard drives, and the network may face serious risks of losing nodes if the ledger gets too vast for users to access and maintain.
Now, when we have discussed the pros and cons, let's take a look at several usage cases and how people can use blockchain for business.
Supply chain management
With the blockchain, products can be monitored in real-time as they move and change hands throughout the supply chain. Blockchain was designed to provide enterprises carrying these items with various possibilities. Blockchain transactions can be utilized to monitor events in a supply chain, such as distributing freshly received products to different shipping containers. Blockchain technology provides an innovative and flexible method for managing and utilizing tracking data.
Transaction of finances
Traditional trade finance techniques have been a significant source of discomfort for firms since extensive transactions frequently disrupt operations and make liquidity challenging to control. When exchanging information, such as place of origin and product characteristics, cross-border trade requires a vast number of variables, and transactions create large amounts of paperwork.
Thanks to blockchain, users and businesses can enjoy the potential to improve trade finance transactions and simplify cross-border processes.
Blockchain makes it easier for companies to interact with one another across regional or international borders.
Data management
Personal details, such as birthdays, dates, family statuses, and ownership acquisitions, are typically maintained by national or municipal governments. However, organizing this data may be problematic, and some of these documents are still only available on paper. That said, residents are often required to physically visit their local authority departments to make changes, which is always time-consuming, expensive, and certainly annoying. Blockchain technology has the potential to ease recordkeeping while also making data significantly more reliable.
Global payments
As already mentioned, blockchain technology allows for the safe and efficient creation of an encrypted ledger. As a result, it is ideal for online transfers and financial transactions.
For example, Banco Santander introduced the world's first blockchain-based money transfer service in 2018. The service, known as "Santander One Pay FX," employs one of the most prominent blockchains in the world of crypto — Ripple. It allows clients to perform extremely quick foreign transfers of money utilizing their top-notch network.
Santander has lowered the number of middlemen traditionally necessary in these transactions by automating the whole procedure with a blockchain, making the whole system more efficient.
Santander, being a big commercial bank, has many retail clients who can profit from more efficient and less expensive operations, especially when it comes to money transfers between clients. By eliminating the requirement for institutions to process payments individually, blockchain technology may be utilized to reduce the cost of these payments.
Aside from those cases mentioned above, there are several other industries and business scenarios where blockchain can be used on a daily basis.
Final Thoughts
According to several experts within several industries, there will be significant development in the blockchain space over time. Whether you are a technology enthusiast or not, blockchain technology will offer new and exciting opportunities and investment prospects, all of which will be worth examining. If it weren't that promising and attractive, numerous companies wouldn't invest their capital into something in which they see no future.
As a technology with numerous useful features and which is constantly being improved and researched, blockchain is now creating a reputation of its own, thanks in large part to Bitcoin payments and the use of other cryptocurrencies. As this concept is being discussed across multiple industries on a daily basis, the blockchain has the potential to make corporate and government processes more effective and safe by eliminating centralized components.
As blockchain enters another decade, the question is not whether traditional organizations will embrace the technology, but when. Furthermore, we are now seeing a boom in NFTs and asset tokenization, which has brought even more attention to this field. Thus, blockchain is expected to experience significant expansion in the near future.




